- Page 1 and 2:
simatic SIMATIC PCS 7 Process Contr
- Page 3 and 4:
SIMATIC PCS 7 Process Control Syste
- Page 5 and 6:
© Siemens AG 2007 Siemens ST PCS 7
- Page 7 and 8:
SIMATIC IT SIMATIC NET Industrial C
- Page 9 and 10:
Maintenance Substation Distribution
- Page 11 and 12:
© Siemens AG 2007 Siemens ST PCS 7
- Page 13 and 14:
■ Benefits With its pioneering de
- Page 15 and 16:
© Siemens AG 2007 System-neutral c
- Page 17 and 18:
■ Selection and Ordering Data Ord
- Page 19 and 20:
■ Selection and Ordering Data onl
- Page 21 and 22:
© Siemens AG 2007 System-neutral c
- Page 23 and 24:
Additional recommendations/limitati
- Page 25 and 26:
■ Design Operational display Hard
- Page 27 and 28:
■ Technical specifications (cont.
- Page 29 and 30:
Additional and expansion components
- Page 31 and 32:
■ Overview Operating devices In a
- Page 33 and 34:
© Siemens AG 2007 Starter systems
- Page 35 and 36:
ES Ethernet onboard Plant bus Ether
- Page 37 and 38:
© Siemens AG 2007 Starter systems
- Page 39 and 40:
■ Selection and Ordering Data Ord
- Page 41 and 42:
© Siemens AG 2007 Starter systems
- Page 43 and 44:
■ Technical specifications (cont.
- Page 45 and 46:
© Siemens AG 2007 Starter systems
- Page 47 and 48:
© Siemens AG 2007 Engineering syst
- Page 49 and 50:
■ Overview © Siemens AG 2007 Eng
- Page 51 and 52:
© Siemens AG 2007 Engineering syst
- Page 53 and 54:
The OS areas and the image hierarch
- Page 55 and 56:
© Siemens AG 2007 Engineering syst
- Page 57 and 58:
■ Overview Project Multi project
- Page 59 and 60:
■ Overview Plant bus DP/PA link P
- Page 61 and 62:
Predefined product configurations S
- Page 63 and 64:
© Siemens AG 2007 Engineering syst
- Page 65 and 66:
■ Selection and Ordering Data Ord
- Page 67 and 68:
■ Benefits Safety Integrated for
- Page 69 and 70:
© Siemens AG 2007 Engineering syst
- Page 71 and 72:
© Siemens AG 2007 Engineering syst
- Page 73 and 74:
© Siemens AG 2007 Operator system
- Page 75 and 76:
■ Technical specifications Defini
- Page 77 and 78:
SIMATIC PCS 7 supports multi-user s
- Page 79 and 80:
■ Selection and Ordering Data Ord
- Page 81 and 82:
■ Overview OS basic hardware and
- Page 83 and 84:
Central user management, access con
- Page 85 and 86:
■ Selection and Ordering Data Ord
- Page 87 and 88:
■ Overview Using the SIMATIC Safe
- Page 89 and 90:
Redundant OS single stations / OS s
- Page 91 and 92:
■ Overview OS server: short-term
- Page 93 and 94:
■ Overview OS clients OS-LAN OS s
- Page 95 and 96:
■ Overview OS clients OS server (
- Page 97 and 98:
■ Overview SIMATIC PCS 7 Web clie
- Page 99 and 100:
© Siemens AG 2007 Operator systemw
- Page 101 and 102:
© Siemens AG 2007 Batch automation
- Page 103 and 104:
■ Design SIMATIC BATCH clients an
- Page 105 and 106:
■ Overview The basic software for
- Page 107 and 108:
© Siemens AG 2007 Batch automation
- Page 109 and 110:
■ Overview Note: The SIMATIC BATC
- Page 111 and 112:
■ Overview Plant Unit Hierarchica
- Page 113 and 114:
© Siemens AG 2007 SIMATIC Route Co
- Page 115 and 116:
■ Configuration SIMATIC Route Con
- Page 117 and 118:
■ Selection and Ordering Data RC
- Page 119 and 120:
© Siemens AG 2007 SIMATIC Route Co
- Page 121 and 122:
Configuration of the partial routes
- Page 123 and 124:
© Siemens AG 2007 Asset Management
- Page 125 and 126:
■ Overview The maintenance engine
- Page 127 and 128:
Typical sequence of a maintenance c
- Page 129 and 130:
© Siemens AG 2007 Communication 9/
- Page 131 and 132:
■ Overview SCALANCE X-400 Enginee
- Page 133 and 134:
■ Function Decision aid for Indus
- Page 135 and 136:
Operator Station Switch SCALANCE X4
- Page 137 and 138:
SCALANCE X414-3E and X408-2 • Mod
- Page 139 and 140:
SCALANCE X-200 IRT With the X204 IR
- Page 141 and 142:
Network size parameters / TP cable
- Page 143 and 144:
Communication Industrial Ethernet S
- Page 145 and 146:
Communication Industrial Ethernet S
- Page 147 and 148:
Type SCALANCE X216 SCALANCE X224 Tr
- Page 149 and 150:
■ Overview The Industrial Etherne
- Page 151 and 152:
■ Overview Industrial Ethernet Fa
- Page 153 and 154: © Siemens AG 2007 Communication In
- Page 155 and 156: ■ Selection and Ordering Data FO
- Page 157 and 158: ■ Selection and Ordering Data Ord
- Page 159 and 160: SCALANCE W788-1PRO access point The
- Page 161 and 162: ■ Overview Plant bus 1 INTERNET E
- Page 163 and 164: © Siemens AG 2007 Communication PR
- Page 165 and 166: ■ Overview Shielded twisted-pair
- Page 167 and 168: © Siemens AG 2007 Communication PR
- Page 169 and 170: ■ Overview PROFIBUS DP lines can
- Page 171 and 172: ■ Overview Direct interfacing of
- Page 173 and 174: ■ Overview To create a smooth net
- Page 175 and 176: ■ Technical specifications DP/PA
- Page 177 and 178: ■ Overview © Siemens AG 2007 Com
- Page 179 and 180: System components The basic compone
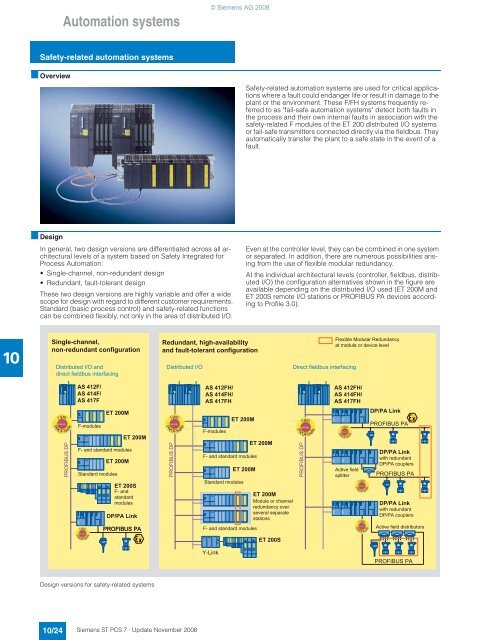
- Page 181 and 182: © Siemens AG 2008 Automation syste
- Page 183 and 184: ■ Technical specifications AS 412
- Page 185 and 186: Two Ethernet interfaces 10/100/1000
- Page 187 and 188: ■ Overview The AS 414-3 / 414-3IE
- Page 189 and 190: Selection and Ordering Data Order N
- Page 191 and 192: Recommended preferred types ■ Sel
- Page 193 and 194: ■ Selection and Ordering Data Ord
- Page 195 and 196: ■ Overview Fault-tolerant automat
- Page 197 and 198: Selection and ordering data Order N
- Page 199 and 200: Selection and ordering data Order N
- Page 201 and 202: ■ Selection and Ordering Data Ord
- Page 203: ■ Selection and Ordering Data Ord
- Page 207 and 208: Selection and ordering data Order N
- Page 209 and 210: Selection and ordering data Order N
- Page 211 and 212: ■ Selection and Ordering Data Ord
- Page 213 and 214: Individual components ■ Selection
- Page 215 and 216: 11/2 Introduction © Siemens AG 200
- Page 217 and 218: Ex I/O modules from the ET 200M ran
- Page 219 and 220: ■ Overview PS CPU IM 461-x IM 460
- Page 221 and 222: Product overview with information o
- Page 223 and 224: ■ Overview Within the ET 200 rang
- Page 225 and 226: ■ Overview The IM 153-2 High Feat
- Page 227 and 228: © Siemens AG 2007 Process I/O ET 2
- Page 229 and 230: ■ Selection and Ordering Data Ord
