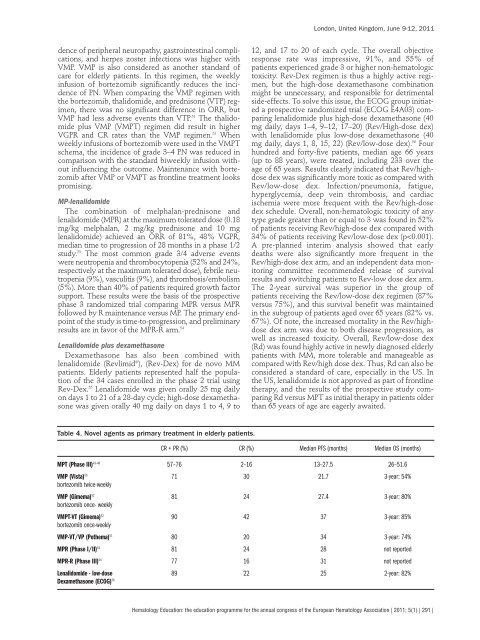
dence of peripheral neuropathy, gastrointestinal complicat<strong>io</strong>ns, and herpes zoster infect<strong>io</strong>ns was higher with VMP. VMP is also considered as another standard of care for elderly patients. In this regimen, the weekly infus<strong>io</strong>n of bortezomib significantly reduces the incidence of PN. When comparing the VMP regimen with the bortezomib, thalidomide, and prednisone (VTP) regimen, there was no significant difference in ORR, but VMP had less adverse events than VTP. 51 The thalidomide plus VMP (VMPT) regimen did result in higher VGPR and CR rates than the VMP regimen. 52 When weekly infus<strong>io</strong>ns of bortezomib were used in the VMPT schema, the incidence of grade 3–4 PN was reduced in comparison with the standard biweekly infus<strong>io</strong>n without influencing the outcome. Maintenance with bortezomib after VMP or VMPT as frontline treatment <strong>lo</strong>oks promising. MP-lenalidomide The combinat<strong>io</strong>n of melphalan-prednisone and lenalidomide (MPR) at the maximum tolerated dose (0.18 mg/kg melphalan, 2 mg/kg prednisone and 10 mg lenalidomide) achieved an ORR of 81%, 48% VGPR, median time to progress<strong>io</strong>n of 28 months in a phase 1/2 study. 53 The most common grade 3/4 adverse events were neutropenia and thrombocytopenia (52% and 24%, respectively at the maximum tolerated dose), febrile neutropenia (9%), vasculitis (9%), and thrombosis/embolism (5%). More than 40% of patients required growth factor support. These results were the basis of the prospective phase 3 randomized trial comparing MPR versus MPR fol<strong>lo</strong>wed by R maintenance versus MP. The primary endpoint of the study is time-to-progress<strong>io</strong>n, and preliminary results are in favor of the MPR-R arm. 54 Lenalidomide plus dexamethasone Dexamethasone has also been combined with lenalidomide (Revlimid ® ), (Rev-Dex) for de novo MM patients. Elderly patients represented half the populat<strong>io</strong>n of the 34 cases enrolled in the phase 2 trial using Rev-Dex. 55 Lenalidomide was given orally 25 mg daily on days 1 to 21 of a 28-day cycle; high-dose dexamethasone was given orally 40 mg daily on days 1 to 4, 9 to Table 4. Novel agents as primary treatment in elderly patients. London, United Kingdom, June 9-12, 2011 12, and 17 to 20 of each cycle. The overall objective response rate was impressive, 91%, and 55% of patients experienced grade 3 or higher non-hemato<strong>lo</strong>gic toxicity. Rev-Dex regimen is thus a highly active regimen, but the high-dose dexamethasone combinat<strong>io</strong>n might be unnecessary, and responsible for detrimental side-effects. To solve this issue, the ECOG group initiated a prospective randomized trial (ECOG E4A03) comparing lenalidomide plus high-dose dexamethasone (40 mg daily, days 1–4, 9–12, 17–20) (Rev/High-dose dex) with lenalidomide plus <strong>lo</strong>w-dose dexamethasone (40 mg daily, days 1, 8, 15, 22) (Rev/<strong>lo</strong>w-dose dex). 56 Four hundred and forty-five patients, median age 66 years (up to 88 years), were treated, including 233 over the age of 65 years. Results clearly indicated that Rev/highdose dex was significantly more toxic as compared with Rev/<strong>lo</strong>w-dose dex. Infect<strong>io</strong>n/pneumonia, fatigue, hyperglycemia, deep vein thrombosis, and cardiac ischemia were more frequent with the Rev/high-dose dex schedule. Overall, non-hemato<strong>lo</strong>gic toxicity of any type grade greater than or equal to 3 was found in 52% of patients receiving Rev/high-dose dex compared with 34% of patients receiving Rev/<strong>lo</strong>w-dose dex (p
