Development of hot-melt extrusion as a novel technique for the ...
Development of hot-melt extrusion as a novel technique for the ...
Development of hot-melt extrusion as a novel technique for the ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
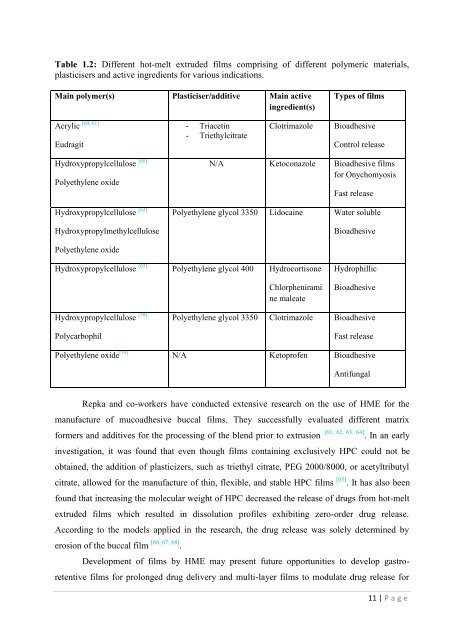
Table 1.2: Different <strong>hot</strong>-<strong>melt</strong> extruded films comprising <strong>of</strong> different polymeric materials,pl<strong>as</strong>ticisers and active ingredients <strong>for</strong> various indications.Main polymer(s) Pl<strong>as</strong>ticiser/additive Main activeingredient(s)Types <strong>of</strong> filmsAcrylicEudragit[60, 61]- Triacetin- TriethylcitrateClotrimazoleBioadhesiveControl rele<strong>as</strong>eHydroxypropylcellulose [60]Polyethylene oxideHydroxypropylcellulose [62]HydroxypropylmethylcelluloseN/A Ketoconazole Bioadhesive films<strong>for</strong> OnychomyosisF<strong>as</strong>t rele<strong>as</strong>ePolyethylene glycol 3350 Lidocaine Water solubleBioadhesivePolyethylene oxideHydroxypropylcellulose [65] Polyethylene glycol 400 HydrocortisoneChlorpheniramine maleateHydrophillicBioadhesiveHydroxypropylcellulose [58]PolycarbophilPolyethylene glycol 3350 Clotrimazole BioadhesiveF<strong>as</strong>t rele<strong>as</strong>ePolyethylene oxide [59] N/A Ketopr<strong>of</strong>en BioadhesiveAntifungalRepka and co-workers have conducted extensive research on <strong>the</strong> use <strong>of</strong> HME <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong>manufacture <strong>of</strong> mucoadhesive buccal films. They successfully evaluated different matrix<strong>for</strong>mers and additives <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> processing <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> blend prior to <strong>extrusion</strong> [61, 62, 63, 64] . In an earlyinvestigation, it w<strong>as</strong> found that even though films containing exclusively HPC could not beobtained, <strong>the</strong> addition <strong>of</strong> pl<strong>as</strong>ticizers, such <strong>as</strong> triethyl citrate, PEG 2000/8000, or acetyltributylcitrate, allowed <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> manufacture <strong>of</strong> thin, flexible, and stable HPC films [65] . It h<strong>as</strong> also beenfound that incre<strong>as</strong>ing <strong>the</strong> molecular weight <strong>of</strong> HPC decre<strong>as</strong>ed <strong>the</strong> rele<strong>as</strong>e <strong>of</strong> drugs from <strong>hot</strong>-<strong>melt</strong>extruded films which resulted in dissolution pr<strong>of</strong>iles exhibiting zero-order drug rele<strong>as</strong>e.According to <strong>the</strong> models applied in <strong>the</strong> research, <strong>the</strong> drug rele<strong>as</strong>e w<strong>as</strong> solely determined byerosion <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> buccal film [66, 67, 68] .<strong>Development</strong> <strong>of</strong> films by HME may present future opportunities to develop g<strong>as</strong>troretentivefilms <strong>for</strong> prolonged drug delivery and multi-layer films to modulate drug rele<strong>as</strong>e <strong>for</strong>11 | P a g e