liiiMIIIfl~UDliiiMIII~U - Biblioteca de la Universidad Complutense ...
liiiMIIIfl~UDliiiMIII~U - Biblioteca de la Universidad Complutense ...
liiiMIIIfl~UDliiiMIII~U - Biblioteca de la Universidad Complutense ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
EFFECTS OF EXTRACEI<br />
4LULARATP Di HEPATOCVTES<br />
G705<br />
Tab<strong>la</strong> 3. Effect of extracellu<strong>la</strong>r 2ÉL inAIF, iso<strong>la</strong>tedhepatocytes<br />
thapsigargin,<br />
RHQ, azul A-23187 on[Ca<br />
Fíoore sca oce<br />
ity (as a parcentaga of incubations with no additiens,<br />
n = 3) were 73 ±4% (incubations with 1 pM PMA?1,<br />
73 t 3% (incubations with 1 pM PMA plus 10 pM<br />
BHQ), 72 5% (incubatiens with 1 pM PMA plus 0.1<br />
Additions tú tlie Incuhatione<br />
Intensity, %<br />
Nona 100<br />
1iM thapsigargin), and 75 t 5% (incubatiens with 1 piM<br />
PMAplus 2 pMA-23187).<br />
100pMATP<br />
0.1 pM thapsigargin<br />
0.1 iM thapsigargin±100 pMATP<br />
iO<br />
4MBHQ<br />
1OpMBHQ+100pMATP<br />
2 gMA-23187<br />
2jMA-23187 + 100 p.MATP<br />
296<br />
304<br />
371<br />
297<br />
355<br />
230<br />
Afta indo 1 ¡oadirxg, hapatocytas wera jncubated wjth tha additiona<br />
indicatad at 37’C, aad tha intracallu<strong>la</strong>r indo 1-emjttad fluorascanee<br />
light was <strong>de</strong>tarmined by flow cvtúmatry. Data are % of<br />
jncubatjons with no additjons (% of control) and reprasent marimuin<br />
value of fluorescenca intensjty at 395 12.5 ma re<strong>la</strong>tiva tú that at<br />
488 5 nm. ISaac peak valuas 2~-mebihzjng ware routinaly agente. obtajnad f<strong>la</strong>ta correspoad 45—75 a after tú a<br />
representativa addition offha djffereat experjment Ca that was rapeatad 3 times with simi<strong>la</strong>r<br />
resulta. BHQ, 2,5~di.(t-buty¡)-1,4-benzohYdrOqmnOaC.<br />
both ACC activity (Fig. 2) arid [Ca2’]t (Tab<strong>la</strong> 3) was<br />
markedly potentiated by extracellu<strong>la</strong>r ATE<br />
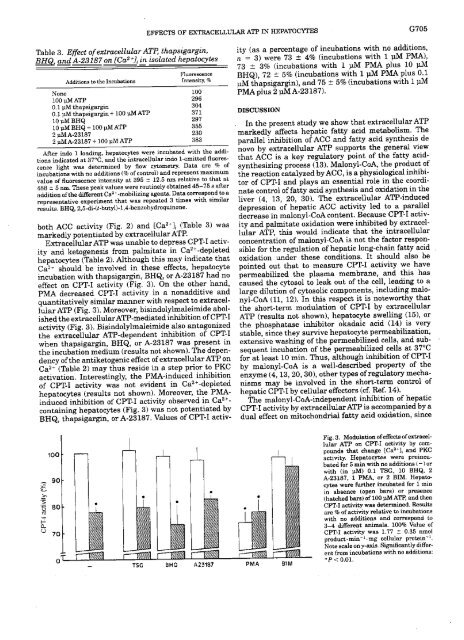
Extracallu<strong>la</strong>r ATPwas unable te <strong>de</strong>prasa CPT-I actiyity<br />
arid Rateganasis frem palmitate in Ca2’-dapletad<br />
hapatocytas (Tab<strong>la</strong> 2).Although this may indicate that<br />
Ca2’ should be involvad in thasa affects, hepatocyta<br />
incubation with thapsigargin, BHQ, er A-23187 had no<br />
effect en CPT-I activity (Fig. 3). Qn the othar hand,<br />
PMA <strong>de</strong>creased CPT-I activity in a nonadditive and<br />
quantitativaly simi<strong>la</strong>r marinar with respact te axtracellu<strong>la</strong>r<br />
ATP (Fig. 3). Moreover, bisindolylnia<strong>la</strong>imida abelished<br />
the extraeeilu<strong>la</strong>rAl?-ínediated inhibition of CPT-I<br />
activity (Fig. 3). Bisin<strong>de</strong>lylmaleimi<strong>de</strong> also antagenizad<br />
tha extracallu<strong>la</strong>r ATP-<strong>de</strong>pan<strong>de</strong>nt inhibition of CPT-I<br />
whan thapsiga.rgin, BHQ, or A-23187 waa presant in<br />
the incubation medium (resulta net shown). The <strong>de</strong>pen<strong>de</strong>ncy<br />
of the antilcetogenie affact ofextracellu<strong>la</strong>rATP en<br />
Ca2~ (Tab<strong>la</strong> 2) may thus resi<strong>de</strong> in a step prior te PKC<br />
activatien. Interestingly, tite PMA-induced inhibition<br />
of CPT-I activity waa not avidant in Ca2’-<strong>de</strong>pleted<br />
hepatecytas (results not shown). Moreovar, tite PMAinduced<br />
inhibition of CPT-I activity observad in Ca2’contaiing<br />
hepatocytas (Fig. 3) was not potentiatad by<br />
BHQ, titapaigargin, er A-23 187. Values of CPT-I activ-<br />
