APV Dryer Handbook - Umbc
APV Dryer Handbook - Umbc
APV Dryer Handbook - Umbc
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
8<br />
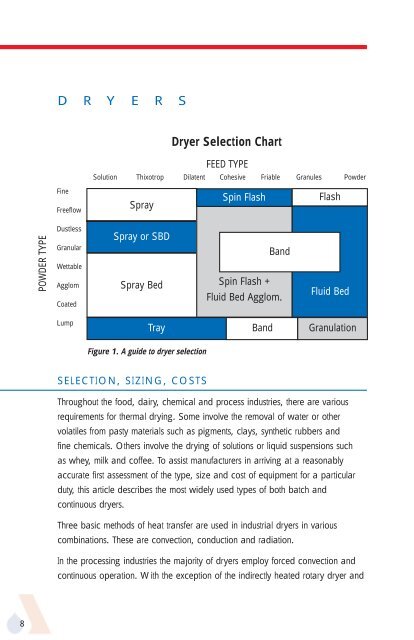
POWDER TYPE<br />
D R Y E R S<br />
Fine<br />
Freeflow<br />
Dustless<br />
Granular<br />
Wettable<br />
Agglom<br />
Coated<br />
Lump<br />
SELECTION, SIZING, COSTS<br />
<strong>Dryer</strong> Selection Chart<br />
FEED TYPE<br />
Solution Thixotrop Dilatent Cohesive Friable Granules Powder<br />
Spray<br />
Spray or SBD<br />
Spray Bed<br />
Figure 1. A guide to dryer selection<br />
Spin Flash Flash<br />
Band<br />
Spin Flash +<br />
Fluid Bed Agglom.<br />
Fluid Bed<br />
Tray Band Granulation<br />
Throughout the food, dairy, chemical and process industries, there are various<br />
requirements for thermal drying. Some involve the removal of water or other<br />
volatiles from pasty materials such as pigments, clays, synthetic rubbers and<br />
fine chemicals. Others involve the drying of solutions or liquid suspensions such<br />
as whey, milk and coffee. To assist manufacturers in arriving at a reasonably<br />
accurate first assessment of the type, size and cost of equipment for a particular<br />
duty, this article describes the most widely used types of both batch and<br />
continuous dryers.<br />
Three basic methods of heat transfer are used in industrial dryers in various<br />
combinations. These are convection, conduction and radiation.<br />
In the processing industries the majority of dryers employ forced convection and<br />
continuous operation. With the exception of the indirectly heated rotary dryer and