- Page 1 and 2:
H e m a t o l o g y E d u c a t i o
- Page 3 and 4:
Copyright Information ©2011 by Eur
- Page 5 and 6:
Editorial Board Education Book Edit
- Page 7 and 8:
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia 1-8 Th
- Page 10 and 11:
S. Schnell P. Van Vlierberghe A. Fe
- Page 12 and 13:
lineage cells, and in differentiati
- Page 14 and 15:
FLT3 mutations The FMS-like tyrosin
- Page 16 and 17:
44. Bar-Eli M, Ahuja H, Foti A, Cli
- Page 18 and 19:
J.M. Rowe 1,2 C. Ganzel 1 1 Shaare
- Page 20 and 21:
treated on the MRC UKALL XII/ECOG29
- Page 22 and 23:
asparaginase (PEG), where the Esche
- Page 24 and 25:
or higher. It is, however, importan
- Page 26 and 27:
25. Bruggemann M, Schrauder A, Raff
- Page 28 and 29:
lymphoblastic leukemia: prospective
- Page 30 and 31:
such as high white blood cell count
- Page 32 and 33:
doxorubicine, there was a trend tow
- Page 34 and 35:
of the aging process with respect t
- Page 36 and 37:
K.L. Rice 1 M. Buzzai 2 J. Altman 1
- Page 38 and 39:
ing FLT3-ITD, wild-type NPM1, or bo
- Page 40 and 41:
ciated with gene activation, via th
- Page 42 and 43:
leukemia with inv(16) and t(8;21):
- Page 44 and 45:
99. Parsons DW, Jones S, Zhang X, e
- Page 46 and 47:
abnormalities, some of which are al
- Page 48 and 49:
file. 27,31 Thus, the double gene-m
- Page 50 and 51:
karyotype represents a distinct gen
- Page 52 and 53:
Table 1. Meta-analysis of 23 random
- Page 54 and 55:
A recent study by the Center for In
- Page 56 and 57:
Patients with HLA-matched related o
- Page 58 and 59:
After allogeneic HSCT, an autologou
- Page 60 and 61:
A. Bacigalupo Ospedale San Martino,
- Page 62 and 63:
Table 2. The effect of HLA mismatch
- Page 64 and 65:
References 1. Petersdorf EW, Malkki
- Page 66 and 67:
neutrophil and platelet recovery an
- Page 68 and 69:
Figure 2. One Year-Overall Survival
- Page 70 and 71:
infused on day 21. No serious adver
- Page 72 and 73:
W, et al. Effect of graft source on
- Page 74 and 75:
TRM was higher for patients who rec
- Page 76 and 77:
following a myeloablative preparati
- Page 78 and 79:
effect. Surprisingly, none of the p
- Page 80 and 81:
nancies. Bone Marrow Transplant. 20
- Page 82 and 83:
J.G. Gilles Center for Molecular an
- Page 84 and 85:
14C12 was humanized by grafting VH
- Page 86 and 87:
Table 1. VWD Classification. VWD Su
- Page 88 and 89:
Figure 1. Missense mutations found
- Page 90 and 91:
associated with an increased bleedi
- Page 92 and 93:
49. Brown SA, Eldridge A, Collins P
- Page 94 and 95:
leed. These issues are especially i
- Page 96 and 97:
estored function. 43,44 A phase I t
- Page 98 and 99:
years’ experience of prophylactic
- Page 100 and 101:
J.A. Burger Department of Leukemia,
- Page 102 and 103:
chemotaxis, migration across vascul
- Page 104 and 105:
Regulatory T cells (T reg), identif
- Page 106 and 107:
16. Burger JA, Ghia P, Rosenwald A,
- Page 108 and 109:
TE, Nowakowski GS, et al. CD49d exp
- Page 110 and 111:
andomized trial demonstrating impro
- Page 112 and 113:
Conclusions Chemoimmunotherapy has
- Page 114 and 115:
with multiple comorbidities (≥ 2)
- Page 116 and 117:
ment was finished in all 100 patien
- Page 118 and 119:
Table 2. Treatment recommendation f
- Page 120 and 121:
34. Ferrajoli A. The combination of
- Page 122 and 123:
to be the source of additional gene
- Page 124 and 125:
potential to prevent LSCs from acce
- Page 126 and 127:
ABL1 confirms that eradication of d
- Page 128 and 129:
65. Fiskus W, Pranpat M, Balasis M,
- Page 130 and 131:
alive after 10 years. 11 Hence, CCy
- Page 132 and 133:
each arm). A minimal change in myel
- Page 134 and 135:
Any discussion about the definition
- Page 136 and 137:
H. Kantarjian J. Cortes Leukemia De
- Page 138 and 139:
59%; the CCyR rate was 44%. Among p
- Page 140 and 141:
ern era of BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase
- Page 142 and 143:
the hematopoietic system, 10 nor in
- Page 144 and 145:
over the period of 6 weeks, demonst
- Page 146 and 147:
Data on clonal changes in the blood
- Page 148 and 149:
2006 Feb 1;107(3):924-30. 41. Liang
- Page 150 and 151:
demonstrated that changes in osteob
- Page 152 and 153:
“Mafia” transgenic mice in whic
- Page 154 and 155:
68. Coetzee T, Fujita N, Dupree J,
- Page 156 and 157:
ization. In WASP deficiency, lympho
- Page 158 and 159:
Currently the epistatic relationshi
- Page 160 and 161:
R. Küppers Institute of Cell Biolo
- Page 162 and 163:
Figure 1. TNFAIP3 mutation in HL ce
- Page 164 and 165:
Figure 2. HRS cells and their precu
- Page 166 and 167:
Hansmann ML, et al. Detection of cl
- Page 168 and 169:
fying patients for whom different a
- Page 170 and 171:
prognosis HL, whilst those with res
- Page 172 and 173:
12. Noordijk EM, Carde P, Dupouy N,
- Page 174 and 175:
A. Sureda Consultant in Haematology
- Page 176 and 177:
Figure 1. Long-term outcome of pati
- Page 178 and 179:
from a MRD and 18 from MUDs. All pa
- Page 180 and 181:
Parker PM, Stein AS, et al. High-do
- Page 182 and 183:
R. Stasi Department of Haematology,
- Page 184 and 185:
common variants in the regulatory r
- Page 186 and 187:
against the TPO receptor (cMpl). 61
- Page 188 and 189:
W.B. Mitchell A.A. Miller J.B. Buss
- Page 190 and 191:
platelet counts and/or bleeding. Th
- Page 192 and 193:
Mpl. Cell. 1994;77(7):1117-24. 6. d
- Page 194 and 195:
ity and mortality associated with t
- Page 196 and 197:
to azathioprine, and is particularl
- Page 198 and 199:
stemming from antibodies against PE
- Page 200 and 201:
L. Pasqualucci Institute for Cancer
- Page 202 and 203:
cation of molecularly distinct subg
- Page 204 and 205:
of cases) 46 and amplifications of
- Page 206 and 207:
gene alterations in B cell lymphoma
- Page 208 and 209:
W. Wilson National Cancer Institute
- Page 210 and 211:
clear distinction among the lymphom
- Page 212 and 213:
Treatment strategies in germinal ce
- Page 214 and 215:
in ABC DLBCL (Hernandez et al., 201
- Page 216 and 217:
DLBCL that mostly occurs in young p
- Page 218 and 219:
phoma. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:5347-5
- Page 220 and 221:
Table 1. Diffuse Large B cell Lymph
- Page 222 and 223:
sion/relapse are similar to those i
- Page 224 and 225:
intensive therapy with curative int
- Page 226 and 227:
A. Karsan Genome Sciences Centre an
- Page 228 and 229:
Balanced translocations In contrast
- Page 230 and 231:
some arm 5q have also been implicat
- Page 232 and 233:
(H3K27) methyltransferase, and is a
- Page 234 and 235:
38. Starczynowski DT, Morin R, McPh
- Page 236 and 237:
G. Garcia-Manero Department of Leuk
- Page 238 and 239:
trial evaluating different doses an
- Page 240 and 241:
acid. 62 The second was a large mul
- Page 242 and 243:
Borthakur G, et al. Cause of death
- Page 244 and 245:
P. Krishnamurthy 1 G.J. Mufti 1,2 1
- Page 246 and 247:
etween 1995 and 2005. 11 Five hundr
- Page 248 and 249:
London, United Kingdom, June 9-12,
- Page 250 and 251:
attainment of FDC post DLI. Interes
- Page 252 and 253:
myelodysplastic syndromes is associ
- Page 254 and 255:
ubiquitous chaperone that promotes
- Page 256 and 257:
was thought that they are linked to
- Page 258 and 259:
pathologic induction of miR-28 in M
- Page 260 and 261:
STATs. Second, levels of HP1 alpha
- Page 262 and 263:
72. Irandoust MI, Aarts LH, Roovers
- Page 264 and 265:
A.M. Vannucchi Section of Hematolog
- Page 266 and 267:
2,559 patients with a diagnosis of
- Page 268 and 269:
tant use of aspirin should be caref
- Page 270 and 271:
sions at this regard. Based on thes
- Page 272 and 273:
in bcr-abl-negative myeloproliferat
- Page 274 and 275:
Table 1. Prognostic scoring systems
- Page 276 and 277:
Figure 1. Current inhibitors of JAK
- Page 278 and 279:
Table 4. A risk-based approach to d
- Page 280 and 281:
the flexibility to be adjusted as t
- Page 282 and 283:
A. Vacca 1 D. Ribatti 2 1 Departmen
- Page 284 and 285:
neovessel building together with MM
- Page 286 and 287:
Mevastatin, a specific inhibitor of
- Page 288 and 289:
egression of tumor vessels, and app
- Page 290 and 291:
diagnosis does not require genetic
- Page 292 and 293:
Genetics prognostic tools should be
- Page 294 and 295:
sone induction improves outcome of
- Page 296 and 297:
Table 1. Conventional chemotherapy
- Page 298 and 299:
Novel agents given as consolidation
- Page 300 and 301:
dence of peripheral neuropathy, gas
- Page 302 and 303:
31. Barlogie B, Tricot G, Anaissie
- Page 304 and 305:
Table 1. Major differences between
- Page 306 and 307:
first line therapy have shown survi
- Page 308 and 309: transplantation, 7,91 and generally
- Page 310 and 311: methylation characterizes juvenile
- Page 312 and 313: Table 1. Clinical signs of possible
- Page 314 and 315: Table 4. Distribution of CSF involv
- Page 316 and 317: ently results in a less than 5% cum
- Page 318 and 319: 90. German-Austrian-Swiss ALL-BFM S
- Page 320 and 321: U. Nowak-Göttl 1 R. Junker 1 A. Kr
- Page 322 and 323: Based on the data obtained from the
- Page 324 and 325: 59. Male C, Chait P, Ginsberg JS, e
- Page 326 and 327: Table 1. Characteristic features of
- Page 328 and 329: Table 2. Mutational spectrum of CDA
- Page 330 and 331: megarakaryoblastic leukemia (AMKL)
- Page 332 and 333: R.E. Ware Professor and Vice-Chairm
- Page 334 and 335: protein, cytokines, and soluble adh
- Page 336 and 337: example, improving blood viscosity
- Page 338 and 339: 92(9):1266-7. 36. Bensinger TA, Gil
- Page 340 and 341: London, United Kingdom, June 9-12,
- Page 342 and 343: port have also been used. 5 Combina
- Page 344 and 345: Wingard JR, Young J-AH, Boeckh MJ.
- Page 346 and 347: K. Rezvani 1 J. Barrett 2 1 Haemato
- Page 348 and 349: include the childhood infectious il
- Page 350 and 351: Summary Patients undergoing hematop
- Page 352 and 353: Table 1. Key issues. In a retrospec
- Page 354 and 355: invasive method to assess iron over
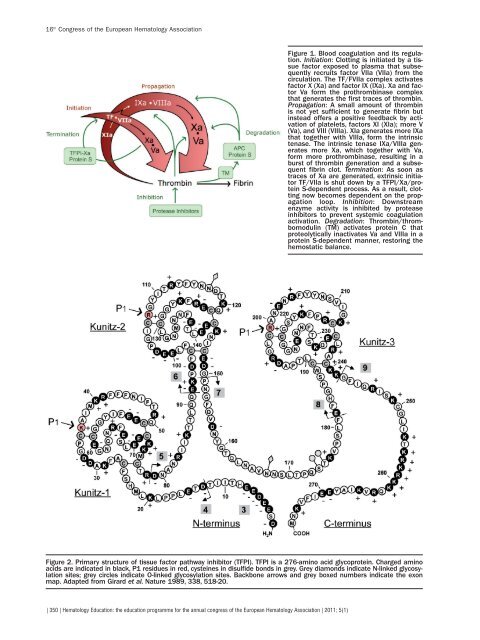
- Page 356 and 357: stitution but even with optimal sub
- Page 360 and 361: and inhibits FVIIa, and that the se
- Page 362 and 363: Figure 4. Regulation of coagulation
- Page 364 and 365: T. Baglin Department of Haematology
- Page 366 and 367: Figure 1. Illustration of alternati
- Page 368 and 369: compared with 3.5% in patients with
- Page 370 and 371: 49. Hron G, Kollars M, Binder BR, E
- Page 372 and 373: Women receiving vitamin K antagonis
- Page 374 and 375: molecular weight heparin as prophyl
- Page 376 and 377: eral morbidity and mortality. 17-21
- Page 378 and 379: the HOD construct. Furthermore, the
- Page 380 and 381: Goals of future murine studies incl
- Page 382 and 383: F. Noizat-Pirenne C. Tournamille Et
- Page 384 and 385: phenotype. 26 In 2010, we investiga
- Page 386 and 387: ody has been involved in DHTR. 37 T
- Page 388 and 389: antigen. Cases can be encountered d
- Page 390 and 391: S.R. Sloan Harvard Medical School &
- Page 392 and 393: We also analyzed patient databases
- Page 394 and 395: Index of authors Altman J. 27 Bacig
- Page 396 and 397: Cornelissen J. Affiliations to disc
- Page 398 and 399: GlaxoSmithKline (Research Support;