Development of hot-melt extrusion as a novel technique for the ...
Development of hot-melt extrusion as a novel technique for the ...
Development of hot-melt extrusion as a novel technique for the ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
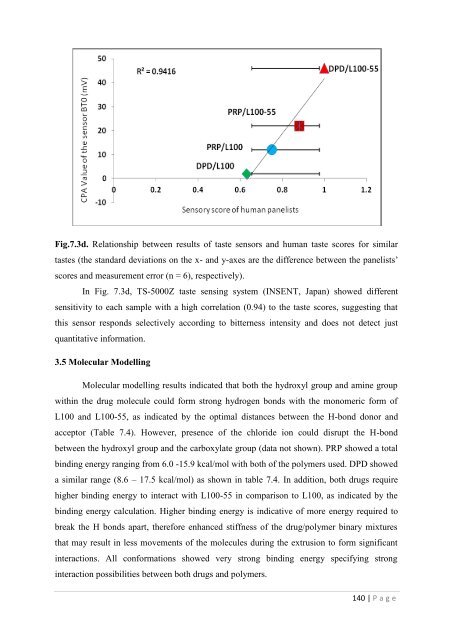
Fig.7.3d. Relationship between results <strong>of</strong> t<strong>as</strong>te sensors and human t<strong>as</strong>te scores <strong>for</strong> similart<strong>as</strong>tes (<strong>the</strong> standard deviations on <strong>the</strong> x- and y-axes are <strong>the</strong> difference between <strong>the</strong> panelists‘scores and me<strong>as</strong>urement error (n = 6), respectively).In Fig. 7.3d, TS-5000Z t<strong>as</strong>te sensing system (INSENT, Japan) showed differentsensitivity to each sample with a high correlation (0.94) to <strong>the</strong> t<strong>as</strong>te scores, suggesting thatthis sensor responds selectively according to bitterness intensity and does not detect justquantitative in<strong>for</strong>mation.3.5 Molecular ModellingMolecular modelling results indicated that both <strong>the</strong> hydroxyl group and amine groupwithin <strong>the</strong> drug molecule could <strong>for</strong>m strong hydrogen bonds with <strong>the</strong> monomeric <strong>for</strong>m <strong>of</strong>L100 and L100-55, <strong>as</strong> indicated by <strong>the</strong> optimal distances between <strong>the</strong> H-bond donor andacceptor (Table 7.4). However, presence <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> chloride ion could disrupt <strong>the</strong> H-bondbetween <strong>the</strong> hydroxyl group and <strong>the</strong> carboxylate group (data not shown). PRP showed a totalbinding energy ranging from 6.0 -15.9 kcal/mol with both <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> polymers used. DPD showeda similar range (8.6 – 17.5 kcal/mol) <strong>as</strong> shown in table 7.4. In addition, both drugs requirehigher binding energy to interact with L100-55 in comparison to L100, <strong>as</strong> indicated by <strong>the</strong>binding energy calculation. Higher binding energy is indicative <strong>of</strong> more energy required tobreak <strong>the</strong> H bonds apart, <strong>the</strong>re<strong>for</strong>e enhanced stiffness <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> drug/polymer binary mixturesthat may result in less movements <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> molecules during <strong>the</strong> <strong>extrusion</strong> to <strong>for</strong>m significantinteractions. All con<strong>for</strong>mations showed very strong binding energy specifying stronginteraction possibilities between both drugs and polymers.140 | P a g e