- Page 2 and 3:
A Textbook of Clinical Pharmacology
- Page 4 and 5:
A Textbook of Clinical Pharmacology
- Page 6 and 7:
This fifth edition is dedicated to
- Page 8 and 9:
FOREWORD viii PREFACE ix ACKNOWLEDG
- Page 10 and 11:
PREFACE Clinical pharmacology is th
- Page 12 and 13:
PART I GENERAL PRINCIPLES
- Page 14 and 15:
● Use of drugs 3 ● Adverse effe
- Page 16 and 17:
and acquired factors, notably disea
- Page 18 and 19:
100 Effect (%) 0 0 5 10 1 10 100 (a
- Page 20 and 21:
Dose ratio -1 100 50 The relationsh
- Page 22 and 23:
● Introduction 11 ● Constant-ra
- Page 24 and 25:
In reality, processes of eliminatio
- Page 26 and 27:
lood (from which samples are taken
- Page 28 and 29:
● Introduction 17 ● Bioavailabi
- Page 30 and 31:
ROUTES OF ADMINISTRATION ORAL ROUTE
- Page 32 and 33:
Transdermal absorption is sufficien
- Page 34 and 35:
FURTHER READING Fix JA. Strategies
- Page 36 and 37:
and thromboxanes are CYP450 enzymes
- Page 38 and 39:
and lorazepam. Some patients inheri
- Page 40 and 41:
Orally administered drug Parenteral
- Page 42 and 43:
● Introduction 31 ● Glomerular
- Page 44 and 45:
ACTIVE TUBULAR REABSORPTION This is
- Page 46 and 47:
DISTRIBUTION Drug distribution is a
- Page 48 and 49:
Detailed recommendations on dosage
- Page 50 and 51:
DIGOXIN Myxoedematous patients are
- Page 52 and 53:
● Introduction 41 ● Role of dru
- Page 54 and 55:
25 20 10 Life-threatening toxicity
- Page 56 and 57:
● Introduction 45 ● Harmful eff
- Page 58 and 59:
vagina in girls in their late teens
- Page 60 and 61:
an anti-analgesic effect when combi
- Page 62 and 63:
Case history A 20-year-old female m
- Page 64 and 65:
METABOLISM At birth, the hepatic mi
- Page 66 and 67:
lifelong effects as a result of tox
- Page 68 and 69:
DISTRIBUTION Ageing is associated w
- Page 70 and 71:
DIGOXIN Digoxin toxicity is common
- Page 72 and 73:
FURTHER READING Dhesi JK, Allain TJ
- Page 74 and 75:
Factors involved in the aetiology o
- Page 76 and 77:
analgesic. Following its release, t
- Page 78 and 79:
antibiotics, such as penicillin or
- Page 80 and 81:
predisposes to non-immune haemolysi
- Page 82 and 83:
● Introduction 71 ● Useful inte
- Page 84 and 85:
Response Therapeutic range Toxic ra
- Page 86 and 87:
Table 13.1: Interactions outside th
- Page 88 and 89:
Table 13.5: Competitive interaction
- Page 90 and 91:
● Introduction: ‘personalized m
- Page 92 and 93:
Table 14.2: Variations in drug resp
- Page 94 and 95:
lipoprotein (LDL) is impaired. LDL
- Page 96 and 97:
Key points • Genetic differences
- Page 98 and 99:
• Discovery • • Screening Pre
- Page 100 and 101:
Too many statistical comparisons pe
- Page 102 and 103:
ETHICS COMMITTEES Protocols for all
- Page 104 and 105:
Table 16.1: Recombinant proteins/en
- Page 106 and 107:
duration and benefit. Adenoviral ve
- Page 108 and 109:
● Introduction 97 ● Garlic 97
- Page 110 and 111:
A case report has suggested a possi
- Page 112 and 113:
including hypericin and pseudohyper
- Page 114 and 115:
PART II THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
- Page 116 and 117:
● Introduction 105 ● Sleep diff
- Page 118 and 119:
and daytime sleeping should be disc
- Page 120 and 121:
Key points • Insomnia and anxiety
- Page 122 and 123:
Box 19.1: Dopamine theory of schizo
- Page 124 and 125:
The Boston Collaborative Survey ind
- Page 126 and 127:
Oral medication, especially in liqu
- Page 128 and 129:
e.g. interpersonal difficulties or
- Page 130 and 131:
Partial response to first-line trea
- Page 132 and 133:
Key points Drug treatment of depres
- Page 134 and 135:
Case history A 45-year-old man with
- Page 136 and 137:
Levodopa PRINCIPLES OF TREATMENT IN
- Page 138 and 139:
• pulmonary, retroperitoneal and
- Page 140 and 141:
CHOREA The γ-aminobutyric acid con
- Page 142 and 143:
Cholinergic crisis Treatment of mya
- Page 144 and 145:
● Introduction 133 ● Mechanisms
- Page 146 and 147:
absolute arbiter. The availability
- Page 148 and 149:
Table 22.2: Metabolic interactions
- Page 150 and 151:
FURTHER ANTI-EPILEPTICS Other drugs
- Page 152 and 153:
Case history A 24-year-old woman wh
- Page 154 and 155:
Assessment of migraine severity and
- Page 156 and 157:
● General anaesthetics 145 ● In
- Page 158 and 159:
is the theoretical concern of a ‘
- Page 160 and 161:
• Respiratory system - apnoea fol
- Page 162 and 163:
Competitive antagonists (vecuronium
- Page 164 and 165:
have also proved useful in combinat
- Page 166 and 167:
● Introduction 155 ● Pathophysi
- Page 168 and 169:
ASPIRIN (ACETYLSALICYLATE) Use Anti
- Page 170 and 171:
Key points Drugs for mild pain •
- Page 172 and 173:
increases, correlating with the hig
- Page 174 and 175:
• If possible, use oral medicatio
- Page 176 and 177:
PART III THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM
- Page 178 and 179:
● Introduction: inflammation 167
- Page 180 and 181:
Chapter 33). All NSAIDs cause wheez
- Page 182 and 183:
• Stomatitis suggests the possibi
- Page 184 and 185:
Pharmacokinetics Allopurinol is wel
- Page 186 and 187:
PART IV THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
- Page 188 and 189:
● Introduction 177 ● Pathophysi
- Page 190 and 191:
esponsible for the strong predilect
- Page 192 and 193:
Ezetimibe Fat Muscle Dietary fat In
- Page 194 and 195:
educed). The risk of muscle damage
- Page 196 and 197:
● Introduction 185 ● Pathophysi
- Page 198 and 199:
Each of these classes of drug reduc
- Page 200 and 201:
AT 1 receptor) produce good 24-hour
- Page 202 and 203:
Table 28.2: Examples of calcium-cha
- Page 204 and 205:
Key points Drugs used in essential
- Page 206 and 207:
Case history A 72-year-old woman se
- Page 208 and 209:
Assess risk factors Investigations:
- Page 210 and 211:
Persistent ST segment elevation Thr
- Page 212 and 213:
Mechanism of action GTN works by re
- Page 214 and 215:
Because of the risks of haemorrhage
- Page 216 and 217:
Intrinsic pathway XIIa XIa the acti
- Page 218 and 219:
that the pharmacodynamic response i
- Page 220 and 221:
used with apparent benefit in acute
- Page 222 and 223:
● Introduction 211 ● Pathophysi
- Page 224 and 225:
The drugs that are most effective i
- Page 226 and 227:
therapeutic plasma concentration ca
- Page 228 and 229:
● Common dysrhythmias 217 ● Gen
- Page 230 and 231:
BASIC LIFE SUPPORT CARDIOPULMONARY
- Page 232 and 233:
arrest. The electrocardiogram is li
- Page 234 and 235:
should be given to insertion of an
- Page 236 and 237:
Drug interactions Amiodarone potent
- Page 238 and 239:
effect when treating sinus bradycar
- Page 240 and 241:
Case history A 24-year-old medical
- Page 242 and 243:
