- Page 2:
THESIS CASE STUDIES OF TEACHING AND
- Page 5 and 6:
TABLE OF CONTENTS Page LIST OF TABL
- Page 7 and 8:
TABLE OF CONTENTS (CONTINUED) iii P
- Page 9 and 10:
TABLE OF CONTENTS (CONTINUED) v Pag
- Page 11 and 12:
LIST OF TABLES Table Page 2.1 Struc
- Page 13 and 14:
LIST OF TABLES (CONTINUED) Table Pa
- Page 15 and 16:
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION This chapter
- Page 17 and 18:
led to improvement in the promotion
- Page 19 and 20:
water worked as food transported wi
- Page 21 and 22:
suggested peer collaboration for hi
- Page 23 and 24:
chloroplasts and pigments, the ligh
- Page 25 and 26:
would like to develop a new teachin
- Page 27 and 28:
concepts, such as absorption of lig
- Page 29 and 30:
conceptions, the scope of biology e
- Page 31 and 32:
3, and 8. In Grades 11-12, the scie
- Page 33 and 34:
Table 2.3 Basic Science Content Sta
- Page 35 and 36:
Table 2.3 (Cont’d) Contents Conte
- Page 37 and 38:
light energy and chlorophyll 2 H O
- Page 39 and 40:
2. Photosynthesis Itself Plants, al
- Page 41 and 42:
of chlorophyll. The students believ
- Page 43 and 44:
Up to this point, those previous st
- Page 45 and 46:
partly because of the biology educa
- Page 47 and 48:
(Matthews, 1997: 6). Philosophicall
- Page 49 and 50:
understanding capability of environ
- Page 51 and 52:
4. Social Constructivism The Russia
- Page 53 and 54:
5. Constructivist-Based Teaching ab
- Page 55 and 56:
peers, while the control group work
- Page 57 and 58:
generation to the next” (Cobb and
- Page 59 and 60:
2.1) Thai Living Styles Thailand is
- Page 61 and 62:
focuses prepare them to take the Na
- Page 63 and 64:
culture. First, Thai existing views
- Page 65 and 66:
Third, the nature of science is the
- Page 67 and 68:
democratic view, that the understan
- Page 69 and 70:
4. Summary: Integrating the Nature
- Page 71 and 72:
elationship between one concept and
- Page 73 and 74:
Brown (2003) used a combination of
- Page 75 and 76:
Focusing on thinking and encouragin
- Page 77 and 78:
Which aspect of the nature of scien
- Page 79 and 80: teaching photosynthesis needs impro
- Page 81 and 82: − encouraging students to partici
- Page 83 and 84: The attempt to understand and inter
- Page 85 and 86: Figure 3.1 Research Design of the T
- Page 87 and 88: was considered to differentiate the
- Page 89 and 90: 2.1) Teacher Preparation for Implem
- Page 91 and 92: 3. Evaluating Impacts of Photosynth
- Page 93 and 94: Figure 3.2 Survey Developmental Pro
- Page 95 and 96: 1.2) Advanced Photosynthesis Survey
- Page 97 and 98: 1. accessibility - is enabling the
- Page 99 and 100: implementation of the teaching inte
- Page 101 and 102: Table 3.4 Data Collection Program S
- Page 103 and 104: students. The learning culture in t
- Page 105 and 106: 1. Surveys: Content Analysis Conten
- Page 107 and 108: They were confirmed by the teachers
- Page 109 and 110: CHAPTER IV THE PHOTOSYNTHESIS TEACH
- Page 111 and 112: structures and functions of chlorop
- Page 113 and 114: Therefore, this study focused on us
- Page 115 and 116: from constructivism to socio0cultur
- Page 117 and 118: Sub-stand 1: Living Things and Livi
- Page 119 and 120: stroma. 5.3) Lists of Concept Propo
- Page 121 and 122: c) Light independent (dark) phase
- Page 123 and 124: Figure 4.1 Photosynthesis Concept M
- Page 125 and 126: Lesson 1 ‘Plant food’, aimed to
- Page 127 and 128: Lesson 5 ‘Light independent (dark
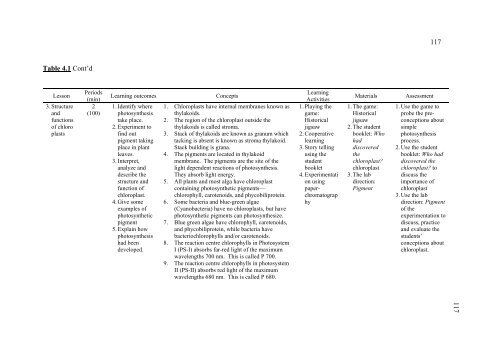
- Page 129: Table 4.1 Photosynthesis Lesson Pla
- Page 133 and 134: Table 4.1 Cont’d Lesson 5. Light
- Page 135 and 136: Table 4.1 Cont’d Lesson 6. Studen
- Page 137 and 138: After the researcher finished devel
- Page 139 and 140: per a week, namely two 60-min perio
- Page 141 and 142: always asked what she really did no
- Page 143 and 144: schooling studying, she studied Phy
- Page 145 and 146: B = blackboard C = instrument cupbo
- Page 147 and 148: Forty nine percentages had partial
- Page 149 and 150: for photosynthesis. Only seven perc
- Page 151 and 152: Table 5.3 Correcting the Introducto
- Page 153 and 154: Mrs. Engka: Right (confirmed). You
- Page 155 and 156: structures might be a metaphor of u
- Page 157 and 158: Table 5.4 Advanced Photosynthesis C
- Page 159 and 160: In her planning for the nature of s
- Page 161 and 162: participating in role play discussi
- Page 163 and 164: 5.4) Principle IV: Enabling Student
- Page 165 and 166: inside and outside teaching period.
- Page 167 and 168: Activities 5.6) Principle VI: Encou
- Page 169 and 170: 6. Summary of the Border School In
- Page 171 and 172: 2. Background Information about Mr.
- Page 173 and 174: Table 5.7 Mr. Vyn’s Students Sele
- Page 175 and 176: Mr. Vyn had his own style of teachi
- Page 177 and 178: 5. Mr. Vyn’s Implementation of th
- Page 179 and 180: Mr. Vyn: …No. 4…mineral is plan
- Page 181 and 182:
The misconception that CO2, mineral
- Page 183 and 184:
Although the students incompletely
- Page 185 and 186:
model of chloroplast structure base
- Page 187 and 188:
undle-sheath cells. Both cells cont
- Page 189 and 190:
Table 5.9 Advanced Photosynthesis C
- Page 191 and 192:
However, there was no discussion ab
- Page 193 and 194:
change in term of application of ol
- Page 195 and 196:
5.4) Principle IV: Enabling Student
- Page 197 and 198:
discussion. “The teacher always d
- Page 199 and 200:
photosynthesis e.g. dark phase. Als
- Page 201 and 202:
2. Background Information about Mrs
- Page 203 and 204:
Table 5.12 Mrs. Amp’s Students Se
- Page 205 and 206:
laboratory activities and concept m
- Page 207 and 208:
misconceptions about plant food, pa
- Page 209 and 210:
The misconceptions about plant and
- Page 211 and 212:
Table 5.13 Correcting the Introduct
- Page 213 and 214:
percentages misunderstood that the
- Page 215 and 216:
Table 5.14 Advanced Photosynthesis
- Page 217 and 218:
One conception about science demand
- Page 219 and 220:
Table 5.15 The Nature of Science of
- Page 221 and 222:
Not only relating photosynthesis kn
- Page 223 and 224:
the book and summarized the concept
- Page 225 and 226:
Cross Case Studies: Implementation
- Page 227 and 228:
In case of the teachers e.g. Mrs. A
- Page 229 and 230:
students’ own views about plants
- Page 231 and 232:
CHAPTER VI SUMMARY, DISCUSSION AND
- Page 233 and 234:
5. The students’ understanding of
- Page 235 and 236:
learning participation rarely appea
- Page 237 and 238:
the students to understand the rela
- Page 239 and 240:
the science project for environment
- Page 241 and 242:
ecause old knowledge was reinterpre
- Page 243 and 244:
Table 6.2 Learning Activities Sugge
- Page 245 and 246:
understandings about the light inde
- Page 247 and 248:
Therefore, this research suggested
- Page 249 and 250:
Amir, R. and P. Tamir. 1995. Propos
- Page 251 and 252:
Bell, B. 1998. Teacher development
- Page 253 and 254:
Campbell, N. and J. Reece. 2002. Bi
- Page 255 and 256:
Duit, R. and D. Treagust. 2003. Lea
- Page 257 and 258:
Govindjee, J., T. Beatty, and H. Ge
- Page 259 and 260:
Institute for the Promotion of Teac
- Page 261 and 262:
Lin, H. and C. Chen. 2002. Promotin
- Page 263 and 264:
Merriam, S. 1988. Case Study Resear
- Page 265 and 266:
Patton, M. 1990. Qualitative Evalua
- Page 267 and 268:
Smith, M. and L. Scharmann. 1999. D
- Page 269 and 270:
Von Glasersfeld, E. 1995. Radical C
- Page 271 and 272:
APPENDIX A: INTRODUCTORY PHOTOSYNTH
- Page 273 and 274:
1. Tick any of these items which ca
- Page 275 and 276:
6.5) Plants need carbohydrate for t
- Page 277 and 278:
APPENDIX B: ADVANCED PHOTOSYNTHESIS
- Page 279 and 280:
5. Tick any item (s) which you thin
- Page 281 and 282:
12. Here is a statement about plant