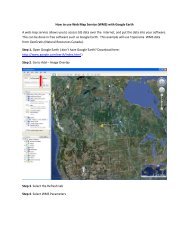
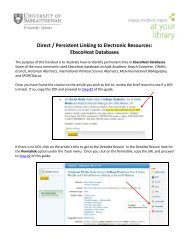
GREEN SEED COAT COLOUR RETENTION IN LENTIL - University ...
GREEN SEED COAT COLOUR RETENTION IN LENTIL - University ...
GREEN SEED COAT COLOUR RETENTION IN LENTIL - University ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
2.1 Introduction<br />
2.1.1 Lentil (Lens culinaris)<br />
2.0 LITERATURE REVIEW<br />
Lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.) is a dicotyledonous legume plant. Lentil is<br />
the fifth largest pulse crop grown in the world (Hymowitz, 1990). It grows as an<br />
indeterminate annual in a semi-erect pattern. The leaves are compound and usually<br />
have tendrils at the leaf tips. Lentil is capable of obtaining nitrogen through a<br />
symbiotic relationship with nitrogen-fixing Rhizobium bacteria, thereby reducing<br />
requirements for added nitrogen. Depending upon the genotype and environment<br />
there may be one to four flowers per peduncle. The small blue and white flowers<br />
develop pods usually containing one or two lens-shaped seeds, but in some cases<br />
may have up to four.<br />
Lentil is a diploid plant with a haploid chromosome number, n=7. It is<br />
native to the Fertile Crescent and has been an important food crop for over 8500<br />
years (Oplinger et al., 1990). Hundreds of millions of people in the world have<br />
made lentil a staple in their diet and receive a portion of their daily protein, fiber,<br />
4