Health Policy Issues and Health Programmes in ... - Amazon S3
Health Policy Issues and Health Programmes in ... - Amazon S3
Health Policy Issues and Health Programmes in ... - Amazon S3
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
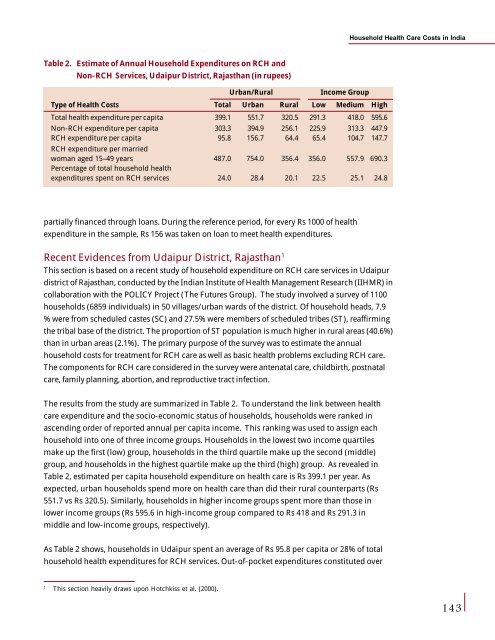
Household <strong>Health</strong> Care Costs <strong>in</strong> IndiaTable 2. Estimate of Annual Household Expenditures on RCH <strong>and</strong>Non-RCH Services, Udaipur District, Rajasthan (<strong>in</strong> rupees)Urban/RuralIncome GroupType of <strong>Health</strong> Costs Total Urban Rural Low Medium HighTotal health expenditure per capita 399.1 551.7 320.5 291.3 418.0 595.6Non-RCH expenditure per capita 303.3 394.9 256.1 225.9 313.3 447.9RCH expenditure per capita 95.8 156.7 64.4 65.4 104.7 147.7RCH expenditure per marriedwoman aged 15–49 years 487.0 754.0 356.4 356.0 557.9 690.3Percentage of total household healthexpenditures spent on RCH services 24.0 28.4 20.1 22.5 25.1 24.8partially f<strong>in</strong>anced through loans. Dur<strong>in</strong>g the reference period, for every Rs 1000 of healthexpenditure <strong>in</strong> the sample, Rs 156 was taken on loan to meet health expenditures.Recent Evidences from Udaipur District, Rajasthan 1This section is based on a recent study of household expenditure on RCH care services <strong>in</strong> Udaipurdistrict of Rajasthan, conducted by the Indian Institute of <strong>Health</strong> Management Research (IIHMR) <strong>in</strong>collaboration with the POLICY Project (The Futures Group). The study <strong>in</strong>volved a survey of 1100households (6859 <strong>in</strong>dividuals) <strong>in</strong> 50 villages/urban wards of the district. Of household heads, 7.9% were from scheduled castes (SC) <strong>and</strong> 27.5% were members of scheduled tribes (ST), reaffirm<strong>in</strong>gthe tribal base of the district. The proportion of ST population is much higher <strong>in</strong> rural areas (40.6%)than <strong>in</strong> urban areas (2.1%). The primary purpose of the survey was to estimate the annualhousehold costs for treatment for RCH care as well as basic health problems exclud<strong>in</strong>g RCH care.The components for RCH care considered <strong>in</strong> the survey were antenatal care, childbirth, postnatalcare, family plann<strong>in</strong>g, abortion, <strong>and</strong> reproductive tract <strong>in</strong>fection.The results from the study are summarized <strong>in</strong> Table 2. To underst<strong>and</strong> the l<strong>in</strong>k between healthcare expenditure <strong>and</strong> the socio-economic status of households, households were ranked <strong>in</strong>ascend<strong>in</strong>g order of reported annual per capita <strong>in</strong>come. This rank<strong>in</strong>g was used to assign eachhousehold <strong>in</strong>to one of three <strong>in</strong>come groups. Households <strong>in</strong> the lowest two <strong>in</strong>come quartilesmake up the first (low) group, households <strong>in</strong> the third quartile make up the second (middle)group, <strong>and</strong> households <strong>in</strong> the highest quartile make up the third (high) group. As revealed <strong>in</strong>Table 2, estimated per capita household expenditure on health care is Rs 399.1 per year. Asexpected, urban households spend more on health care than did their rural counterparts (Rs551.7 vs Rs 320.5). Similarly, households <strong>in</strong> higher <strong>in</strong>come groups spent more than those <strong>in</strong>lower <strong>in</strong>come groups (Rs 595.6 <strong>in</strong> high-<strong>in</strong>come group compared to Rs 418 <strong>and</strong> Rs 291.3 <strong>in</strong>middle <strong>and</strong> low-<strong>in</strong>come groups, respectively).As Table 2 shows, households <strong>in</strong> Udaipur spent an average of Rs 95.8 per capita or 28% of totalhousehold health expenditures for RCH services. Out-of-pocket expenditures constituted over1This section heavily draws upon Hotchkiss et al. (2000).143