Technical Guidelines for Integrated Disease Surveillance ... - PHRplus
Technical Guidelines for Integrated Disease Surveillance ... - PHRplus
Technical Guidelines for Integrated Disease Surveillance ... - PHRplus
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
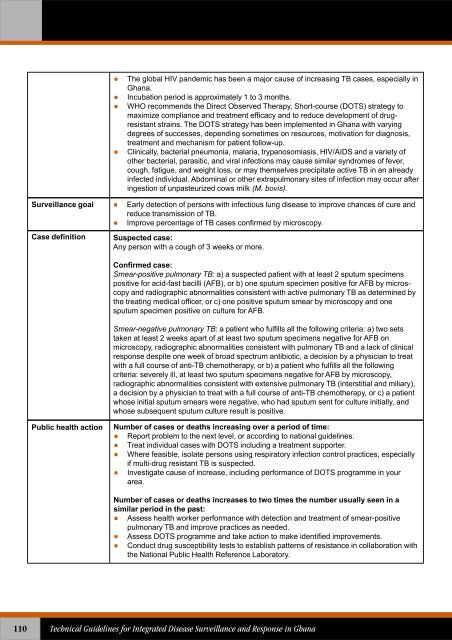
The global HIV pandemic has been a major cause of increasing TB cases, especially inGhana.Incubation period is approximately 1 to 3 months.WHO recommends the Direct Observed Therapy, Short-course (DOTS) strategy tomaximize compliance and treatment efficacy and to reduce development of drugresistantstrains. The DOTS strategy has been implemented in Ghana with varyingdegrees of successes, depending sometimes on resources, motivation <strong>for</strong> diagnosis,treatment and mechanism <strong>for</strong> patient follow-up.Clinically, bacterial pneumonia, malaria, trypanosomiasis, HIV/AIDS and a variety ofother bacterial, parasitic, and viral infections may cause similar syndromes of fever,cough, fatigue, and weight loss, or may themselves precipitate active TB in an alreadyinfected individual. Abdominal or other extrapulmonary sites of infection may occur afteringestion of unpasteurized cows milk (M. bovis).<strong>Surveillance</strong> goal Early detection of persons with infectious lung disease to improve chances of cure andreduce transmission of TB.Improve percentage of TB cases confirmed by microscopy.Case definitionSuspected case:Any person with a cough of 3 weeks or more.Confirmed case:Smear-positive pulmonary TB: a) a suspected patient with at least 2 sputum specimenspositive <strong>for</strong> acid-fast bacilli (AFB), or b) one sputum specimen positive <strong>for</strong> AFB by microscopyand radiographic abnormalities consistent with active pulmonary TB as determined bythe treating medical officer, or c) one positive sputum smear by microscopy and onesputum specimen positive on culture <strong>for</strong> AFB.Smear-negative pulmonary TB: a patient who fulfills all the following criteria: a) two setstaken at least 2 weeks apart of at least two sputum specimens negative <strong>for</strong> AFB onmicroscopy, radiographic abnormalities consistent with pulmonary TB and a lack of clinicalresponse despite one week of broad spectrum antibiotic, a decision by a physician to treatwith a full course of anti-TB chemotherapy, or b) a patient who fulfills all the followingcriteria: severely ill, at least two sputum specimens negative <strong>for</strong> AFB by microscopy,radiographic abnormalities consistent with extensive pulmonary TB (interstitial and miliary),a decision by a physician to treat with a full course of anti-TB chemotherapy, or c) a patientwhose initial sputum smears were negative, who had sputum sent <strong>for</strong> culture initially, andwhose subsequent sputum culture result is positive.Public health actionNumber of cases or deaths increasing over a period of time: Report problem to the next level, or according to national guidelines. Treat individual cases with DOTS including a treatment supporter. Where feasible, isolate persons using respiratory infection control practices, especiallyif multi-drug resistant TB is suspected. Investigate cause of increase, including per<strong>for</strong>mance of DOTS programme in yourarea.Number of cases or deaths increases to two times the number usually seen in asimilar period in the past: Assess health worker per<strong>for</strong>mance with detection and treatment of smear-positivepulmonary TB and improve practices as needed. Assess DOTS programme and take action to make identified improvements. Conduct drug susceptibility tests to establish patterns of resistance in collaboration withthe National Public Health Reference Laboratory.110<strong>Technical</strong> <strong>Guidelines</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Integrated</strong> <strong>Disease</strong> <strong>Surveillance</strong> and Response in Ghana