Embedded Systems Design with the Atmel AVR Microcontroller Part II
Embedded Systems Design with the Atmel AVR Microcontroller Part II
Embedded Systems Design with the Atmel AVR Microcontroller Part II
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
232 CHAPTER 7. ATMEL <strong>AVR</strong> OPERATING PARAMETERS AND INTERFACING<br />
240<br />
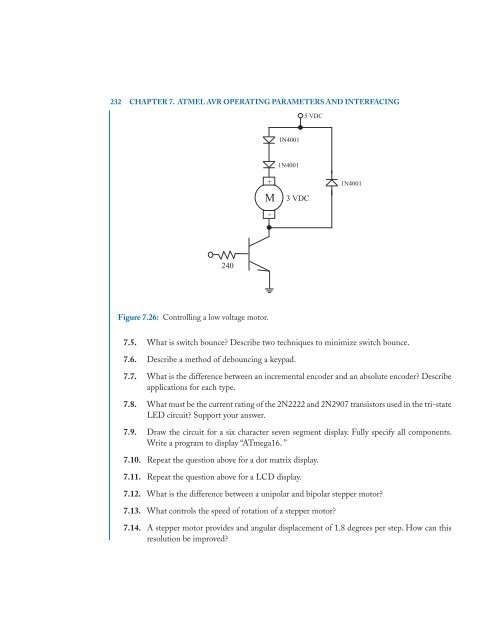
Figure 7.26: Controlling a low voltage motor.<br />
+<br />
M 3 VDC<br />
-<br />
1N4001<br />
1N4001<br />
5 VDC<br />
1N4001<br />
7.5. What is switch bounce? Describe two techniques to minimize switch bounce.<br />
7.6. Describe a method of debouncing a keypad.<br />
7.7. What is <strong>the</strong> difference between an incremental encoder and an absolute encoder? Describe<br />
applications for each type.<br />
7.8. What must be <strong>the</strong> current rating of <strong>the</strong> 2N2222 and 2N2907 transistors used in <strong>the</strong> tri-state<br />
LED circuit? Support your answer.<br />
7.9. Draw <strong>the</strong> circuit for a six character seven segment display. Fully specify all components.<br />
Write a program to display “ATmega16. ”<br />
7.10. Repeat <strong>the</strong> question above for a dot matrix display.<br />
7.11. Repeat <strong>the</strong> question above for a LCD display.<br />
7.12. What is <strong>the</strong> difference between a unipolar and bipolar stepper motor?<br />
7.13. What controls <strong>the</strong> speed of rotation of a stepper motor?<br />
7.14. A stepper motor provides and angular displacement of 1.8 degrees per step. How can this<br />
resolution be improved?