Download all Technical Policy Briefing Notes in a single ... - Mediation
Download all Technical Policy Briefing Notes in a single ... - Mediation
Download all Technical Policy Briefing Notes in a single ... - Mediation
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
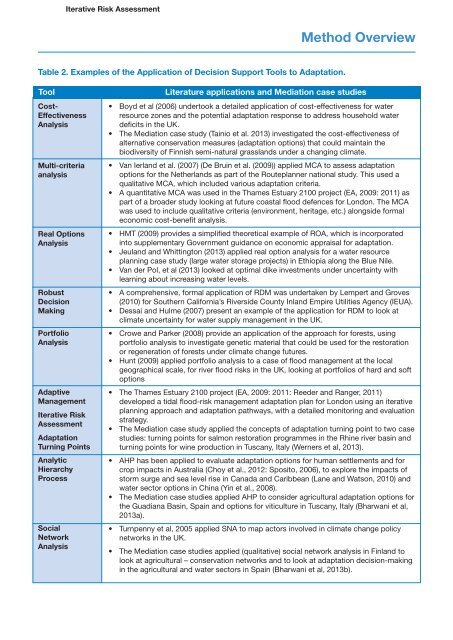
Iterative Risk AssessmentMethod OverviewTable 2. Examples of the Application of Decision Support Tools to Adaptation.ToolCost-EffectivenessAnalysisMulti-criteriaanalysisReal OptionsAnalysisRobustDecisionMak<strong>in</strong>gPortfolioAnalysisAdaptiveManagementIterative RiskAssessmentAdaptationTurn<strong>in</strong>g Po<strong>in</strong>tsAnalyticHierarchyProcessSocialNetworkAnalysisLiterature applications and <strong>Mediation</strong> case studies• Boyd et al (2006) undertook a detailed application of cost-effectiveness for waterresource zones and the potential adaptation response to address household waterdeficits <strong>in</strong> the UK.• The <strong>Mediation</strong> case study (Ta<strong>in</strong>io et al. 2013) <strong>in</strong>vestigated the cost-effectiveness ofalternative conservation measures (adaptation options) that could ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong> thebiodiversity of F<strong>in</strong>nish semi-natural grasslands under a chang<strong>in</strong>g climate.• Van Ierland et al. (2007) (De Bru<strong>in</strong> et al. (2009)) applied MCA to assess adaptationoptions for the Netherlands as part of the Routeplanner national study. This used aqualitative MCA, which <strong>in</strong>cluded various adaptation criteria.• A quantitative MCA was used <strong>in</strong> the Thames Estuary 2100 project (EA, 2009: 2011) aspart of a broader study look<strong>in</strong>g at future coastal flood defences for London. The MCAwas used to <strong>in</strong>clude qualitative criteria (environment, heritage, etc.) alongside formaleconomic cost-benefit analysis.• HMT (2009) provides a simplified theoretical example of ROA, which is <strong>in</strong>corporated<strong>in</strong>to supplementary Government guidance on economic appraisal for adaptation.• Jeuland and Whitt<strong>in</strong>gton (2013) applied real option analysis for a water resourceplann<strong>in</strong>g case study (large water storage projects) <strong>in</strong> Ethiopia along the Blue Nile.• Van der Pol, et al (2013) looked at optimal dike <strong>in</strong>vestments under uncerta<strong>in</strong>ty withlearn<strong>in</strong>g about <strong>in</strong>creas<strong>in</strong>g water levels.• A comprehensive, formal application of RDM was undertaken by Lempert and Groves(2010) for Southern California’s Riverside County Inland Empire Utilities Agency (IEUA).• Dessai and Hulme (2007) present an example of the application for RDM to look atclimate uncerta<strong>in</strong>ty for water supply management <strong>in</strong> the UK.• Crowe and Parker (2008) provide an application of the approach for forests, us<strong>in</strong>gportfolio analysis to <strong>in</strong>vestigate genetic material that could be used for the restorationor regeneration of forests under climate change futures.• Hunt (2009) applied portfolio analysis to a case of flood management at the localgeographical scale, for river flood risks <strong>in</strong> the UK, look<strong>in</strong>g at portfolios of hard and softoptions• The Thames Estuary 2100 project (EA, 2009: 2011: Reeder and Ranger, 2011)developed a tidal flood-risk management adaptation plan for London us<strong>in</strong>g an iterativeplann<strong>in</strong>g approach and adaptation pathways, with a detailed monitor<strong>in</strong>g and evaluationstrategy.• The <strong>Mediation</strong> case study applied the concepts of adaptation turn<strong>in</strong>g po<strong>in</strong>t to two casestudies: turn<strong>in</strong>g po<strong>in</strong>ts for salmon restoration programmes <strong>in</strong> the Rh<strong>in</strong>e river bas<strong>in</strong> andturn<strong>in</strong>g po<strong>in</strong>ts for w<strong>in</strong>e production <strong>in</strong> Tuscany, Italy (Werners et al, 2013).• AHP has been applied to evaluate adaptation options for human settlements and forcrop impacts <strong>in</strong> Australia (Choy et al., 2012: Sposito, 2006), to explore the impacts ofstorm surge and sea level rise <strong>in</strong> Canada and Caribbean (Lane and Watson, 2010) andwater sector options <strong>in</strong> Ch<strong>in</strong>a (Y<strong>in</strong> et al., 2008).• The <strong>Mediation</strong> case studies applied AHP to consider agricultural adaptation options forthe Guadiana Bas<strong>in</strong>, Spa<strong>in</strong> and options for viticulture <strong>in</strong> Tuscany, Italy (Bharwani et al,2013a).• Turnpenny et al, 2005 applied SNA to map actors <strong>in</strong>volved <strong>in</strong> climate change policynetworks <strong>in</strong> the UK.• The <strong>Mediation</strong> case studies applied (qualitative) social network analysis <strong>in</strong> F<strong>in</strong>land tolook at agricultural – conservation networks and to look at adaptation decision-mak<strong>in</strong>g<strong>in</strong> the agricultural and water sectors <strong>in</strong> Spa<strong>in</strong> (Bharwani et al, 2013b).