an innovative approach
an innovative approach
an innovative approach
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
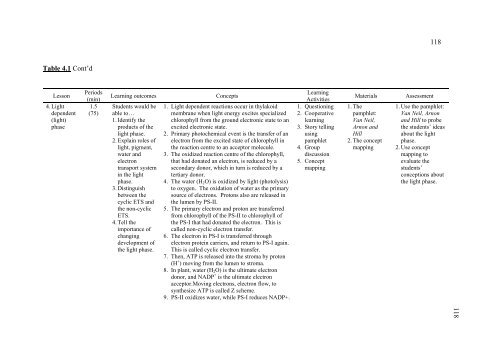
Table 4.1 Cont’d<br />
Lesson<br />
4. Light<br />
dependent<br />
(light)<br />
phase<br />
Periods<br />
(min)<br />
1.5<br />
(75)<br />
Learning outcomes Concepts<br />
Students would be<br />
able to…<br />
1. Identify the<br />
products of the<br />
light phase.<br />
2. Explain roles of<br />
light, pigment,<br />
water <strong>an</strong>d<br />
electron<br />
tr<strong>an</strong>sport system<br />
in the light<br />
phase.<br />
3. Distinguish<br />
between the<br />
cyclic ETS <strong>an</strong>d<br />
the non-cyclic<br />
ETS.<br />
4. Tell the<br />
import<strong>an</strong>ce of<br />
ch<strong>an</strong>ging<br />
development of<br />
the light phase.<br />
1. Light dependent reactions occur in thylakoid<br />
membr<strong>an</strong>e when light energy excites specialized<br />
chlorophyll from the ground electronic state to <strong>an</strong><br />
excited electronic state.<br />
2. Primary photochemical event is the tr<strong>an</strong>sfer of <strong>an</strong><br />
electron from the excited state of chlorophyll in<br />
the reaction centre to <strong>an</strong> acceptor molecule.<br />
3. The oxidized reaction centre of the chlorophyll,<br />
that had donated <strong>an</strong> electron, is reduced by a<br />
secondary donor, which in turn is reduced by a<br />
tertiary donor.<br />
4. The water (H2O) is oxidized by light (photolysis)<br />
to oxygen. The oxidation of water as the primary<br />
source of electrons. Protons also are released in<br />
the lumen by PS-II.<br />
5. The primary electron <strong>an</strong>d proton are tr<strong>an</strong>sferred<br />
from chlorophyll of the PS-II to chlorophyll of<br />
the PS-I that had donated the electron. This is<br />
called non-cyclic electron tr<strong>an</strong>sfer.<br />
6. The electron in PS-I is tr<strong>an</strong>sferred through<br />
electron protein carriers, <strong>an</strong>d return to PS-I again.<br />
This is called cyclic electron tr<strong>an</strong>sfer.<br />
7. Then, ATP is released into the stroma by proton<br />
(H + ) moving from the lumen to stroma.<br />
8. In pl<strong>an</strong>t, water (H2O) is the ultimate electron<br />
donor, <strong>an</strong>d NADP + is the ultimate electron<br />
acceptor.Moving electrons, electron flow, to<br />
synthesize ATP is called Z scheme.<br />
9. PS-II oxidizes water, while PS-I reduces NADP+.<br />
Learning<br />
Activities<br />
1. Questioning<br />
2. Cooperative<br />
learning<br />
3. Story telling<br />
using<br />
pamphlet<br />
4. Group<br />
discussion<br />
5. Concept<br />
mapping<br />
Materials Assessment<br />
1. The<br />
pamphlet:<br />
V<strong>an</strong> Neil,<br />
Arnon <strong>an</strong>d<br />
Hill<br />
2. The concept<br />
mapping<br />
118<br />
1. Use the pamphlet:<br />
V<strong>an</strong> Neil, Arnon<br />
<strong>an</strong>d Hill to probe<br />
the students’ ideas<br />
about the light<br />
phase.<br />
2. Use concept<br />
mapping to<br />
evaluate the<br />
students’<br />
conceptions about<br />
the light phase.<br />
118