You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Pittura ID Sistema legante Resistenza alla presa<br />
di sporco<br />
Paint ID Binder System Dirt Pick Up Resistance<br />
after 7 Days<br />
Y-ref Y-ref Ratio<br />
Before After After/Before<br />
Pittura / Paint #4 100% Polimero A<br />
100% Polymer A<br />
88.54 84.43 0.954<br />
Pittura / Paint #5 70% Polimero A & 30%<br />
Polimero DD- tipo PUD<br />
70% Polymer A & 30%<br />
Polymer DD-PUD type<br />
90.37 87.59 0.969<br />
Pittura / Paint #6 70% Polimero A & 30%<br />
Polimero DD- tipo acrilico<br />
70% Polymer A & 30%<br />
Polymer DD-Acrylic type<br />
89.25 87.95 0.985<br />
Tab. 6 Resistenza all’assorbimento dello sporco dei p.v. a sviluppo diffusivo<br />
Dirt Pick Up Resistance of Designed Diffusion Coatings<br />
Dopo il processo di essiccazione ad aria<br />
per 4 ore, la riflettanza Y è stata nuovamente<br />
misurata (rif. –Y dopo).<br />
I rif Yprima, i rif. Y dopo e i loro rapporti<br />
sono elencati in tab. 6. I rapporti più<br />
elevati (quasi 1) indicano una migliore<br />
resistenza all’assorbimento dello sporco.<br />
In generale, le superfici più dure e/o<br />
più idrofobe sono più resistenti all’assorbimento<br />
dello sporco. I Polimeri DD<br />
a sviluppo diffusivo sono più idrofili del<br />
Polimero A, ma essi formano film più<br />
duri a tempi brevi. In generale, in que-<br />
ste formulazioni e test, il Polimero a sviluppo<br />
diffusivo aumenta il DPUR. I test<br />
della durezza al pendolo sono stati eseguiti<br />
con le stesse serie di pitture sui<br />
pannelli di alluminio rivestiti con applicatore<br />
a blocco da 5 mil ed essiccati<br />
in CTR a 25°C e umidità relativa al<br />
50% per 7 giorni.<br />
I dati sono elencati in tab. 7. Con il polimero<br />
DD a sviluppo diffusivo del tipo<br />
PUD, essa ha subito una miglioria pari<br />
a circa 2 unità, mentre con il tipo acrilico<br />
non si è osservato alcun migliora-<br />
Pittura ID Sistema legante Durezza Brillantezza<br />
alla matita 20° 60°<br />
7 giorni<br />
Paint ID Binder System Pencil Gloss<br />
Hardness 20 Degree 60 Degree<br />
(7Days)<br />
Pittura #4 100% Polimero A 2B 62 85<br />
Paint #4 100% Polymer A<br />
Pittura #5 70% Polimero A & 30% HB 56 82<br />
Paint #5 Polimero DD- tipo PUD<br />
70% Polymer A &<br />
30% Polymer DD-PUD type<br />
Pittura #6 70% Polimero A & 30% 2B 65 85<br />
Paint #6 Polimero DD- tipo acrilico<br />
70% Polymer A & 30%<br />
Polymer DD-Acrylic type<br />
Tab. 7 Durezza alla matita e brillantezza dl p.v a sviluppo diffusivo<br />
Pencil Hardness and Gloss of Designed Diffusion Coatings<br />
Designed Diffusion technology provides the<br />
formulator with the flexibility to improve<br />
the cost performance of the polymer system<br />
at lower VOC when compared to AUH<br />
polymers.<br />
Figure 7 and Table 8 demonstrate the comparable<br />
film properties of Designed Diffusion<br />
polymers versus commercial AUH<br />
polymers.<br />
Table 8 also demonstrates the poor film<br />
property performance over the porous wood<br />
substrate due to poor film formation at low<br />
VOC.<br />
Conclusions<br />
Addition of a low Tg (< -5°C) specially designed<br />
diffusion polymer DD to a higher Tg<br />
(>20°C) Polymer A dominant phase coating<br />
formulation at or slightly above the percolation<br />
threshold (typically between 20 to<br />
35%) forms a pathway for selected coalescent<br />
to escape from the polymer A dominant<br />
phase, which enhances film<br />
formation, reduces VOC and accelerates<br />
the development of hardness and hardnessrelated<br />
property such as block, print, and<br />
RESINE<br />
mento. Risulta evidente che la durezza<br />
alla matita misura una proprietà differente<br />
del film rispetto alla durezza Konig.<br />
Infatti il progresso della durezza<br />
alla matita nel film modificato con il tipo<br />
PUD del Polimero DD a sviluppo diffusivo<br />
è dovuto principalmente alla<br />
proprietà del PUD piuttosto che all’accelerazione<br />
della rimozione del coalescente<br />
dal Polimero A. La brillantezza<br />
ad angoli speculari di 20 e 60 gradi per<br />
la stessa serie di pitture è stata misurata<br />
utilizzando gli stessi pannelli del<br />
test della matita e i dati sono elencati<br />
in tab. 7. È noto che i leganti PUD tendono<br />
a produrre una bassa brillantezza<br />
nei sistemi pigmentati. L’effetto esercitato<br />
dal tipo PUD del polimero DD a<br />
sviluppo diffusivo sulla brillantezza è<br />
stato ridotto al minimo con l’impiego<br />
del tipo appropriato di polimero acrilico<br />
A, che, a volte, può apportare migliorie<br />
alla brillantezza. Il polimero DD<br />
a sviluppo diffusivo perfeziona le proprietà<br />
filmogene ed accelera lo svilup-<br />
DPUR at a much faster rate without significantly<br />
compromising other properties.<br />
It was found that both PUD and Acrylic polymers<br />
can be made to function as designed<br />
diffusion Polymers DD.<br />
It is more preferable that the designed diffusion<br />
polymer DD is slightly more hydrophilic<br />
than the dominant phase Polymer<br />
A or protected by a more hydrophilic layer<br />
because this way, the coalescent is more<br />
selectively partitioned into the high Tg polymer.<br />
A phase and film formation and water<br />
evaporation triggers the acceleration of<br />
removal of the coalescent from the polymer<br />
A phase.<br />
This work offered a totally new strategy in<br />
enhancing film formation, reducing VOC<br />
po della durezza oltre ad essere tipicamente<br />
più idrofilo del Polimero A di fase<br />
dominante. A causa di questi fattori<br />
concorrenti, sono state osservate le variazioni<br />
della resistenza agli agenti chimici,<br />
all’acqua e al processo corrosivo.<br />
Queste proprietà possono essere bilanciate<br />
mediante le formulazioni. Il<br />
confronto della tecnologia dello sviluppo<br />
diffusivo con gli ibridi uretanoacrilici<br />
in commercio (AUH) è<br />
inevitabile. La prima fornisce al formulatore<br />
la flessibilità per migliorare il<br />
rapporto costi/prestazione del sistema<br />
polimerico a bassa emissione VOC rispetto<br />
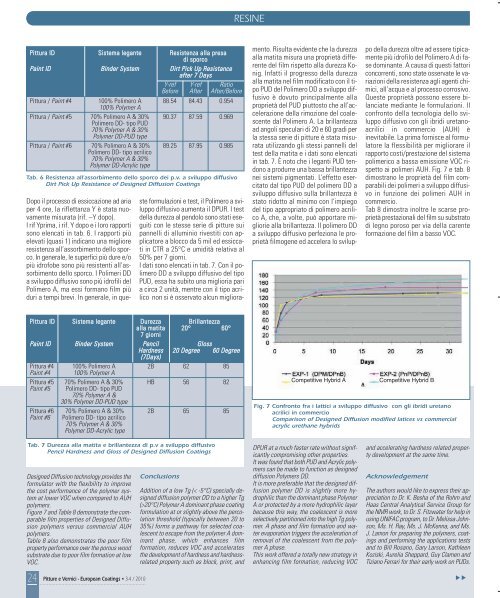
ai polimeri AUH. Fig. 7 e tab. 8<br />
dimostrano le proprietà del film comparabili<br />
dei polimeri a sviluppo diffusivo<br />
in funzione dei polimeri AUH in<br />
commercio.<br />
Tab 8 dimostra inoltre le scarse proprietà<br />
prestazionali del film su substrato<br />
di legno poroso per via della carente<br />
formazione del film a basso VOC.<br />
Competitive Hybrid A Competitive Hybrid B<br />
Fig. 7 Confronto fra i lattici a sviluppo diffusivo con gli ibridi uretano<br />
acrilici in commercio<br />
Comparison of Designed Diffusion modified latices vs commercial<br />
acrylic urethane hybrids<br />
and accelerating hardness related property<br />
development at the same time.<br />
Acknowledgement<br />
The authors would like to express their appreciation<br />
to Dr. K. Besha of the Rohm and<br />
Haas Central Analytical Service Group for<br />
the NMR work, to Dr. S. Fitzwater for help in<br />
using UNIFAC program, to Dr. Melissa Johnson,<br />
Ms. H. Ray, Ms. J. McKenna, and Ms.<br />
J. Lamon for preparing the polymers, coatings<br />
and performing the applications tests<br />
and to Bill Rosano, Gary Larson, Kathleen<br />
Koziski, Aurelia Sheppard, Guy Clamen and<br />
Tiziano Ferrari for their early work on PUDs.<br />
24 Pitture e Vernici - European Coatings • 3-4 / <strong>2010</strong><br />
▼<br />
▼