Technical Guidelines for Integrated Disease Surveillance ... - PHRplus
Technical Guidelines for Integrated Disease Surveillance ... - PHRplus
Technical Guidelines for Integrated Disease Surveillance ... - PHRplus
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
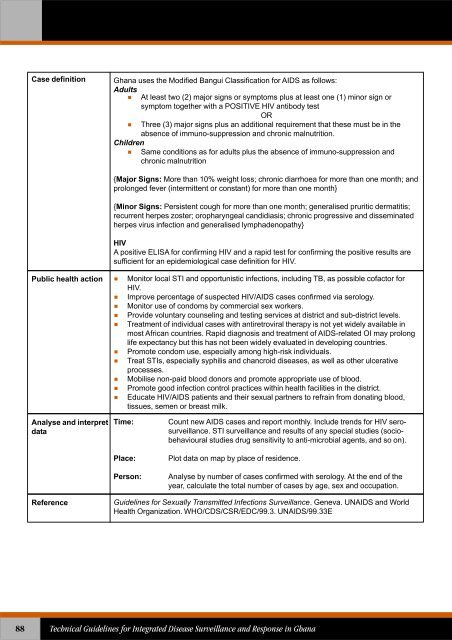
Case definitionGhana uses the Modified Bangui Classification <strong>for</strong> AIDS as follows:Adults At least two (2) major signs or symptoms plus at least one (1) minor sign orsymptom together with a POSITIVE HIV antibody testOR Three (3) major signs plus an additional requirement that these must be in theabsence of immuno-suppression and chronic malnutrition.ChildrenSame conditions as <strong>for</strong> adults plus the absence of immuno-suppression andchronic malnutrition{Major Signs: More than 10% weight loss; chronic diarrhoea <strong>for</strong> more than one month; andprolonged fever (intermittent or constant) <strong>for</strong> more than one month}{Minor Signs: Persistent cough <strong>for</strong> more than one month; generalised pruritic dermatitis;recurrent herpes zoster; oropharyngeal candidiasis; chronic progressive and disseminatedherpes virus infection and generalised lymphadenopathy}HIVA positive ELISA <strong>for</strong> confirming HIV and a rapid test <strong>for</strong> confirming the positive results aresufficient <strong>for</strong> an epidemiological case definition <strong>for</strong> HIV.Public health action Monitor local STI and opportunistic infections, including TB, as possible cofactor <strong>for</strong>HIV. Improve percentage of suspected HIV/AIDS cases confirmed via serology. Monitor use of condoms by commercial sex workers. Provide voluntary counseling and testing services at district and sub-district levels. Treatment of individual cases with antiretroviral therapy is not yet widely available inmost African countries. Rapid diagnosis and treatment of AIDS-related OI may prolonglife expectancy but this has not been widely evaluated in developing countries. Promote condom use, especially among high-risk individuals. Treat STIs, especially syphilis and chancroid diseases, as well as other ulcerativeprocesses. Mobilise non-paid blood donors and promote appropriate use of blood. Promote good infection control practices within health facilities in the district. Educate HIV/AIDS patients and their sexual partners to refrain from donating blood,tissues, semen or breast milk.Analyse and interpretdataTime:Place:Person:Count new AIDS cases and report monthly. Include trends <strong>for</strong> HIV serosurveillance.STI surveillance and results of any special studies (sociobehaviouralstudies drug sensitivity to anti-microbial agents, and so on).Plot data on map by place of residence.Analyse by number of cases confirmed with serology. At the end of theyear, calculate the total number of cases by age, sex and occupation.Reference<strong>Guidelines</strong> <strong>for</strong> Sexually Transmitted Infections <strong>Surveillance</strong>. Geneva. UNAIDS and WorldHealth Organization. WHO/CDS/CSR/EDC/99.3. UNAIDS/99.33E88<strong>Technical</strong> <strong>Guidelines</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Integrated</strong> <strong>Disease</strong> <strong>Surveillance</strong> and Response in Ghana