Health Policy Issues and Health Programmes in ... - Amazon S3
Health Policy Issues and Health Programmes in ... - Amazon S3
Health Policy Issues and Health Programmes in ... - Amazon S3
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
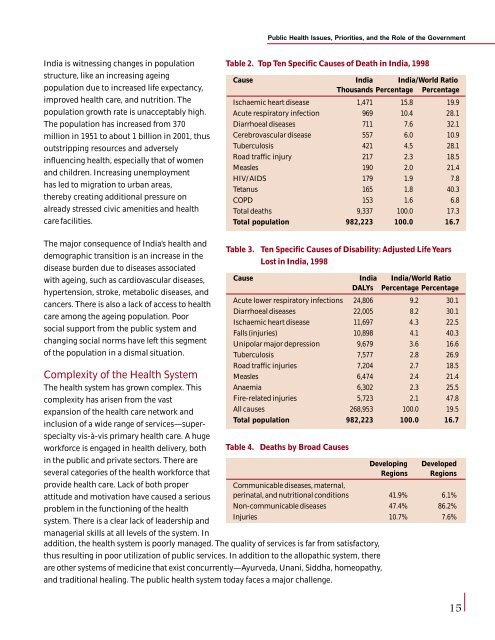
Public <strong>Health</strong> <strong>Issues</strong>, Priorities, <strong>and</strong> the Role of the GovernmentIndia is witness<strong>in</strong>g changes <strong>in</strong> populationstructure, like an <strong>in</strong>creas<strong>in</strong>g age<strong>in</strong>gpopulation due to <strong>in</strong>creased life expectancy,improved health care, <strong>and</strong> nutrition. Thepopulation growth rate is unacceptably high.The population has <strong>in</strong>creased from 370million <strong>in</strong> 1951 to about 1 billion <strong>in</strong> 2001, thusoutstripp<strong>in</strong>g resources <strong>and</strong> adversely<strong>in</strong>fluenc<strong>in</strong>g health, especially that of women<strong>and</strong> children. Increas<strong>in</strong>g unemploymenthas led to migration to urban areas,thereby creat<strong>in</strong>g additional pressure onalready stressed civic amenities <strong>and</strong> healthcare facilities.Table 2. Top Ten Specific Causes of Death <strong>in</strong> India, 1998Cause India India/World RatioThous<strong>and</strong>s Percentage PercentageIschaemic heart disease 1,471 15.8 19.9Acute respiratory <strong>in</strong>fection 969 10.4 28.1Diarrhoeal diseases 711 7.6 32.1Cerebrovascular disease 557 6.0 10.9Tuberculosis 421 4.5 28.1Road traffic <strong>in</strong>jury 217 2.3 18.5Measles 190 2.0 21.4HIV/AIDS 179 1.9 7.8Tetanus 165 1.8 40.3COPD 153 1.6 6.8Total deaths 9,337 100.0 17.3Total population 982,223 100.0 16.7The major consequence of India’s health <strong>and</strong>Table 3. Ten Specific Causes of Disability: Adjusted Life Yearsdemographic transition is an <strong>in</strong>crease <strong>in</strong> theLost <strong>in</strong> India, 1998disease burden due to diseases associatedwith age<strong>in</strong>g, such as cardiovascular diseases, Cause India India/World Ratiohypertension, stroke, metabolic diseases, <strong>and</strong>DALYs Percentage Percentagecancers. There is also a lack of access to healthAcute lower respiratory <strong>in</strong>fections 24,806 9.2 30.1Diarrhoeal diseases 22,005 8.2 30.1care among the age<strong>in</strong>g population. PoorIschaemic heart disease 11,697 4.3 22.5social support from the public system <strong>and</strong>Falls (<strong>in</strong>juries) 10,898 4.1 40.3chang<strong>in</strong>g social norms have left this segment Unipolar major depression 9,679 3.6 16.6of the population <strong>in</strong> a dismal situation.Tuberculosis 7,577 2.8 26.9Complexity of the <strong>Health</strong> SystemRoad traffic <strong>in</strong>juries 7,204 2.7 18.5Measles 6,474 2.4 21.4The health system has grown complex. This Anaemia 6,302 2.3 25.5complexity has arisen from the vastFire-related <strong>in</strong>juries 5,723 2.1 47.8expansion of the health care network <strong>and</strong>All causes 268,953 100.0 19.5<strong>in</strong>clusion of a wide range of services—superspecialtyvis-à-vis primary health care. A hugeTotal population 982,223 100.0 16.7workforce is engaged <strong>in</strong> health delivery, both Table 4. Deaths by Broad Causes<strong>in</strong> the public <strong>and</strong> private sectors. There areseveral categories of the health workforce thatDevelop<strong>in</strong>gRegionsDevelopedRegionsprovide health care. Lack of both properattitude <strong>and</strong> motivation have caused a seriousproblem <strong>in</strong> the function<strong>in</strong>g of the healthsystem. There is a clear lack of leadership <strong>and</strong>managerial skills at all levels of the system. InCommunicable diseases, maternal,per<strong>in</strong>atal, <strong>and</strong> nutritional conditionsNon-communicable diseasesInjuries41.9%47.4%10.7%6.1%86.2%7.6%addition, the health system is poorly managed. The quality of services is far from satisfactory,thus result<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> poor utilization of public services. In addition to the allopathic system, thereare other systems of medic<strong>in</strong>e that exist concurrently—Ayurveda, Unani, Siddha, homeopathy,<strong>and</strong> traditional heal<strong>in</strong>g. The public health system today faces a major challenge.15