Predictive Control of Three Phase AC/DC Converters
Predictive Control of Three Phase AC/DC Converters
Predictive Control of Three Phase AC/DC Converters
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
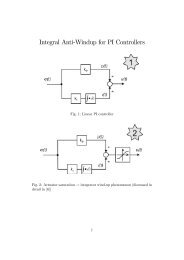
56 CHAPTER 4. PREDICTIVE DIRECT POWER CONTROL<br />
( ))<br />
1<br />
Q err = Q ref − Q − 2<br />
(f q1 t 1 + f q2 t 2 + f q3<br />
2 T s − t 1 − t 2<br />
(4.39)<br />
To minimize power errors, least square optimization method has been introduced.<br />
The cost function J has been defined as a sum <strong>of</strong> squared errors:<br />
and after replacing (4.38) and (4.39) into (4.40):<br />
J = P 2 err + Q 2 err (4.40)<br />
J = [ P ref − P − 2 ( f p1 t 1 + f p2 t 2 + f p3<br />
( 1<br />
2 T s − t 1 − t 2<br />
))] 2<br />
+ [ Q ref − Q − 2 ( f q1 t 1 + f q2 t 2 + f q3<br />
( 1<br />
2 T s − t 1 − t 2<br />
))] 2 (4.41)<br />
The optimal application times t 1 , t 2 , t 3 , which minimize cost function value J,<br />
during sampling time T s , satisfies minimum value condition:<br />
⎧<br />
⎪⎨<br />
⎪⎩<br />
∂J<br />
∂t 1<br />
= 0<br />
∂J<br />
∂t 2<br />
= 0<br />
(4.42)<br />
Partial differences <strong>of</strong> J function are expressed as:<br />
∂J<br />
∂t 1<br />
= 4 [ (P ref − P − f p3 T s ) (f p3 − f p1 ) + (Q ref − Q − f q3 T s ) (f q3 − f q1 ) ]<br />
+ 8 [ (f p3 − f p1 ) 2 + (f q3 − f q1 ) 2] t 1<br />
+ 8 [ (f p3 − f p2 )(f p3 − f p1 ) + (f q3 − f q2 )(f q3 − f q1 ) ] (4.43)<br />
t 2<br />
∂J<br />
∂t 2<br />
= 4 [(P ref − P − f p3 T s ) (f p3 − f p2 ) + (Q ref − Q − f q3 T s ) (f q3 − f q2 )]<br />
+ 8 [(f p3 − f p1 )(f p3 − f p2 ) + (f q3 − f q1 )(f q3 − f q2 )] t 1<br />
+ 8 [ (4.44)<br />
(f p3 − f p2 ) 2 + (f q3 − f q2 ) 2] t 2<br />
The J gets minimum value when (4.43), (4.44) are equal to zero (4.42). The solution<br />
<strong>of</strong> sets <strong>of</strong> conditions are application times given by:<br />
[<br />
t 1 = (P ref − P )(f q2 − f q3 ) + (Q ref − Q)(f p3 − f p2 )<br />
+ (f p2 f q3 − f p3 f q2 )T s<br />
]/<br />
[<br />
]<br />
2((f q2 − f q3 )f p1 + (f q3 − f q1 )f p2 + (f q1 − f q2 )f p3 )<br />
(4.45)<br />
t 2 =<br />
[<br />
(P ref − P )(f q3 − f q1 ) + (Q ref − Q)(f p1 − f p3 )<br />
+ (f q1 f p3 − f q3 f p1 )T s<br />
]/<br />
[<br />
]<br />
2((f q2 − f q3 )f p1 + (f q3 − f q1 )f p2 + (f q1 − f q2 )f p3 )<br />
(4.46)<br />
t 3 = 1 2 T s − t 1 − t 2 (4.47)<br />
Appendix C shows an example operation <strong>of</strong> presented control method for<br />
specified conditions.















![[TCP] Opis układu - Instytut Sterowania i Elektroniki Przemysłowej ...](https://img.yumpu.com/23535443/1/184x260/tcp-opis-ukladu-instytut-sterowania-i-elektroniki-przemyslowej-.jpg?quality=85)