u<br />
ce<br />
o<br />
-¡00<br />
90<br />
80<br />
70<br />
383<br />
DISCUSSION<br />
o ~I~sc RHO AfllS7 PMA SIM<br />
In tha praaant atudy we show that axtracellu<strong>la</strong>rATP<br />
markadly affecta hapatic fatty acid matabolism. Tha<br />
parallel inhibitien of ACC arid fatty acid syntheaia <strong>de</strong><br />
nove by extracallu<strong>la</strong>r ATP supperts tite general view<br />
that ACC is a key regu<strong>la</strong>tory point of tha fatty acidsynthasizing<br />
proceas (13). Malonyl-CeA, tite preduct of<br />
tite reactien catalyzad byACC, isa phyaielogical inhibiter<br />
of CPT-I and p<strong>la</strong>ya an essential reía in tite ceerdinata<br />
control of fatty acid synthasis and exidatien in tite<br />
livar (4, 13, 20, 30). Tha extracellu<strong>la</strong>r ATP-induced<br />
dapressien of itepatie ACC activity <strong>la</strong>d te a parallel<br />
<strong>de</strong>crease in malonyl-CoA centent. Bacause CPT-I actívity<br />
and palmitata oxidation were inhibitad by extracellu<strong>la</strong>r<br />
ATP, titis would indicate that tha intracallu<strong>la</strong>r<br />
cencentration of malonyl-CoA is net tha factor raspensible<br />
for the ragu<strong>la</strong>tion of hapatie leng-chain fatty acid<br />
oxidation un<strong>de</strong>r theaa conditiona. It should also be<br />
pointad eut that te measure CPT-I activity we haya<br />
permeabilized tite p<strong>la</strong>sma membrane, arad titis has<br />
causad tite cytesol te leak out of tite calí, <strong>la</strong>achng te a<br />
<strong>la</strong>rga dilutien of cytoaolic componanta, including malonyl-CoA<br />
(11, 12). In titis respect it is netewortity that<br />
tite shoñ-term modu<strong>la</strong>tien of CPT-I by extracailu<strong>la</strong>r<br />
ATP (rasults not shown), hepatocyta awalling (15), er<br />
tite piteapitatasa inhibiter ekadaic acid (14) <strong>la</strong> very<br />
stable, since thay survive hepatocyte permeabihzation,<br />
extensive waahing of the permeabilizad cal<strong>la</strong>, arad sub-<br />
sequent incubation of tha parmeabilizad celís at 37 0C<br />
for at leaat 10 mm. Thus, although inhibition of CPT-I<br />
by malenyl-CoA <strong>la</strong> a wall-<strong>de</strong>scribed property of tite<br />
anzyme (4, 13, 20, 30), ether types e!ragu<strong>la</strong>tery machanisma<br />
may be invelvad in tite shert-tertn control of<br />
hapatic CPT-I by cellu<strong>la</strong>r effactors (cf. Ref. 14).<br />
Tha malonyl-CeA-in<strong>de</strong>pandant inltbition of hapatic<br />
CPT-I activity by extracallui<strong>la</strong>r ATP is accempaniad by a<br />
dual effect en mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation, sinca<br />
Fig. 3. Medu<strong>la</strong>tion ofcifacte of extracallu<strong>la</strong>r<br />
ATP on CPT-I activity by conpounds<br />
that changa [Ca2’]<br />
1 and PKC<br />
actjvity. Hepatocytes were preeneabatod<br />
fer 5 mii, with no additiona (—br<br />
with (ja pM) 0.1 TSG, 10 BHQ, 2<br />
A-23187, 1 PMA, or 2 BlM. Hepatocytes<br />
wera further incubated for 1 mm<br />
ja abseace (opea bara) or prasence<br />
(hatehad bara) of100 pM ATP, and ten<br />
CPT-I activity was <strong>de</strong>terminad. Results<br />
are % of activity ra¡ative tú incubationa<br />
with no additions and correspond tú<br />
3—4 differant anima<strong>la</strong>. 100% Value of<br />
CPT-I actjvity ng 177 : 0.35 mno¡<br />
preduct.mia< -mg celu<strong>la</strong>r pretein’.<br />
Note ecale en y-axis. Significantly differant<br />
5P < fron 0.01. jacubationa with no additions: