Measurement of the Z boson cross-section in - Harvard University ...
Measurement of the Z boson cross-section in - Harvard University ...
Measurement of the Z boson cross-section in - Harvard University ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Chapter 3: Lum<strong>in</strong>osity <strong>Measurement</strong> at <strong>the</strong> LHC and <strong>in</strong> ATLAS 75<br />
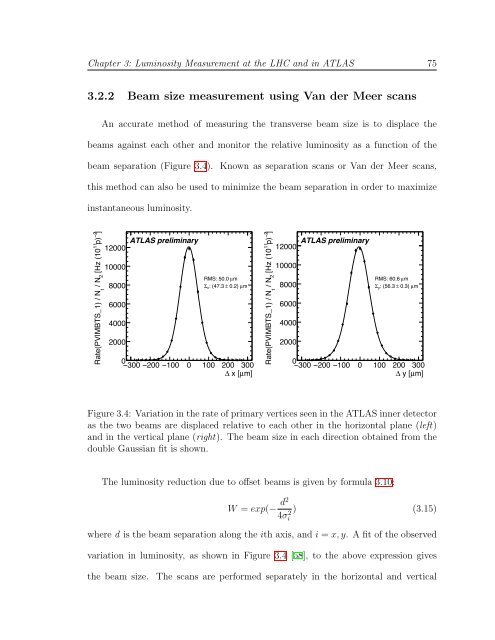
3.2.2 Beam size measurement us<strong>in</strong>g Van der Meer scans<br />
An accurate method <strong>of</strong> measur<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong> transverse beam size is to displace <strong>the</strong><br />
beams aga<strong>in</strong>st each o<strong>the</strong>r and monitor <strong>the</strong> relative lum<strong>in</strong>osity as a function <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
beam separation (Figure 3.4). Known as separation scans or Van der Meer scans,<br />
this method can also be used to m<strong>in</strong>imize <strong>the</strong> beam separation <strong>in</strong> order to maximize<br />
<strong>in</strong>stantaneous lum<strong>in</strong>osity.<br />
]<br />
−2<br />
p)<br />
11<br />
[Hz (10<br />
2<br />
/ N<br />
1<br />
Rate(PV|MBTS_1) / N<br />
12000<br />
10000<br />
8000<br />
6000<br />
4000<br />
2000<br />
ATLAS prelim<strong>in</strong>ary<br />
RMS: 50.0 µ m<br />
Σx:<br />
(47.3 ± 0.2) µ m<br />
0<br />
−300 −200 −100 0 100 200 300<br />
Δ x [ µ m]<br />
]<br />
−2<br />
p)<br />
11<br />
[Hz (10<br />
2<br />
/ N<br />
1<br />
Rate(PV|MBTS_1) / N<br />
12000<br />
10000<br />
8000<br />
6000<br />
4000<br />
2000<br />
ATLAS prelim<strong>in</strong>ary<br />
RMS: 60.6 µ m<br />
Σy:<br />
(56.3 ± 0.3) µ m<br />
0<br />
−300 −200 −100 0 100 200 300<br />
Δ y [ µ m]<br />
Figure 3.4: Variation <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> rate <strong>of</strong> primary vertices seen <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> ATLAS <strong>in</strong>ner detector<br />
as <strong>the</strong> two beams are displaced relative to each o<strong>the</strong>r <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> horizontal plane (left)<br />
and <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> vertical plane (right). The beam size <strong>in</strong> each direction obta<strong>in</strong>ed from <strong>the</strong><br />
double Gaussian fit is shown.<br />
The lum<strong>in</strong>osity reduction due to <strong>of</strong>fset beams is given by formula 3.10:<br />
W = exp(− d2<br />
4σ2 ) (3.15)<br />
i<br />
where d is <strong>the</strong> beam separation along <strong>the</strong> ith axis, and i = x, y. A fit <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> observed<br />
variation <strong>in</strong> lum<strong>in</strong>osity, as shown <strong>in</strong> Figure 3.4 [58], to <strong>the</strong> above expression gives<br />
<strong>the</strong> beam size. The scans are performed separately <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> horizontal and vertical