Predictive Control of Three Phase AC/DC Converters
Predictive Control of Three Phase AC/DC Converters
Predictive Control of Three Phase AC/DC Converters
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
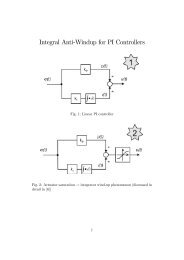
132 APPENDIX C. PREDICTIVE DIRECT POWER CONTROL<br />
Next, from (4.40) cost function J is described as:<br />
[ (−15.45481322062509<br />
J =<br />
∗ 10<br />
6 ) t 1 + ( −4.141104721640333 ∗ 10 6) t 2<br />
2 [ (15.45481322062509<br />
+ 721.1485808337910]<br />
+ ∗ 10<br />
6 ) t 1<br />
(C.2)<br />
+ ( 26.76852171960985 ∗ 10 6) ] 2<br />
t 2 − 971.4140632912274<br />
In order to find minimum value <strong>of</strong> J function, partial derivatives (4.43), (4.44)<br />
are calculated:<br />
∂J<br />
∂t 1<br />
= 0 ⇒ (955405006.7376324<br />
∗ 10<br />
6 ) t 1 + ( 955405006.7376324 ∗ 10 6) t 2 (C.3)<br />
= 52316.47905831899 ∗ 10 6<br />
∂J<br />
∂t 2<br />
= 0 ⇒ (955405006.7376324<br />
∗ 10<br />
6 ) t 1 + ( 1467405006.737632 ∗ 10 6) t 2 (C.4)<br />
= 57979.34049008143 ∗ 10 6<br />
Figure C.1 (a), (b) show cost function J diagram versus voltage vector application<br />
time t 1 , t 2 for conditions listed in Tab. C.1. The minimum value <strong>of</strong> J<br />
function is reached by (4.45), (4.46):<br />
t 1 = 43.69815468216835 µs<br />
t 2 = 11.06027623391102 µs<br />
t 3 = 45.24156908392062 µs<br />
(C.5)<br />
where t 3 is calculated from (4.47).















![[TCP] Opis układu - Instytut Sterowania i Elektroniki Przemysłowej ...](https://img.yumpu.com/23535443/1/184x260/tcp-opis-ukladu-instytut-sterowania-i-elektroniki-przemyslowej-.jpg?quality=85)