16 th Congress of the <strong>European</strong> Hemato<strong>lo</strong>gy Associat<strong>io</strong>n Conclus<strong>io</strong>n During the last 3 years, results of several phase 1/2 or phase 3 trials have clearly shown that the prognosis and the survival of de novo MM in elderly patients have been markedly improved. MP is no <strong>lo</strong>nger the reference treatment and should be abandoned. At least four highly active new treatment opt<strong>io</strong>ns are available, MPT, VMP, MPR, and Rd, with different toxicity profiles (Table 4). The goal of future trials will be to determine the best treatment strategy in this group of patients and to tai<strong>lo</strong>r, if possible, therapeutic opt<strong>io</strong>ns, taking into account distinct variables, such as tolerability, efficacy, cytogenetics, or comorbidity. The role of maintenance therapy in this group of patients also needs further evaluat<strong>io</strong>n. References 1. Munshi NC, Anderson KC, Bergsagel PL, Shaughnessy J, Palumbo A, Durie B, et al. Guidelines for risk stratificat<strong>io</strong>n in multiple mye<strong>lo</strong>ma: report of the Internat<strong>io</strong>nal Mye<strong>lo</strong>ma Workshop Consensus panel 2. B<strong>lo</strong>od. 2011 Feb 3 doi:10.1182 2. Mc Elwain TJ, Powles RL. High-dose intravenous melphalan for plasma-cell leukaemia and mye<strong>lo</strong>ma. Lancet. 1983;16:822-4. 3. Attal M, Harousseau JL, Stoppa AM, Sotto JJ, Fuzibet JG, Rossi JF, et al. A prospective, randomized trial of auto<strong>lo</strong>gous bone marrow transplantat<strong>io</strong>n and chemotherapy in multiple mye<strong>lo</strong>ma. Intergroupe Francais du Mye<strong>lo</strong>me. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:91-7. 4. Child JA, Morgan GJ, Davies FE, Owen RG, Bell SE, Hawkins K, et al. High-dose chemotherapy with hematopoietic stem-cell rescue for multiple mye<strong>lo</strong>ma. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1875-83. 5. Fermand JP, Ravaud P, Chevret S, Divine M, Leb<strong>lo</strong>nd V, Belanger C, et al. High-dose therapy and auto<strong>lo</strong>gous peripheral b<strong>lo</strong>od stem cell transplantat<strong>io</strong>n in multiple mye<strong>lo</strong>ma: upfront or rescue treatment? Results of a multicenter sequential randomized trial. B<strong>lo</strong>od. 1998;92:3131-6. 6. Bladé J, Rosiñol L, Sureda A, Ribera JM, Díaz-Mediavilla J, García-Laraña J, et al. High-dose therapy intensificat<strong>io</strong>n compared with continued standard chemotherapy in multiple mye<strong>lo</strong>ma patients responding to the initial chemotherapy: <strong>lo</strong>ng-term results from a prospective randomized trial from the Spanish Cooperative Group PETHEMA. B<strong>lo</strong>od. 2005;106:3755-9. 