PART V THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
- Page 244 and 245:
CHAPTER 33 THERAPY OF ASTHMA, CHRON
- Page 246 and 247:
STEP 5: CONTINUOUS OR FREQUENT USE
- Page 248 and 249:
Adenylyl cyclase Table 33.1: Compar
- Page 250 and 251:
Drug interactions Although synergis
- Page 252 and 253:
use in asthma has declined consider
- Page 254 and 255:
α 1-antitrypsin deficiency, neutro
- Page 256 and 257:
PART VI THE ALIMENTARY SYSTEM
- Page 258 and 259:
● Peptic ulceration 247 ● Oesop
- Page 260 and 261:
PEPTIC ULCERATION 249 • With rega
- Page 262 and 263:
Ranitidine has a similar profile of
- Page 264 and 265:
Vestibular stimulation ? via cerebe
- Page 266 and 267:
cortical centres affecting vomiting
- Page 268 and 269:
• in hepatocellular failure to re
- Page 270 and 271:
Ciprofloxacin is occasionally used
- Page 272 and 273:
withdrawal), small doses of benzodi
- Page 274 and 275:
Table 34.7: Dose-independent hepato
- Page 276 and 277:
● Introduction 265 ● General ph
- Page 278 and 279:
dinucleotide (NAD) and nicotinamide
- Page 280 and 281:
Table 35.1: Common trace element de
- Page 282 and 283:
PART VII FLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTES
- Page 284 and 285:
● Introduction 273 ● Volume ove
- Page 286 and 287:
Key points Diuretics Diuretics are
- Page 288 and 289:
is sometimes caused by drugs, notab
- Page 290 and 291:
or with potassium-sparing diuretics
- Page 292 and 293:
Greger R, Lang F, Sebekova, Heidlan
- Page 294 and 295:
PART VIII THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
- Page 296 and 297:
● Introduction 285 ● Pathophysi
- Page 298 and 299:
in prefilled injection devices (‘
- Page 300 and 301:
Metformin should be withdrawn and i
- Page 302 and 303:
FURTHER READING American Diabetes A
- Page 304 and 305:
deficiency. Potassium iodide (3 mg
- Page 306 and 307:
fertility. It is contraindicated du
- Page 308 and 309:
● Introduction 297 ● Vitamin D
- Page 310 and 311:
effective in life-threatening hyper
- Page 312 and 313:
Further reading Block GA, Martin KJ
- Page 314 and 315:
Table 40.1: Actions of cortisol and
- Page 316 and 317:
injection may be useful, but if don
- Page 318 and 319:
CHAPTER 41 REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLO
- Page 320 and 321:
elease by the pituitary via negativ
- Page 322 and 323:
Treatment with depot progestogen in
- Page 324 and 325:
infusion using an infusion pump to
- Page 326 and 327:
significant proportion of men who r
- Page 328 and 329:
with symptoms caused by the release
- Page 330 and 331:
FURTHER READING Birnbaumer M. Vasop
- Page 332 and 333:
PART IX SELECTIVE TOXICITY
- Page 334 and 335:
● Principles of antibacterial che
- Page 336 and 337:
2. transfer of resistance between o
- Page 338 and 339:
Pharmacokinetics Absorption of thes
- Page 340 and 341:
Mechanism of action Macrolides bind
- Page 342 and 343:
asic quinolone structure dramatical
- Page 344 and 345:
Case history A 70-year-old man with
- Page 346 and 347:
PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT OF MYCOBAC
- Page 348 and 349:
Pharmacokinetics Absorption from th
- Page 350 and 351:
MYCOBACTERIUM LEPRAE INFECTION Lepr
- Page 352 and 353:
POLYENES AMPHOTERICIN B Uses Amphot
- Page 354 and 355:
therapy is adequate though more fre
- Page 356 and 357:
NUCLEOSIDE ANALOGUES ACICLOVIR Uses
