Introductory Physics Volume Two
Introductory Physics Volume Two
Introductory Physics Volume Two
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
94 Magnetic Fields 4.7<br />
in the positive z direction. If the electric field has a strength of 20N/C<br />
in the positive z direction, what is the magnetic field in the region?<br />
⊲ Problem 4.10<br />
A duck flying due north at 15 m s<br />
passes over Atlanta, where the Earth’s<br />
magnetic field is 5.0 × 10 −5 T in a direction 60 ◦ below the horizontal<br />
line running north and south. If the duck has a net positive charge of<br />
0.040µC, what is the magnetic force acting on it?<br />
⊲ Problem 4.11<br />
A proton moves with a velocity of v = (2î − 4ĵ + ˆk) m s<br />
in a region in<br />
which the magnetic field is B ⃗ = (î + 2ĵ − 3ˆk)T. What is the magnitude<br />
of the magnetic force this charge experiences?<br />
⊲ Problem 4.12<br />
Show that the work done by the magnetic force on a charged particle<br />
moving in a magnetic field is zero for any displacement of the particle.<br />
⊲ Problem 4.13<br />
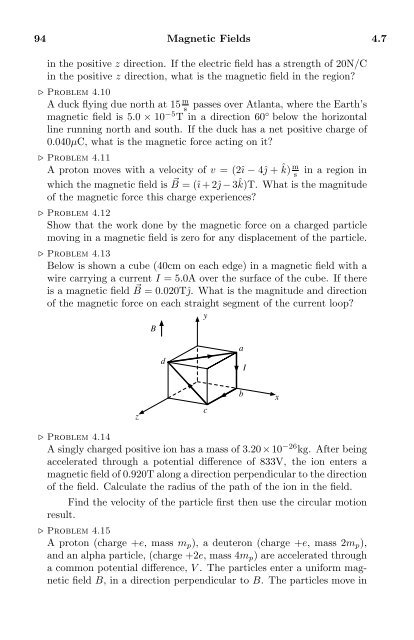
Below is shown a cube (40cm on each edge) in a magnetic field with a<br />
wire carrying a current I = 5.0A over the surface of the cube. If there<br />
is a magnetic field B ⃗ = 0.020Tĵ. What is the magnitude and direction<br />
of the magnetic force on each straight segment of the current loop?<br />
y<br />
B<br />
d<br />
a<br />
I<br />
z<br />
c<br />
b<br />
x<br />
⊲ Problem 4.14<br />
A singly charged positive ion has a mass of 3.20×10 −26 kg. After being<br />
accelerated through a potential difference of 833V, the ion enters a<br />
magnetic field of 0.920T along a direction perpendicular to the direction<br />
of the field. Calculate the radius of the path of the ion in the field.<br />
Find the velocity of the particle first then use the circular motion<br />
result.<br />
⊲ Problem 4.15<br />
A proton (charge +e, mass m p ), a deuteron (charge +e, mass 2m p ),<br />
and an alpha particle, (charge +2e, mass 4m p ) are accelerated through<br />
a common potential difference, V . The particles enter a uniform magnetic<br />
field B, in a direction perpendicular to B. The particles move in