7. Palumbo A, Bringhen S, Petrucci MT, Musto P, Rossini F, Nunzi M, et al. Intermediate-dose melphalan improves survival of mye<strong>lo</strong>ma patients aged 50-70: results of a randomized controlled trial. B<strong>lo</strong>od. 2004;104:3052-7. 8. Fermand JP, Katsahian S, Divine M, Leb<strong>lo</strong>nd V, Dreyfus F, Macro M, et al. High-dose therapy and auto<strong>lo</strong>gous b<strong>lo</strong>od stem-cell transplantat<strong>io</strong>n compared with convent<strong>io</strong>nal treatment in mye<strong>lo</strong>ma patients aged 55 to 65 years: <strong>lo</strong>ng-term results of a randomized control trial from the Group Mye<strong>lo</strong>me-Autogreffe. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:9227-33. 9. Bar<strong>lo</strong>gie B, Kyle RA, Anderson KC, Greipp PR, Lazarus HM, Hurd DD, et al. Standard chemotherapy compared with highdose chemorad<strong>io</strong>therapy for multiple mye<strong>lo</strong>ma: final results of Phase III US Intergroup trial S9321. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:929-36. 10. Moreau P, Facon T, Attal M, Hulin C, Michallet M, Ma<strong>lo</strong>isel F, et al. Comparison of 200mg/m 2 melphalan and 8Gy total body irradiat<strong>io</strong>n plus 140mg/m 2 melphalan as condit<strong>io</strong>ning regimen for peripheral b<strong>lo</strong>od stem cell transplantat<strong>io</strong>n in patients with newly diagnosed multiple mye<strong>lo</strong>ma: final analysis of the Intergroupe Francophone du Mye<strong>lo</strong>me 9502 trial. B<strong>lo</strong>od. 2002; 99:731-5. 11. Attal M, Harousseau JL, Facon T, Guilhot F, Doyen C, Fuzibet JG, et al. Single versus double auto<strong>lo</strong>gous stem-cell transplantat<strong>io</strong>n for multiple mye<strong>lo</strong>ma. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:2495-502. 12. Cavo M, Tosi P, Zamagni E, Cellini C, Tacchetti P, Patriarca F, et al. Prospective, randomized study of single compared with double auto<strong>lo</strong>gous stem-cell transplantat<strong>io</strong>n for multiple mye<strong>lo</strong>ma: Bo<strong>lo</strong>gna 96 clinical study. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25: 2434-41. 13. Sonneveld P, van der Holt B, Segeren CM, Vellenga E, Croockewit AJ, Verhoe GE, et al. Intermediate-dose melphalan compared with mye<strong>lo</strong>ablative treatment in multiple mye<strong>lo</strong>ma: <strong>lo</strong>ng-term results of the Dutch Cooperative group HOVON 24 trial. Haemato<strong>lo</strong>gica. 2007;92:928-35. 14. Margaret Macro, Marine Divine, Yurdagul Uzunhan, Arnaud Jaccard, Didier Bouscary, Veronique Leb<strong>lo</strong>nd, et al. Dexamethasone + Thalidomide compared to VAD as pre-transplant treatment in newly diagnosed multiple mye<strong>lo</strong>ma: a randomized trial. B<strong>lo</strong>od. 2006;108:22a. 15. Lokhorst HM, Schmidt-Wolf I, Sonneveld P, van der Holt B, Martin H, Barge R, et al. Thalidomide in induct<strong>io</strong>n treatment increases the very good partial remiss<strong>io</strong>n rate before and after high-dose therapy in prev<strong>io</strong>usly untreated multiple mye<strong>lo</strong>ma. Haemato<strong>lo</strong>gica. 2008;93:124-7. 