H e m a t o lo g y E d u c a t io n - European Hematology Association
H e m a t o lo g y E d u c a t io n - European Hematology Association
H e m a t o lo g y E d u c a t io n - European Hematology Association
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
estored funct<strong>io</strong>n. 43,44 A phase I trial has been completed<br />
with this compound (NCT00956345, Novo Nordisk).<br />
Polysialic acid<br />
Polysialic acid (PSA) is an an<strong>io</strong>nic moiety that adds<br />
multiple negative charges to the protein thereby changing<br />
its surface charge and binding capabilities. PSA is<br />
thought to interfere with receptor-mediated clearance<br />
processes of FVIII as a result of these changes. 45 The<br />
compound is under preclinical evaluat<strong>io</strong>n.<br />
Albumin fus<strong>io</strong>n<br />
Albumin has a <strong>lo</strong>ng half-life which exceeds 20 hours. 46<br />
As albumin is a product with a <strong>lo</strong>ng safety record and<br />
does not seem to be immunogenic, it would be an<br />
opt<strong>io</strong>n for extens<strong>io</strong>n of c<strong>lo</strong>tting factor half-life using<br />
genetic fus<strong>io</strong>n. Weimer et al. 47 reported the generat<strong>io</strong>n<br />
of a recombinant FVIIa molecule with an extended halflife<br />
based on genetic fus<strong>io</strong>n to human albumin. The<br />
recombinant FVII albumin fus<strong>io</strong>n protein (rVII-FP) was<br />
expressed in mammalian cells and upon activat<strong>io</strong>n, displayed<br />
a FVII activity c<strong>lo</strong>se to that of wild type FVIIa.<br />
Pharmacokinetic studies in rats demonstrated that the<br />
half-life of the activated recombinant FVII albumin<br />
fus<strong>io</strong>n protein (rVIIa-FP) was extended six- to sevenfold<br />
compared with wild type rFVIIa. The in-vitro and<br />
in-vivo efficacy was evaluated and was found to be<br />
comparable with a commercially available rFVIIa<br />
(NovoSeven, Novo Nordisk). The results of this study<br />
demonstrated that it is feasible to deve<strong>lo</strong>p a half-life<br />
extended FVIIa molecule with haemostatic properties<br />
very similar to the wild-type factor. Albumin has also<br />
been fused to FIX and a phase I trial has started<br />
(NCT01233440,CSL Behring) but no results are yet<br />
available.<br />
London, United Kingdom, June 9-12, 2011<br />
Fc fus<strong>io</strong>n<br />
The neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) is a MHC class I like<br />
molecule that funct<strong>io</strong>ns to protect IgG and albumin<br />
from catabolism, mediates transport of IgG across<br />
epithelial cells, and is involved in antigen presentat<strong>io</strong>n<br />
by profess<strong>io</strong>nal antigen presenting cells. Its funct<strong>io</strong>n is<br />
evident in early life in the transport of IgG from mother<br />
to fetus and neonate for passive immunity, and later in<br />
the deve<strong>lo</strong>pment of adaptive immunity and other funct<strong>io</strong>ns<br />
throughout life. The unique ability of this receptor<br />
to pro<strong>lo</strong>ng the half-life of IgG and albumin has guided<br />
engineering of novel therapeutics. 48 Peters et al. 49 have<br />
summarized studies where Fc has been fused to FIX.<br />
Taken together, these studies showed the enhanced<br />
pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties of<br />
the rFIXFc fus<strong>io</strong>n protein and provided the basis for<br />
evaluating rFIXFc in patients with hemophilia B.<br />
A recombinant fus<strong>io</strong>n protein (rFIXFc) containing a<br />
single FIX molecule attached to the Fc reg<strong>io</strong>n of<br />
immunog<strong>lo</strong>bulin G was administered intravenously and<br />
found to have an extended half-life, compared with<br />
recombinant FIX (rFIX) in normal mice, rats, monkeys,<br />
and FIX-deficient mice and dogs. The half-life of rFIXFc<br />
was approximately three- to four-fold <strong>lo</strong>nger than that<br />
of rFIX in all species. In contrast, in mice in which the<br />
neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) was deleted, the half-life of<br />
rFIXFc was similar to rFIX, confirming the increased circulatory<br />
time was due to protect<strong>io</strong>n of the rFIXFc via<br />
the Fc/FcRn interact<strong>io</strong>n. Whole b<strong>lo</strong>od c<strong>lo</strong>tting time in<br />
FIX-deficient mice was corrected through 144 hours for<br />
rFIXFc, compared with 72 hours for rFIX; similar results<br />
were observed in FIX-deficient dogs. The fus<strong>io</strong>n of Fc<br />
and FVIII has also been obtained with similar beneficial<br />
results although full publicat<strong>io</strong>ns are still not present.<br />
The phase I trial has been completed for FIX<br />
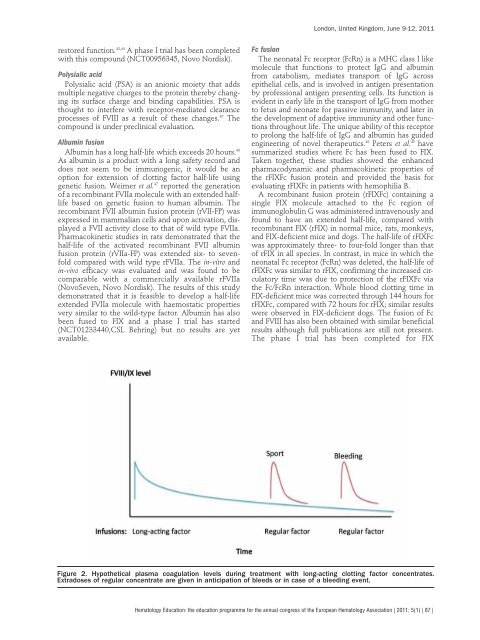
Figure 2. Hypothetical plasma coagulat<strong>io</strong>n levels during treatment with <strong>lo</strong>ng-acting c<strong>lo</strong>tting factor concentrates.<br />
Extradoses of regular concentrate are given in anticipat<strong>io</strong>n of bleeds or in case of a bleeding event.<br />
Hemato<strong>lo</strong>gy Educat<strong>io</strong>n: the educat<strong>io</strong>n programme for the annual congress of the <strong>European</strong> Hemato<strong>lo</strong>gy Associat<strong>io</strong>n | 2011; 5(1) | 87 |