liiiMIIIfl~UDliiiMIII~U - Biblioteca de la Universidad Complutense ...
liiiMIIIfl~UDliiiMIII~U - Biblioteca de la Universidad Complutense ...
liiiMIIIfl~UDliiiMIII~U - Biblioteca de la Universidad Complutense ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
0706<br />
EFFECTS OF EXTRACELLULAR ATP Iii HEPATOGYTES<br />
ketone bedy formatien is <strong>de</strong>prassed while CO<br />
2 productien<br />
ia enhanced. Thus axtracellu<strong>la</strong>r ATP may reduce<br />
tite antry of fatty acyl-CeA into hapatie mitecitendria<br />
and divart mitochondriail acetyl-CoA inte tite tncarbexylic<br />
acid cyc<strong>la</strong> at tite expense of tite keteganic pathway.<br />
Tite atimu<strong>la</strong>tion of CO2 fermation 2~-mobilizing itas alse aganta beensucit observad<br />
as vasopresain in the case andofa etiter Ca<br />
1-adrenergic agents (e.g., sea Re!s.<br />
6, 11, 22), witareas tha inhibition of itepatic CPT-I<br />
activity and ketogenasis by vasopreasin (11, 22) and<br />
a1-adrenergic agenists (results net sitewn) itas been<br />
<strong>de</strong>seribad as well. Heweyar, otitara haya reportad titat<br />
a1-adrenargic agenta stimu<strong>la</strong>ta er haya no effect en<br />
itepatic katoganesis (cf Re!. 13). In any case, eur rasults<br />
are in agraamant witit the netion titat apart frem CPT-I<br />
otitar factors may exert control ovar tite fatty aci<strong>de</strong>xidativa<br />
precass in the liver at tite intramiteehondrial<br />
<strong>la</strong>yal (sea Rafs. 13 and 30 for reviaw).<br />
Tite effects of extracallu<strong>la</strong>r Al? and otiter Ca 2t~<br />
ACC (and hence of fatty acid synthasis <strong>de</strong> nove) by<br />
mebilizing effectera en livar metabolism are believed te<br />
be <strong>de</strong>pendant en receptor-mediated break<strong>de</strong>wn of membrana<br />
phespitatidylinoaitel 4,5-bispitespitate te produce<br />
diacylglycerel and inositol 1,4,5-trispitoapitata<br />
(1, 6). Extracallu<strong>la</strong>r ATP is also able te trigger tite<br />
recepter-mediated hydrelysis of piteaphatidylciteline<br />
and pitospitatidyletitalie<strong>la</strong>mifle by membrana phospitoupases<br />
(8, 9). In soma cali types, sucit as p<strong>la</strong>ta<strong>la</strong>ta and<br />
varleus secretory calís, tite diacylglycarol and the ineaitel<br />
1,4,5-trispitespitate limbs of phosphelipid hydrelysis<br />
act aynargically (1). However, titis is not tite case witit<br />
itepatocytes. Thus it has been sitewn titat tite stimu<strong>la</strong>tion<br />
of glycegan breakdown, gluconeoganesis, and tite<br />
tricarboxylic acid cyc<strong>la</strong> inducad by Ca2~-mobi1izing<br />
agenta in rat liver solely <strong>de</strong>pends en the inesitel<br />
1,4,5-trispitespitate cempenant of membrana phospitoinositida<br />
itydrelysis, i.a., en tite elevatien of [Ca2>]<br />
1(6, 8,<br />
9). Howaver, tite effecta of extracellu<strong>la</strong>r ATP en itepatic<br />
fatty acid metaboliam, as shewn in tite prasent papar,<br />
saam te be mere cemp<strong>la</strong>x (Fig. 4). Titus tite inhibition of<br />
extracellu<strong>la</strong>r Al? may be inadiated by tite e<strong>la</strong>vation of<br />
[Ca2t (as<br />
shown by tite <strong>la</strong>ck of petantiatien of tite PMA effect by<br />
BHQ, titapsigargin, andA-23187).<br />
Because PMA inhibits CPT-I actiyity, it might be<br />
argued that inhibition of PKC by bisin<strong>de</strong>lylmaleimi<strong>de</strong><br />
sitould cause an activation of CPT-I. Hewaver, it sitouid<br />
be pointed eut that tite basal activity of itepatecellu<strong>la</strong>r<br />
PKC ja very low bacause mest of tite anzyme is presant<br />
in tite soluble fraction (a.g., sea Raf. 28). merafora,<br />
inhibition of this marginal aetivity of PiCO should net<br />
haya any important affect en CPT-I activity. In contrast,<br />
bisin<strong>de</strong>lylmaieimida sitonid be expected te abelish<br />
PiCO-mediatad aventa witen PiCO is fully activatad<br />
by itepatocyte incubation witit pitorbol estara. Thus we<br />
haya observad titat bisin<strong>de</strong>lylmaleimida is ab<strong>la</strong> te bleck<br />
tite PMA-inducad inhibition of CPT-I activity (rasults<br />
net sitown), indicating titat tite inlhihitery affect of PMA<br />
en CPT-I ismadiated by activation of PI-CC.<br />
Extracellu<strong>la</strong>r ATP itas been aitown te trigger in vitre<br />
a nuinber ofbielogical responses in different ceil limes of<br />
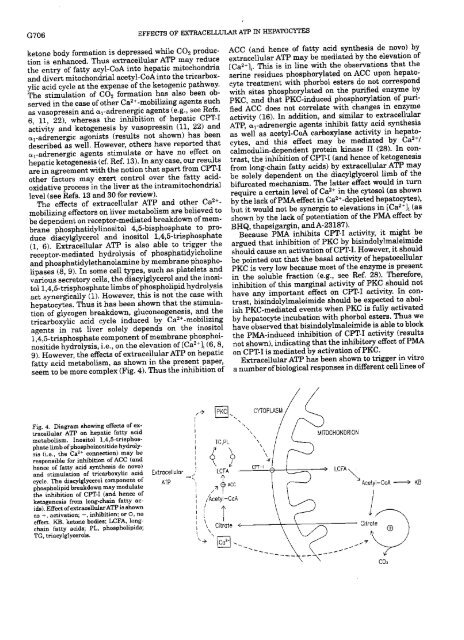
Fjg. 4. Diagram showirg effecta of extracallu<strong>la</strong>r<br />
ATP en hepatic fatty acid<br />
metabolism. <strong>la</strong>esitel 1,4,5-triBpheBphate<br />
[hab of phosphoinositi<strong>de</strong> 2~ connactien) hydroly- may be<br />
sis rasponBib<strong>la</strong> (jo., thafor Cainhibition<br />
ofACO (and<br />
hence of fatty acid synthesis da novo)<br />
and admu<strong>la</strong>tien of tricarbexy¡ic acid<br />
cycle. Tha diacytgtycerol compoaeat of<br />
phosphelipid breakdown may modutate<br />
the inhihitjon of CPT-I (and hanca of<br />
ketogenesis from long-chain fatty acida).<br />
Effect ofextraceltuiaxATP is shown<br />
aB +, activation; —, inhibitioa; oro, no<br />
effact. KB. katúna boches; LCFA, longchau,<br />
fatty acids; PL, phospholipids;<br />
TG. triacylglycaro¡s.<br />
Extrocellulor ><br />
ATP<br />