16. Lokhorst HM, van der Holt B, Zweegman S, Vellenga E, Croockewit S, van Oers MH, et al. A randomized phase 3 study on the effect of thalidomide combined with adriamycin, dexamethasone, and high-dose melphalan, fol<strong>lo</strong>wed by thalidomide maintenance in patients with multiple mye<strong>lo</strong>ma. B<strong>lo</strong>od. 2010;115:1113-20. 17. Gareth J Morgan, Faith E Davies, Roger G Owen, Andrew C Rawstron, Sue Bell, Kim Cocks, et al. Thalidomide combinat<strong>io</strong>ns improve response rates: results from the MRC IX study. B<strong>lo</strong>od. 2007;110:1051a. 18. Harousseau JL, Attal M, Avet-Loiseau H, Marit G, Cail<strong>lo</strong>t D, Mohty M, et al. Bortezomib-dexamethasone is super<strong>io</strong>r to vincristine-doxorubicin-dexamethasone as induct<strong>io</strong>n treatment pr<strong>io</strong>r to auto<strong>lo</strong>gous stem cell transplantat<strong>io</strong>n in newly diagnosed multiple mye<strong>lo</strong>ma: results of the IFM 2005-01 phase 3 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28: 4621-9. 19. Wang M, Giralt S, Delasalle K, Handy B, Alexanian R.. Bortezomib in combinat<strong>io</strong>n with thalidomide-dexamethasone for prev<strong>io</strong>usly untreated multiple mye<strong>lo</strong>ma. Hemato<strong>lo</strong>gy. 2007;12:235-9. 20. Popat R, Oakervee HE, Hallam S, Curry N, Odeh L, Foot N, et al. Bortezomib, doxorubicin and dexamethasone (PAD) frontline treatment of multiple mye<strong>lo</strong>ma: updated results after <strong>lo</strong>ng-term fol<strong>lo</strong>w-up. Br J Haematol. 2008;141:512-6. 21. Richardson PG, Weller E, Lonial S, Jakubowiak AJ, Jagannath S, Raje NS, et al. Lenalidomide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone combinat<strong>io</strong>n therapy in patients with newly diagnosed multiple mye<strong>lo</strong>ma. B<strong>lo</strong>od. 2010;116:679-86. 22. Reeder CB, Reece DE, Kukreti V, Chen C, Trudel S, Hentz J, et al. Cyc<strong>lo</strong>phosphamide, bortezomib and dexamethasone induct<strong>io</strong>n for newly diagnosed multiple mye<strong>lo</strong>ma: high response rates in a phase II clinical trial. Leukemia. 2009;23:1337-41. 23. Cavo M, Tacchetti P, Patriarca F, Petrucci MT, Pantani L, Galli M, et al. Bortezomib with thalidomide plus dexamethasone compared with thalidomide plus dexamethasone as induct<strong>io</strong>n therapy before, and consolidat<strong>io</strong>n therapy after double auto<strong>lo</strong>gous stem-cell transplantat<strong>io</strong>n in newly diagnosed multiple mye<strong>lo</strong>ma: a randomized phase 3 study. Lancet. 2010;376:2075-85. 24. Laura Rosiñol, Ma Teresa Cibeira, Joaquin Martinez, Maria Victoria Mateos, Albert Or<strong>io</strong>l, Ma José Terol, et al. Thalidomide / dexamethasone (TD) vs. bortezomib (Velcade) / thalidomide / dexamethasone (VTD) vs. VBMCP/VBAD/Velcade as induct<strong>io</strong>n regimens pr<strong>io</strong>r auto<strong>lo</strong>gous stem cell transplantat<strong>io</strong>n (ASCT) in multiple mye<strong>lo</strong>ma (MM): results of a phase III PETHEMA/ GEM trial. B<strong>lo</strong>od. 2009;114:59a. 25. P. Moreau, T. Facon, M. Attal, C. Doyen, C. Hulin, G. Marit, et al. Comparison of reduced-dose bortezomib plus thalidomide plus dexamethasone (vTD) to bortezomib plus dexamethasone (VD) as induct<strong>io</strong>n treatment pr<strong>io</strong>r to ASCT in de novo multiple mye<strong>lo</strong>ma (MM): Results of IFM2007-02 study. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(Suppl):8014a. 26. Pieter Sonneveld, Ingo Schmidt-Wolf, Bronno van der Holt, Laila el Jarari, Uta Bertsch, Hans Salwender, et al. HOVON- 65/GMMG-HD4 randomized phase III trial comparing bortezomib, doxorubicin, dexamethasone vs VAD fol<strong>lo</strong>wed by high-dose melphalan and maintenance bortezomib or thalidomide in patients with newly diagnosed multiple mye<strong>lo</strong>ma. B<strong>lo</strong>od (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts). 2010 2010;116:40a. 27. Stewart AK, Richardson PG, San-Miguel JF. How I treat multiple mye<strong>lo</strong>ma in younger patients. B<strong>lo</strong>od. 2009;114:5436-443. 28. Ladetto M, Pagliano G, Ferrero S, Caval<strong>lo</strong> F, Drandi D, Santo L, et al. Major tumor shrinking and persistent molecular remiss<strong>io</strong>ns after consolidat<strong>io</strong>n with bortezomib, thalidomide, and dexamethasone in patients with autografter mye<strong>lo</strong>ma. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:2077-84. 29. Stewart AK, Chen CI, Howson-Jan K, White D, Roy J, Kovacs MJ, et al. Results of a multicenter randomized trial of thalidomide and prednisone maintenance therapy for multiple mye<strong>lo</strong>ma after auto<strong>lo</strong>gous stem cell transplant. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:8170-6. 30. Brinker BT, Waller EK, Leong T, Heffner LT Jr, Redei I, Langston AA, et al. Maintenance therapy with thalidomide improves overall survival after auto<strong>lo</strong>gous hematopoietic progenitor cell transplantat<strong>io</strong>n for multiple mye<strong>lo</strong>ma. Cancer. 2006;106:2171-80. | 292 | Hemato<strong>lo</strong>gy Educat<strong>io</strong>n: the educat<strong>io</strong>n programme for the annual congress of the <strong>European</strong> Hemato<strong>lo</strong>gy Associat<strong>io</strong>n | 2011; 5(1)
- Page 1 and 2:
H e m a t o l o g y E d u c a t i o
- Page 3 and 4:
Copyright Information ©2011 by Eur
- Page 5 and 6:
Editorial Board Education Book Edit
- Page 7 and 8:
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia 1-8 Th
- Page 10 and 11:
S. Schnell P. Van Vlierberghe A. Fe
- Page 12 and 13:
lineage cells, and in differentiati
- Page 14 and 15:
FLT3 mutations The FMS-like tyrosin
- Page 16 and 17:
44. Bar-Eli M, Ahuja H, Foti A, Cli
- Page 18 and 19:
J.M. Rowe 1,2 C. Ganzel 1 1 Shaare
- Page 20 and 21:
treated on the MRC UKALL XII/ECOG29
- Page 22 and 23:
asparaginase (PEG), where the Esche
- Page 24 and 25:
or higher. It is, however, importan
- Page 26 and 27:
25. Bruggemann M, Schrauder A, Raff
- Page 28 and 29:
lymphoblastic leukemia: prospective
- Page 30 and 31:
such as high white blood cell count
- Page 32 and 33:
doxorubicine, there was a trend tow
- Page 34 and 35:
of the aging process with respect t
- Page 36 and 37:
K.L. Rice 1 M. Buzzai 2 J. Altman 1
- Page 38 and 39:
ing FLT3-ITD, wild-type NPM1, or bo
- Page 40 and 41:
ciated with gene activation, via th
- Page 42 and 43:
leukemia with inv(16) and t(8;21):
- Page 44 and 45:
99. Parsons DW, Jones S, Zhang X, e