- Page 358 and 359:
Table 45.3: Summary of available ac
- Page 360 and 361:
Uses Interferon-α when combined wi
- Page 362 and 363:
● Introduction 351 ● Immunopath
- Page 364 and 365:
Table 46.1: Examples of combination
- Page 366 and 367:
NON-NUCLEOSIDE ANALOGUE REVERSE TRA
- Page 368 and 369:
FUSION INHIBITORS Uses Currently, e
- Page 370 and 371:
salvage therapy include azithromyci
- Page 372 and 373:
● Malaria 361 ● Trypanosomal in
- Page 374 and 375:
Pharmacokinetics Chloroquine is rap
- Page 376 and 377:
Table 47.2: Drug therapy of non-mal
- Page 378 and 379:
● Introduction 367 ● Pathophysi
- Page 380 and 381:
Table 48.1: Classification of commo
- Page 382 and 383:
Polymorph count/mm 3 (a) (b) 10 000
- Page 384 and 385:
doses are used to prepare patients
- Page 386 and 387: Adverse effects Methotrexate Inhibi
- Page 388 and 389: Table 48.7: Summary of clinical pha
- Page 390 and 391: Table 48.9: Summary of the clinical
- Page 392 and 393: Plasma membrane Signal transduction
- Page 394 and 395: Table 48.10: Monoclonal antibodies
- Page 396 and 397: INTERFERON-ALFA 2B Interferon-alfa
- Page 398 and 399: PART X HAEMATOLOGY
- Page 400 and 401: ● Haematinics - iron, vitamin B 1
- Page 402 and 403: one marrow to produce red cells. Th
- Page 404 and 405: EPO Erythroid precursors Erythrocyt
- Page 406 and 407: Therapeutic principles The extent o
- Page 408 and 409: PART XI IMMUNOPHARMACOLOGY
- Page 410 and 411: ● Introduction 399 ● Immunity a
- Page 412 and 413: Key points Antigen recognition Expr
- Page 414 and 415: Table 50.1: Novel anti-proliferativ
- Page 416 and 417: Key points Treatment of anaphylacti
- Page 418 and 419: DRUGS THAT ENHANCE IMMUNE SYSTEM FU
- Page 420 and 421: PART XII THE SKIN
- Page 422 and 423: ● Introduction 411 ● Acne 411
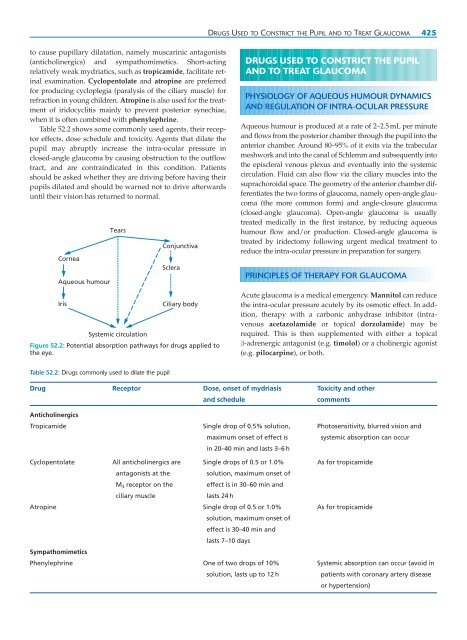
- Page 424 and 425: DERMATITIS (ECZEMA) PRINCIPLES OF T
- Page 426 and 427: SPECIALISTS ONLY SPECIALISTS ONLY E
- Page 428 and 429: TREATMENT OF OTHER SKIN INFECTIONS
- Page 430 and 431: effect of too high a dose of UVB in
- Page 432 and 433: PART XIII THE EYE
- Page 434 and 435: ● Introduction: ocular anatomy, p
- Page 438 and 439: Table 52.3: Antibacterial agents us
- Page 440 and 441: Table 52.6: Common drug-induced pro
- Page 442 and 443: PART XIV CLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- Page 444 and 445: ● Introduction 433 ● Pathophysi
- Page 446 and 447: Table 53.2: Central nervous system
- Page 448 and 449: which provide anonymized data to th
- Page 450 and 451: Peak plasma levels after smoking ci
- Page 452 and 453: Key points Acute effects of alcohol
- Page 454 and 455: FURTHER READING Goldman D, Oroszi G
- Page 456 and 457: Table 54.2: Common indications for
- Page 458 and 459: Table 54.5: Antidotes and other spe
- Page 460 and 461: Commission on Human Medicines (CHM)
- Page 462 and 463: Note: Page numbers in italics refer
- Page 464 and 465: atrial fibrillation 217, 221 digoxi
- Page 466 and 467: Cushing’s syndrome 302 cyclic ade
- Page 468 and 469: 5-fluorouracil 375-6 fluoxetine, mo
- Page 470 and 471: children 54 diazepam 108 iron prepa
- Page 472 and 473: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory dru
- Page 474 and 475: puberty (male), delay 314 puerperiu
- Page 476: tolerance 9, 433 benzodiazepines 10