Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
The Learning Goal for this assignment is:<br />
Distinguish between bonding forces holding compounds together and other attractive<br />
forces, including hyrdrogen bonding and van der waals forces.<br />
Introduction to Ionic Compounds<br />
Those molecules that consist of charged ions with opposite charges are called IONIC. These ionic<br />
compounds are generally solids with high melting points and conduct electrical current. Ionic<br />
compounds are generally formed from metal and a non-metal elements. See Ionic Bonding below.<br />
Ionic Compound Example<br />
For example, you are familiar with the fairly benign unspectacular behavior of common white<br />
crystalline table salt (NaCl). Salt consists of positive sodium ions (Na + ) & negative chloride ions (Cl - ).<br />
On the other hand the element sodium is a silvery gray metal composed of neutral atoms which react<br />
vigorously with water or air. Chlorine as an element is a neutral greenish-yellow, poisonous, diatomic<br />
gas (Cl2).<br />
The main principle to remember is that ions are completely different in physical and chemical<br />
properties from the neutral atoms of the elements.<br />
The notation of the + and - charges on ions is very important as it conveys a definite meaning.<br />
Whereas elements are neutral in charge, IONS have either a positive or negative charge depending<br />
upon whether there is an excess of protons (positive ion) or excess of electrons (negative ion).<br />
Formation of Positive Ions<br />
Metals usually have 1-4 electrons in the outer energy level. The electron arrangement of a rare gas is<br />
most easily achieved by losing the few electrons in the newly started energy level. The number of<br />
electrons lost must bring the electron number "down to" that of a prior rare gas.<br />
How will sodium complete its octet?<br />
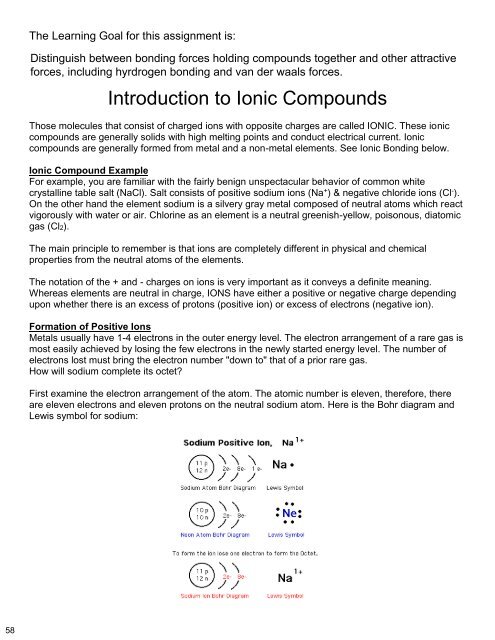
First examine the electron arrangement of the atom. The atomic number is eleven, therefore, there<br />
are eleven electrons and eleven protons on the neutral sodium atom. Here is the Bohr diagram and<br />
Lewis symbol for sodium:<br />
58