- Page 46 and 47:
abnormalities, some of which are al
- Page 48 and 49:
file. 27,31 Thus, the double gene-m
- Page 50 and 51:
karyotype represents a distinct gen
- Page 52 and 53:
Table 1. Meta-analysis of 23 random
- Page 54 and 55:
A recent study by the Center for In
- Page 56 and 57:
Patients with HLA-matched related o
- Page 58 and 59:
After allogeneic HSCT, an autologou
- Page 60 and 61:
A. Bacigalupo Ospedale San Martino,
- Page 62 and 63:
Table 2. The effect of HLA mismatch
- Page 64 and 65:
References 1. Petersdorf EW, Malkki
- Page 66 and 67:
neutrophil and platelet recovery an
- Page 68 and 69:
Figure 2. One Year-Overall Survival
- Page 70 and 71:
infused on day 21. No serious adver
- Page 72 and 73:
W, et al. Effect of graft source on
- Page 74 and 75:
TRM was higher for patients who rec
- Page 76 and 77:
following a myeloablative preparati
- Page 78 and 79:
effect. Surprisingly, none of the p
- Page 80 and 81:
nancies. Bone Marrow Transplant. 20
- Page 82 and 83:
J.G. Gilles Center for Molecular an
- Page 84 and 85:
14C12 was humanized by grafting VH
- Page 86 and 87:
Table 1. VWD Classification. VWD Su
- Page 88 and 89:
Figure 1. Missense mutations found
- Page 90 and 91:
associated with an increased bleedi
- Page 92 and 93:
49. Brown SA, Eldridge A, Collins P
- Page 94 and 95:
leed. These issues are especially i
- Page 96 and 97:
estored function. 43,44 A phase I t
- Page 98 and 99:
years’ experience of prophylactic
- Page 100 and 101:
J.A. Burger Department of Leukemia,
- Page 102 and 103:
chemotaxis, migration across vascul
- Page 104 and 105:
Regulatory T cells (T reg), identif
- Page 106 and 107:
16. Burger JA, Ghia P, Rosenwald A,
- Page 108 and 109:
TE, Nowakowski GS, et al. CD49d exp
- Page 110 and 111:
andomized trial demonstrating impro
- Page 112 and 113:
Conclusions Chemoimmunotherapy has
- Page 114 and 115:
with multiple comorbidities (≥ 2)
- Page 116 and 117:
ment was finished in all 100 patien
- Page 118 and 119:
Table 2. Treatment recommendation f
- Page 120 and 121:
34. Ferrajoli A. The combination of
- Page 122 and 123:
to be the source of additional gene
- Page 124 and 125:
potential to prevent LSCs from acce
- Page 126 and 127:
ABL1 confirms that eradication of d
- Page 128 and 129:
65. Fiskus W, Pranpat M, Balasis M,
- Page 130 and 131:
alive after 10 years. 11 Hence, CCy
- Page 132 and 133:
each arm). A minimal change in myel
- Page 134 and 135:
Any discussion about the definition
- Page 136 and 137:
H. Kantarjian J. Cortes Leukemia De
- Page 138 and 139:
59%; the CCyR rate was 44%. Among p
- Page 140 and 141:
ern era of BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase
- Page 142 and 143:
the hematopoietic system, 10 nor in
- Page 144 and 145:
over the period of 6 weeks, demonst
- Page 146 and 147:
Data on clonal changes in the blood
- Page 148 and 149:
2006 Feb 1;107(3):924-30. 41. Liang
- Page 150 and 151:
demonstrated that changes in osteob
- Page 152 and 153:
“Mafia” transgenic mice in whic
- Page 154 and 155:
68. Coetzee T, Fujita N, Dupree J,
- Page 156 and 157:
ization. In WASP deficiency, lympho
- Page 158 and 159:
Currently the epistatic relationshi
- Page 160 and 161:
R. Küppers Institute of Cell Biolo
- Page 162 and 163:
Figure 1. TNFAIP3 mutation in HL ce
