Contents - SPAD
Contents - SPAD
Contents - SPAD
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
trialling and refining these processes through local trials, the “quick win” process and the more<br />
general staged implementation approach advocated.<br />
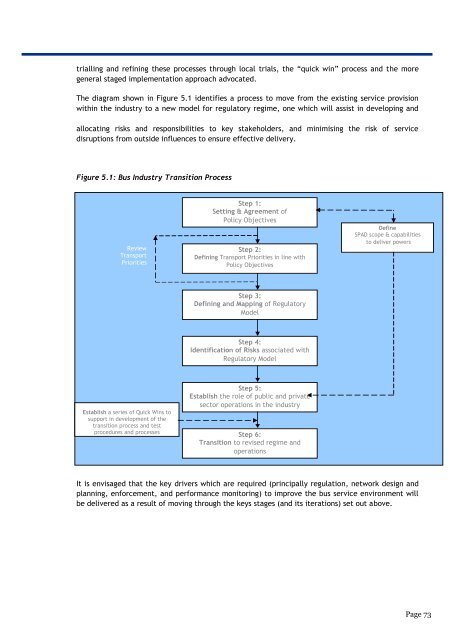
The diagram shown in Figure 5.1 identifies a process to move from the existing service provision<br />
within the industry to a new model for regulatory regime, one which will assist in developing and<br />
allocating risks and responsibilities to key stakeholders, and minimising the risk of service<br />
disruptions from outside influences to ensure effective delivery.<br />
Figure 5.1: Bus Industry Transition Process<br />
Review<br />
Transport<br />
Priorities<br />
Step 1:<br />
Setting & Agreement of<br />
Policy Objectives<br />
Step 2:<br />
Defining Transport Priorities in line with<br />
Policy Objectives<br />
Define<br />
<strong>SPAD</strong> scope & capabilities<br />
to deliver powers<br />
Step 3:<br />
Defining and Mapping of Regulatory<br />
Model<br />
Step 4:<br />
Identification of Risks associated with<br />
Regulatory Model<br />
Establish a series of Quick Wins to<br />
support in development of the<br />
transition process and test<br />
procedures and processes<br />
Step 5:<br />
Establish the role of public and private<br />
sector operations in the industry<br />
Step 6:<br />
Transition to revised regime and<br />
operations<br />
It is envisaged that the key drivers which are required (principally regulation, network design and<br />
planning, enforcement, and performance monitoring) to improve the bus service environment will<br />
be delivered as a result of moving through the keys stages (and its iterations) set out above.<br />
Page 73