proto-southwestern-tai revised: a new reconstruction - seals 22
proto-southwestern-tai revised: a new reconstruction - seals 22
proto-southwestern-tai revised: a new reconstruction - seals 22
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
202 Bradley McDonnell<br />
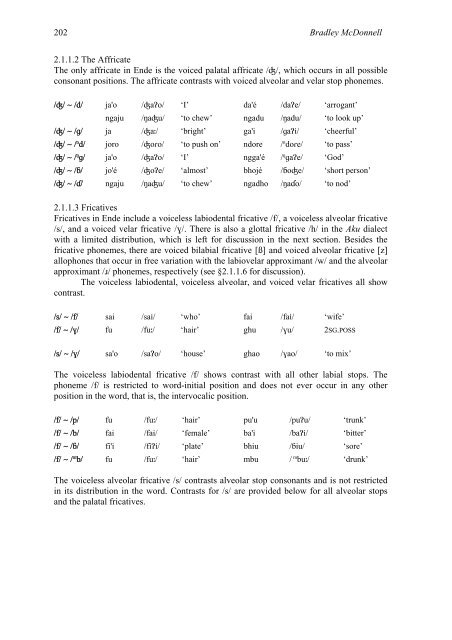
2.1.1.2 The Affricate<br />
The only affricate in Ende is the voiced palatal affricate /ʤ/, which occurs in all possible<br />
consonant positions. The affricate contrasts with voiced alveolar and velar stop phonemes.<br />
/ʤ/ ~ /d/ ja'o /ʤaɁo/ ‘I’ da'é /daɁe/ ‘arrogant’<br />
ngaju /ŋaʤu/ ‘to chew’ ngadu /ŋadu/ ‘to look up’<br />
/ʤ/ ~ /ɡ/ ja /ʤaː/ ‘bright’ ga'i /ɡaɁi/ ‘cheerful’<br />
/ʤ/ ~ / nd/ joro /ʤoɾo/ ‘to push on’ ndore / ndoɾe/ ‘to pass’<br />
/ʤ/ ~ / ŋɡ/ ja'o /ʤaɁo/ ‘I’ ngga'é / ŋɡaɁe/ ‘God’<br />
/ʤ/ ~ /ɓ/ jo'é /ʤoɁe/ ‘almost’ bhojé /�oʤe/ ‘short person’<br />
/ʤ/ ~ /ɗ/ ngaju /ŋaʤu/ ‘to chew’ ngadho /ŋa�o/ ‘to nod’<br />
2.1.1.3 Fricatives<br />
Fricatives in Ende include a voiceless labiodental fricative /f/, a voiceless alveolar fricative<br />
/s/, and a voiced velar fricative /�/. There is also a glottal fricative /h/ in the Aku dialect<br />
with a limited distribution, which is left for discussion in the next section. Besides the<br />
fricative phonemes, there are voiced bilabial fricative [ß] and voiced alveolar fricative [z]<br />
allophones that occur in free variation with the labiovelar approximant /w/ and the alveolar<br />
approximant /ɹ/ phonemes, respectively (see §2.1.1.6 for discussion).<br />
The voiceless labiodental, voiceless alveolar, and voiced velar fricatives all show<br />
contrast.<br />
/s/ ~ /f/ sai /sai/ ‘who’ fai /fai/ ‘wife’<br />
/f/ ~ /ɣ/ fu /fuː/ ‘hair’ ghu /ɣu/ 2SG.POSS<br />
/s/ ~ /ɣ/ sa'o /saɁo/ ‘house’ ghao /ɣao/ ‘to mix’<br />
The voiceless labiodental fricative /f/ shows contrast with all other labial stops. The<br />
phoneme /f/ is restricted to word-initial position and does not ever occur in any other<br />
position in the word, that is, the intervocalic position.<br />
/f/ ~ /p/ fu /fuː/ ‘hair’ pu'u /puɁu/ ‘trunk’<br />
/f/ ~ /b/ fai /fai/ ‘female’ ba'i /baɁi/ ‘bitter’<br />
/f/ ~ /ɓ/ fi'i /fiɁi/ ‘plate’ bhiu /ɓiu/ ‘sore’<br />
/f/ ~ / mb/ fu /fuː/ ‘hair’ mbu / mbuː/ ‘drunk’<br />
The voiceless alveolar fricative /s/ contrasts alveolar stop consonants and is not restricted<br />
in its distribution in the word. Contrasts for /s/ are provided below for all alveolar stops<br />
and the palatal fricatives.