findings by bioregion - Victorian Environmental Assessment Council
findings by bioregion - Victorian Environmental Assessment Council
findings by bioregion - Victorian Environmental Assessment Council
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
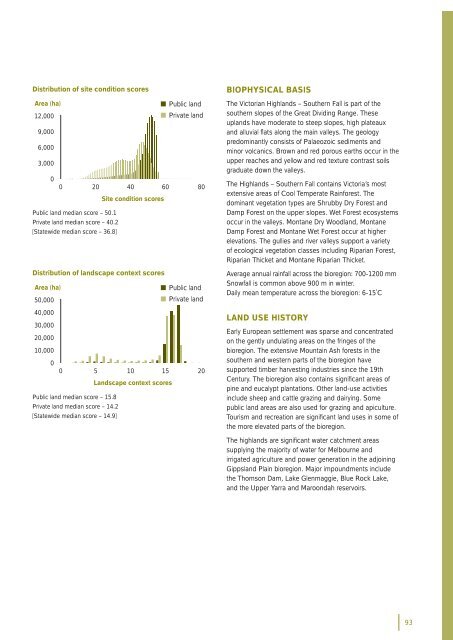
Distribution of site condition scoresArea (ha)• Public land12,000• Private land9,0006,0003,00000 20 40 60 80Site condition scoresPublic land median score – 50.1Private land median score – 40.2[Statewide median score – 36.8]Distribution of landscape context scoresArea (ha)• Public land50,000• Private land40,00030,00020,00010,00000 5 10 15 20Landscape context scoresPublic land median score – 15.8Private land median score – 14.2[Statewide median score – 14.9]BIOPHYSICAL BASISThe <strong>Victorian</strong> Highlands – Southern Fall is part of thesouthern slopes of the Great Dividing Range. Theseuplands have moderate to steep slopes, high plateauxand alluvial fl ats along the main valleys. The geologypredominantly consists of Palaeozoic sediments andminor volcanics. Brown and red porous earths occur in theupper reaches and yellow and red texture contrast soilsgraduate down the valleys.The Highlands – Southern Fall contains Victoria’s mostextensive areas of Cool Temperate Rainforest. Thedominant vegetation types are Shrub<strong>by</strong> Dry Forest andDamp Forest on the upper slopes. Wet Forest ecosystemsoccur in the valleys. Montane Dry Woodland, MontaneDamp Forest and Montane Wet Forest occur at higherelevations. The gullies and river valleys support a varietyof ecological vegetation classes including Riparian Forest,Riparian Thicket and Montane Riparian Thicket.Average annual rainfall across the <strong>bioregion</strong>: 700-1200 mmSnowfall is common above 900 m in winter.Daily mean temperature across the <strong>bioregion</strong>: 6-15˚CLAND USE HISTORYEarly European settlement was sparse and concentratedon the gently undulating areas on the fringes of the<strong>bioregion</strong>. The extensive Mountain Ash forests in thesouthern and western parts of the <strong>bioregion</strong> havesupported timber harvesting industries since the 19thCentury. The <strong>bioregion</strong> also contains signifi cant areas ofpine and eucalypt plantations. Other land-use activitiesinclude sheep and cattle grazing and dairying. Somepublic land areas are also used for grazing and apiculture.Tourism and recreation are signifi cant land uses in some ofthe more elevated parts of the <strong>bioregion</strong>.The highlands are signifi cant water catchment areassupplying the majority of water for Melbourne andirrigated agriculture and power generation in the adjoiningGippsland Plain <strong>bioregion</strong>. Major impoundments includethe Thomson Dam, Lake Glenmaggie, Blue Rock Lake,and the Upper Yarra and Maroondah reservoirs.93