849954 sisus
849954 sisus
849954 sisus
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
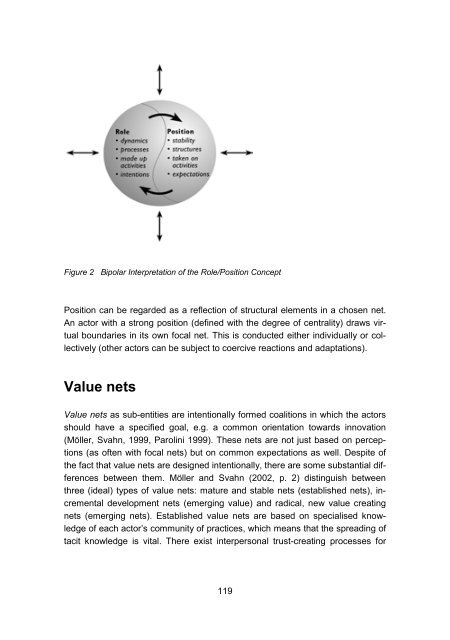
Figure 2 Bipolar Interpretation of the Role/Position Concept<br />
Position can be regarded as a reflection of structural elements in a chosen net.<br />
An actor with a strong position (defined with the degree of centrality) draws virtual<br />
boundaries in its own focal net. This is conducted either individually or collectively<br />
(other actors can be subject to coercive reactions and adaptations).<br />
Value nets<br />
Value nets as sub-entities are intentionally formed coalitions in which the actors<br />
should have a specified goal, e.g. a common orientation towards innovation<br />
(Möller, Svahn, 1999, Parolini 1999). These nets are not just based on perceptions<br />
(as often with focal nets) but on common expectations as well. Despite of<br />
the fact that value nets are designed intentionally, there are some substantial differences<br />
between them. Möller and Svahn (2002, p. 2) distinguish between<br />
three (ideal) types of value nets: mature and stable nets (established nets), incremental<br />
development nets (emerging value) and radical, new value creating<br />
nets (emerging nets). Established value nets are based on specialised knowledge<br />
of each actor’s community of practices, which means that the spreading of<br />
tacit knowledge is vital. There exist interpersonal trust-creating processes for<br />
119