APV Dryer Handbook - Umbc
APV Dryer Handbook - Umbc
APV Dryer Handbook - Umbc
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
fluid bed and are kept in<br />
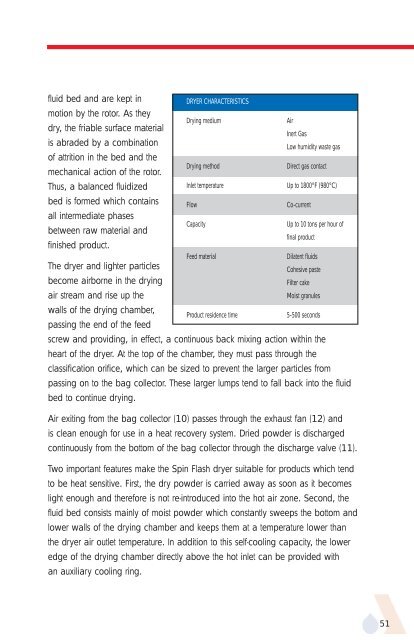
DRYER CHARACTERISTICS<br />
motion by the rotor. As they<br />
dry, the friable surface material<br />
Drying medium Air<br />
Inert Gas<br />
is abraded by a combination<br />
of attrition in the bed and the<br />
Low humidity waste gas<br />
mechanical action of the rotor.<br />
Drying method Direct gas contact<br />
Thus, a balanced fluidized<br />
Inlet temperature Up to 1800°F (980°C)<br />
bed is formed which contains<br />
all intermediate phases<br />
Flow Co-current<br />
between raw material and<br />
finished product.<br />
Capacity Up to 10 tons per hour of<br />
final product<br />
Feed material Dilatent fluids<br />
The dryer and lighter particles<br />
Cohesive paste<br />
become airborne in the drying<br />
Filter cake<br />
air stream and rise up the<br />
Moist granules<br />
walls of the drying chamber,<br />
passing the end of the feed<br />
Product residence time 5-500 seconds<br />
screw and providing, in effect, a continuous back mixing action within the<br />
heart of the dryer. At the top of the chamber, they must pass through the<br />
classification orifice, which can be sized to prevent the larger particles from<br />
passing on to the bag collector. These larger lumps tend to fall back into the fluid<br />
bed to continue drying.<br />
Air exiting from the bag collector (10) passes through the exhaust fan (12) and<br />
is clean enough for use in a heat recovery system. Dried powder is discharged<br />
continuously from the bottom of the bag collector through the discharge valve (11).<br />
Two important features make the Spin Flash dryer suitable for products which tend<br />
to be heat sensitive. First, the dry powder is carried away as soon as it becomes<br />
light enough and therefore is not re-introduced into the hot air zone. Second, the<br />
fluid bed consists mainly of moist powder which constantly sweeps the bottom and<br />
lower walls of the drying chamber and keeps them at a temperature lower than<br />
the dryer air outlet temperature. In addition to this self-cooling capacity, the lower<br />
edge of the drying chamber directly above the hot inlet can be provided with<br />
an auxiliary cooling ring.<br />
51