- Page 164 and 165:
Figure 2. HRS cells and their precu
- Page 166 and 167:
Hansmann ML, et al. Detection of cl
- Page 168 and 169:
fying patients for whom different a
- Page 170 and 171:
prognosis HL, whilst those with res
- Page 172 and 173:
12. Noordijk EM, Carde P, Dupouy N,
- Page 174 and 175:
A. Sureda Consultant in Haematology
- Page 176 and 177:
Figure 1. Long-term outcome of pati
- Page 178 and 179:
from a MRD and 18 from MUDs. All pa
- Page 180 and 181:
Parker PM, Stein AS, et al. High-do
- Page 182 and 183:
R. Stasi Department of Haematology,
- Page 184 and 185:
common variants in the regulatory r
- Page 186 and 187:
against the TPO receptor (cMpl). 61
- Page 188 and 189:
W.B. Mitchell A.A. Miller J.B. Buss
- Page 190 and 191:
platelet counts and/or bleeding. Th
- Page 192 and 193:
Mpl. Cell. 1994;77(7):1117-24. 6. d
- Page 194 and 195:
ity and mortality associated with t
- Page 196 and 197:
to azathioprine, and is particularl
- Page 198 and 199:
stemming from antibodies against PE
- Page 200 and 201:
L. Pasqualucci Institute for Cancer
- Page 202 and 203:
cation of molecularly distinct subg
- Page 204 and 205:
of cases) 46 and amplifications of
- Page 206 and 207:
gene alterations in B cell lymphoma
- Page 208 and 209:
W. Wilson National Cancer Institute
- Page 210 and 211:
clear distinction among the lymphom
- Page 212 and 213:
Treatment strategies in germinal ce
- Page 214 and 215:
in ABC DLBCL (Hernandez et al., 201
- Page 216 and 217:
DLBCL that mostly occurs in young p
- Page 218 and 219:
phoma. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:5347-5
- Page 220 and 221:
Table 1. Diffuse Large B cell Lymph
- Page 222 and 223:
sion/relapse are similar to those i
- Page 224 and 225:
intensive therapy with curative int
- Page 226 and 227:
A. Karsan Genome Sciences Centre an
- Page 228 and 229:
Balanced translocations In contrast
- Page 230 and 231:
some arm 5q have also been implicat
- Page 232 and 233:
(H3K27) methyltransferase, and is a
- Page 234 and 235:
38. Starczynowski DT, Morin R, McPh
- Page 236 and 237:
G. Garcia-Manero Department of Leuk
- Page 238 and 239:
trial evaluating different doses an
- Page 240 and 241:
acid. 62 The second was a large mul
- Page 242 and 243:
Borthakur G, et al. Cause of death
- Page 244 and 245:
P. Krishnamurthy 1 G.J. Mufti 1,2 1
- Page 246 and 247:
etween 1995 and 2005. 11 Five hundr
- Page 248 and 249:
London, United Kingdom, June 9-12,
- Page 250 and 251: attainment of FDC post DLI. Interes
- Page 252 and 253: myelodysplastic syndromes is associ
- Page 254 and 255: ubiquitous chaperone that promotes
- Page 256 and 257: was thought that they are linked to
- Page 258 and 259: pathologic induction of miR-28 in M
- Page 260 and 261: STATs. Second, levels of HP1 alpha
- Page 262 and 263: 72. Irandoust MI, Aarts LH, Roovers
- Page 264 and 265: A.M. Vannucchi Section of Hematolog
- Page 266 and 267: 2,559 patients with a diagnosis of
- Page 268 and 269: tant use of aspirin should be caref
- Page 270 and 271: sions at this regard. Based on thes
- Page 272 and 273: in bcr-abl-negative myeloproliferat
- Page 274 and 275: Table 1. Prognostic scoring systems
- Page 276 and 277: Figure 1. Current inhibitors of JAK
- Page 278 and 279: Table 4. A risk-based approach to d
