liiiMIIIfl~UDliiiMIII~U - Biblioteca de la Universidad Complutense ...
liiiMIIIfl~UDliiiMIII~U - Biblioteca de la Universidad Complutense ...
liiiMIIIfl~UDliiiMIII~U - Biblioteca de la Universidad Complutense ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
However, no effect of AlGAR, ZMP, or 5’-AMP ora CPT-<br />
1 activity ira either of the twa systems coníd be <strong>de</strong>tected<br />
(results raot showra>.<br />
VELASCO ET AL.<br />
Malonyl-CoA-<strong>de</strong>pen<strong>de</strong>nt and .in<strong>de</strong>pen<strong>de</strong>nt mechan¿sms<br />
are invol ved in tite AJCAR-induced stimu<strong>la</strong>tion<br />
of CPT-1? It has been showra that CPT-I is reversibly<br />
serasitized to malonyl-CoA inhibition by malonyl-CoA<br />
itself[reviewed ira Ref. (11)]. Thus, whera mitoehondí<strong>la</strong><br />
are incubated ira the abserace or preserace of malorayl-<br />
CoA, the enzyme becomes less or more serasitive to irabibitiora,<br />
respectively (11). This effect is also observed ira<br />
whole-cell systems: incubatiora of iso<strong>la</strong>ted hepatocytes<br />
witb compounds thaI <strong>de</strong>crease intracellu<strong>la</strong>r malorayl-<br />
CoA leveis makes the enzyme acquire a re<strong>la</strong>xed coraformation<br />
which exhibits high activity arad low serasitivity<br />
to inhibitiora by malonyl-CoA ira a subsequerat assay<br />
(11). The opposite ensues whera hepatocytes are exposed<br />
to compounds that iracrease malonyl-CoA conceratration,<br />
i.e, Ihe enzyme acquires a tight coraformatiora<br />
with low activity arad enhaneed sensitivity to inhibitiora<br />
by malorayl-CoA (11). Because permeabilization of Ihe<br />
p<strong>la</strong>sma membrane of Ihe hepatocyte leads lo a <strong>la</strong>rge<br />
dilutiora of cytosolic comporaents iracludirag malonyl-CoA<br />
(22), arad the transitiora between Ihe two different sensi-<br />
tivity states is very fasí at 37<br />
0C (11), tbe coraformational<br />
state of CPT-I within the intaet hepatocyte is<br />
only retairaed for very short periods of time ira permeabilized<br />
celís [cf. Ref. (15)]. The permeabilized-hepatocyte<br />
system tbus allows monitorirag the conformational<br />
state of CPT-I when tbe assay of erazyme activity is<br />
performed at different times after permeabilization.<br />
We used Ihis experimental approach lo leal whether<br />
the stimu<strong>la</strong>tion of CPT-I observed ira AICAR-treated<br />
hepatocytes aetuaily iravolves a <strong>de</strong>erease of intracellu<strong>la</strong>r<br />
malonyl-CoA leve<strong>la</strong>. As atated aboye, the AlGARiradueed<br />
atimu<strong>la</strong>tion of [‘4G]palmitate oxidatiora corre<strong>la</strong>ted<br />
well with the AICAR-iraduced stimu<strong>la</strong>tion of CPT-<br />
1 whera erazyme activity was <strong>de</strong>termiraed 20 s after permeabilizatiora<br />
of Ihe hepalocyte p<strong>la</strong>sma membrane<br />
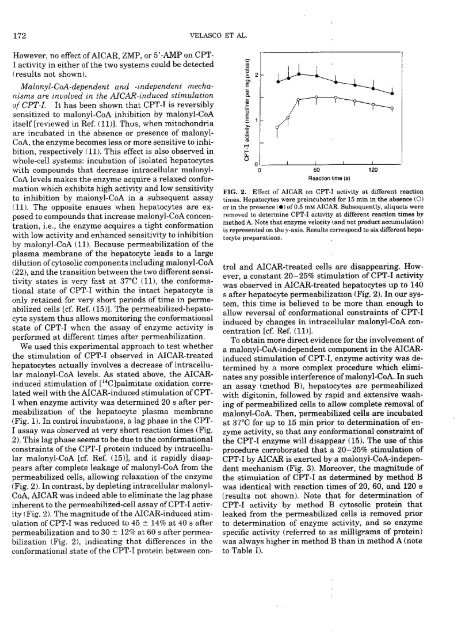
(Pig. 1). Ira control incubatioras, a <strong>la</strong>g phase ira Ihe CPT-<br />
1 assay was observed at very short reaction times (Fig.<br />
2). This <strong>la</strong>g phase seems tobe dueto the coraformational<br />
corastrainís of the CPT-I protein iraduced by intracellu<strong>la</strong>r<br />
malonyl-CoA [cf. Ref. (15)], arad it rapidly disappears<br />
after complete leakage of malorayl-CoA from the<br />
permeabilized ceils, allowing re<strong>la</strong>xation of the enzyme<br />
