Introductory Physics Volume Two
Introductory Physics Volume Two
Introductory Physics Volume Two
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
92 Magnetic Fields 4.6<br />
The net force is<br />
⃗F = îF 1 − ĵF 2<br />
= îIL 1 B − ĵIL 2 B<br />
So the direction is given by<br />
( ) ( )<br />
θ = tan −1 IL2 B<br />
= tan −1 L2<br />
,<br />
IL 1 B<br />
L 1<br />
where θ is below the x-axis. The magnitude of the force is<br />
√<br />
F =<br />
√F1 2 + F 2 2 = IB L 2 1 + L2 2<br />
Example<br />
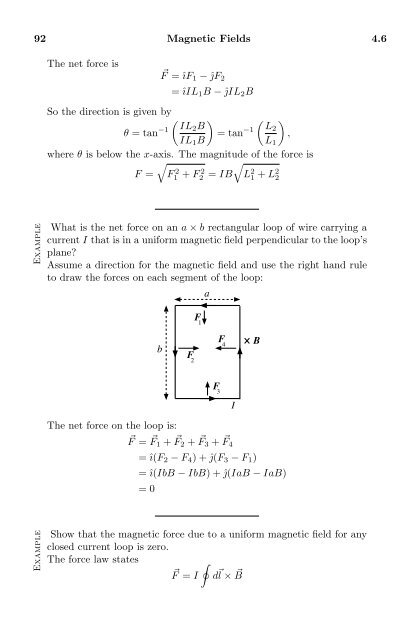
What is the net force on an a × b rectangular loop of wire carrying a<br />
current I that is in a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the loop’s<br />
plane?<br />
Assume a direction for the magnetic field and use the right hand rule<br />
to draw the forces on each segment of the loop:<br />
a<br />
F 1<br />
b<br />
F 2<br />
F 3<br />
F 4<br />
B<br />
The net force on the loop is:<br />
⃗F = ⃗ F 1 + ⃗ F 2 + ⃗ F 3 + ⃗ F 4<br />
= î(F 2 − F 4 ) + ĵ(F 3 − F 1 )<br />
= î(IbB − IbB) + ĵ(IaB − IaB)<br />
= 0<br />
I<br />
Example<br />
Show that the magnetic force due to a uniform magnetic field for any<br />
closed current loop is zero.<br />
The force law states<br />
∮<br />
⃗F = I d ⃗ l × B ⃗