- Page 280 and 281: the flexibility to be adjusted as t
- Page 282 and 283: A. Vacca 1 D. Ribatti 2 1 Departmen
- Page 284 and 285: neovessel building together with MM
- Page 286 and 287: Mevastatin, a specific inhibitor of
- Page 288 and 289: egression of tumor vessels, and app
- Page 290 and 291: diagnosis does not require genetic
- Page 292 and 293: Genetics prognostic tools should be
- Page 294 and 295: sone induction improves outcome of
- Page 296 and 297: Table 1. Conventional chemotherapy
- Page 298 and 299: Novel agents given as consolidation
- Page 302 and 303: 31. Barlogie B, Tricot G, Anaissie
- Page 304 and 305: Table 1. Major differences between
- Page 306 and 307: first line therapy have shown survi
- Page 308 and 309: transplantation, 7,91 and generally
- Page 310 and 311: methylation characterizes juvenile
- Page 312 and 313: Table 1. Clinical signs of possible
- Page 314 and 315: Table 4. Distribution of CSF involv
- Page 316 and 317: ently results in a less than 5% cum
- Page 318 and 319: 90. German-Austrian-Swiss ALL-BFM S
- Page 320 and 321: U. Nowak-Göttl 1 R. Junker 1 A. Kr
- Page 322 and 323: Based on the data obtained from the
- Page 324 and 325: 59. Male C, Chait P, Ginsberg JS, e
- Page 326 and 327: Table 1. Characteristic features of
- Page 328 and 329: Table 2. Mutational spectrum of CDA
- Page 330 and 331: megarakaryoblastic leukemia (AMKL)
- Page 332 and 333: R.E. Ware Professor and Vice-Chairm
- Page 334 and 335: protein, cytokines, and soluble adh
- Page 336 and 337: example, improving blood viscosity
- Page 338 and 339: 92(9):1266-7. 36. Bensinger TA, Gil
- Page 340 and 341: London, United Kingdom, June 9-12,
- Page 342 and 343: port have also been used. 5 Combina
- Page 344 and 345: Wingard JR, Young J-AH, Boeckh MJ.
- Page 346 and 347: K. Rezvani 1 J. Barrett 2 1 Haemato
- Page 348 and 349: include the childhood infectious il
- Page 350 and 351:
Summary Patients undergoing hematop
- Page 352 and 353:
Table 1. Key issues. In a retrospec
- Page 354 and 355:
invasive method to assess iron over
- Page 356 and 357:
stitution but even with optimal sub
- Page 358 and 359:
T.M. Hackeng Department of Biochemi
- Page 360 and 361:
and inhibits FVIIa, and that the se
- Page 362 and 363:
Figure 4. Regulation of coagulation
- Page 364 and 365:
T. Baglin Department of Haematology
- Page 366 and 367:
Figure 1. Illustration of alternati
- Page 368 and 369:
compared with 3.5% in patients with
- Page 370 and 371:
49. Hron G, Kollars M, Binder BR, E
- Page 372 and 373:
Women receiving vitamin K antagonis
- Page 374 and 375:
molecular weight heparin as prophyl
- Page 376 and 377:
eral morbidity and mortality. 17-21
- Page 378 and 379:
the HOD construct. Furthermore, the
- Page 380 and 381:
Goals of future murine studies incl
- Page 382 and 383:
F. Noizat-Pirenne C. Tournamille Et
- Page 384 and 385:
phenotype. 26 In 2010, we investiga
- Page 386 and 387:
ody has been involved in DHTR. 37 T
- Page 388 and 389:
antigen. Cases can be encountered d
- Page 390 and 391:
S.R. Sloan Harvard Medical School &
- Page 392 and 393:
We also analyzed patient databases
- Page 394 and 395:
Index of authors Altman J. 27 Bacig
- Page 396 and 397:
Cornelissen J. Affiliations to disc
- Page 398 and 399:
GlaxoSmithKline (Research Support;