- Page 231 and 232: ■ Selection and Ordering Data Ord
- Page 233 and 234: © Siemens AG 2007 Process I/O ET 2
- Page 235 and 236: © Siemens AG 2007 Process I/O ET 2
- Page 237 and 238: ■ Overview The modules with HART
- Page 239 and 240: © Siemens AG 2007 Process I/O ET 2
- Page 241 and 242: ■ Overview The FM 355 is an intel
- Page 243 and 244: © Siemens AG 2007 Process I/O ET 2
- Page 245 and 246: ■ Integration Distributed ET 200i
- Page 247 and 248: ■ Overview The IM 152 interface m
- Page 249 and 250: ■ Selection and Ordering Data Ord
- Page 251 and 252: ■ Overview Tasks of the RS 485-iS
- Page 253 and 254: ■ Overview The ET 200S is a bit-m
- Page 255 and 256:
■ Overview • Terminal modules a
- Page 257 and 258:
■ Overview • IM 151-1 high feat
- Page 259 and 260:
■ Overview 1) See Manual "ET 200S
- Page 261 and 262:
■ Overview ■ Design Possible co
- Page 263 and 264:
© Siemens AG 2007 Process I/O ET 2
- Page 265 and 266:
■ Selection and Ordering Data Ord
- Page 267 and 268:
■ Overview The SIGUARD safety sys
- Page 269 and 270:
■ Selection and Ordering Data Ord
- Page 271 and 272:
Module support Various module suppo
- Page 273 and 274:
© Siemens AG 2007 Process I/O Deze
- Page 275 and 276:
■ Overview The following analog e
- Page 277 and 278:
■ Overview In combination with th
- Page 279 and 280:
■ Overview The power module PM-E
- Page 281 and 282:
IT world © Siemens AG 2007 12/2 SI
- Page 283 and 284:
© Siemens AG 2007 IT world Siemens
- Page 285 and 286:
© Siemens AG 2007 Migration to SIM
- Page 287 and 288:
■ Function Portfolio of the migra
- Page 289 and 290:
SIMATIC PCS 7 OS clients SIMATIC PC
- Page 291 and 292:
© Siemens AG 2007 Ordering data fo
- Page 293 and 294:
Ordering data for previous version
- Page 295 and 296:
Standard engineering software ■ S
- Page 297 and 298:
SIMATIC PDM ■ Selection and Order
- Page 299 and 300:
Ordering data for previous version
- Page 301 and 302:
© Siemens AG 2007 Ordering data fo
- Page 303 and 304:
Ordering data for previous version
- Page 305 and 306:
Asset Engineering SIMATIC PCS 7 Ass
- Page 307 and 308:
Ordering data for previous version
- Page 309 and 310:
Ordering data for previous version
- Page 311 and 312:
© Siemens AG 2007 Update/ upgrade
- Page 313 and 314:
SUS SIMATIC BATCH Server • PCS 7
- Page 315 and 316:
■ Selection and Ordering Data Ord
- Page 317 and 318:
© Siemens AG 2007 Update/upgrade p
- Page 319 and 320:
OS software ■ Selection and Order
- Page 321 and 322:
© Siemens AG 2007 Update/upgrade p
- Page 323 and 324:
© Siemens AG 2007 Update/upgrade p
- Page 325 and 326:
© Siemens AG 2007 Update/upgrade p
- Page 327 and 328:
Appendix © Siemens AG 2007 16/2 Tr
- Page 329 and 330:
© Siemens AG 2007 Appendix Siemens
- Page 331 and 332:
.I In the face of harsh competition
- Page 333 and 334:
■ Overview Solution Partner Autom
- Page 335 and 336:
■ A Access Point ................
- Page 337 and 338:
■ 3RK1 301-0.... ................
- Page 339 and 340:
■ 6ES7 841-0CA01-0YX2 ..........
- Page 341 and 342:
■ © Siemens AG 2007 Appendix Sie
- Page 343 and 344:
Automation and Drives Catalog Inter