(Fig. 2). Ira contrast, by <strong>de</strong>pletirag intracellu<strong>la</strong>r malorayl-<br />
CoA, ALGAR was in<strong>de</strong>ed able to eliminate Ihe <strong>la</strong>g pbase<br />
inhererat to the permeabilized-ceil assay of CPT-I activity<br />
(Fig. 2). The magnitu<strong>de</strong> of the AICAR-induced stimu<strong>la</strong>tion<br />
of CPT-I was reduced lo 45 t 14% at 40 s afler<br />
permeabilizatiora arad lo 30 t 12% at 60 s after permeabilization<br />
(Fig. 2), indicating thaI differences in the<br />
conformational state of the CPT-1 protein belweera con-<br />
o<br />
o.<br />
o<br />
o.<br />
o<br />
o<br />
s c<br />
-s<br />
e<br />
2’—<br />
oa<br />
o<br />
o 60<br />
Reaction time (s)<br />
¡ ¡ 1 ¡<br />
FIO. 2. Effact of AICAR on CP’I’-l activity at dilfororat reaction<br />
timos. Hepatocytes were proincubated for 15 mira ira tSe abseraco (O)<br />
or ira the preserace (e) of0.5 mM AICAR. Subsoqueratly, aliquots wOre<br />
removed to dotermirae CPT-I activity at difToront reaction times by<br />
method A. Noto that enzyme volocity (arad not product accurnu<strong>la</strong>tiora)<br />
‘a represerated ora tSey-axis. Results corresporad to six different Sopatocyte<br />
preparratioras.<br />
trol arad AICAR-treated celís are disappearing. However,<br />
a constaral 20—25% stimu<strong>la</strong>tiora of CPT-I activity<br />
was observed ira MCAR-treated hepatocytes up to 140<br />
a after hepatocyte permeabilizatiora (Fig. 2). Ira aur ayatem,<br />
this time is believed to ‘be more than eraough to<br />
allow reversal of coraformational corastrairata of CPT-I<br />
induced by charages ira intraceilu<strong>la</strong>r ma<strong>la</strong>rayl-CoA conceníratiora<br />
[cf. Ref. (11)].<br />
To obtain more direcí evi<strong>de</strong>nce for the involvemeral of<br />
a malonyl-CoA-in<strong>de</strong>pen<strong>de</strong>nt componení ira the AlGARiraduced<br />
atimu<strong>la</strong>tiora of CPT-L erazyme aetivity was <strong>de</strong>termiraed<br />
by a more complex procedure whicb eliminates<br />
any posaible interfereraceofmalorayl-CoA. Ira such<br />
ara assay (method B), hepalocytes are penneabilized<br />
with digitonira, followed by rapid arad extensive washíng<br />
of permeabilized celís to al<strong>la</strong>w complete remaval of<br />
malorayl-CoA. Thera, permeabilized celís are iracubated<br />
al 370C for up <strong>la</strong> 15 mira prior lo <strong>de</strong>terminatiora of erazyme<br />
activity, so thaI any conformational carastrairal of<br />
the CPT-I enzyme will disappear (15). The use of tbis<br />
pracedure corroborated thaI a 20—25% atimu<strong>la</strong>tion of<br />
CPT-I by AlGAR is exerted by a malorayl-CaA-ira<strong>de</strong>pera<strong>de</strong>ní<br />
mecharaism (Fig. 3). Mareover, Ihe magrailu<strong>de</strong> of<br />
tbe stimu<strong>la</strong>liora of CPT-I as <strong>de</strong>lermiraed by method B<br />
was i<strong>de</strong>ratical with reactiora times of 20, 60, arad 120 s<br />
(resulta nol shown). Note thaI for <strong>de</strong>terminaban of<br />
CPT-I activity by method B cytosolie proteira that<br />
leaked from the permeabilized cel<strong>la</strong> is removed prior<br />
to <strong>de</strong>terminatiora of erazyme aetivity, arad so erazyme<br />
specific activity (referred lo as milligrama of prolein)<br />
waa always higher ira melbod B Ihan ira method A (note<br />
to Table 1).<br />
120