Introductory Physics Volume Two
Introductory Physics Volume Two
Introductory Physics Volume Two
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
34 Electric Field 1.8<br />
A charged ball of mass 1.00 g is suspended on a light string in the<br />
presence of a uniform electric field as shown. When ⃗ E = (3.00î +<br />
5.00ĵ) × 10 5 N/C, the ball is in equilibrium at θ = 37.0 ◦ .<br />
(a) Find the charge on the ball.<br />
(b) Find the tension in the string.<br />
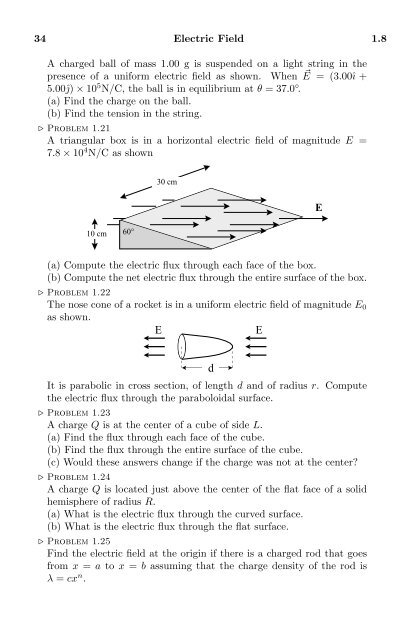
⊲ Problem 1.21<br />
A triangular box is in a horizontal electric field of magnitude E =<br />
7.8 × 10 4 N/C as shown<br />
30 cm<br />
10 cm 60°<br />
E<br />
(a) Compute the electric flux through each face of the box.<br />
(b) Compute the net electric flux through the entire surface of the box.<br />
⊲ Problem 1.22<br />
The nose cone of a rocket is in a uniform electric field of magnitude E 0<br />
as shown.<br />
E<br />
E<br />
It is parabolic in cross section, of length d and of radius r. Compute<br />
the electric flux through the paraboloidal surface.<br />
⊲ Problem 1.23<br />
A charge Q is at the center of a cube of side L.<br />
(a) Find the flux through each face of the cube.<br />
(b) Find the flux through the entire surface of the cube.<br />
(c) Would these answers change if the charge was not at the center?<br />
⊲ Problem 1.24<br />
A charge Q is located just above the center of the flat face of a solid<br />
hemisphere of radius R.<br />
(a) What is the electric flux through the curved surface.<br />
(b) What is the electric flux through the flat surface.<br />
⊲ Problem 1.25<br />
Find the electric field at the origin if there is a charged rod that goes<br />
from x = a to x = b assuming that the charge density of the rod is<br />
λ = cx n .<br />
d