Untitled - Technische Universiteit Eindhoven
Untitled - Technische Universiteit Eindhoven
Untitled - Technische Universiteit Eindhoven
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
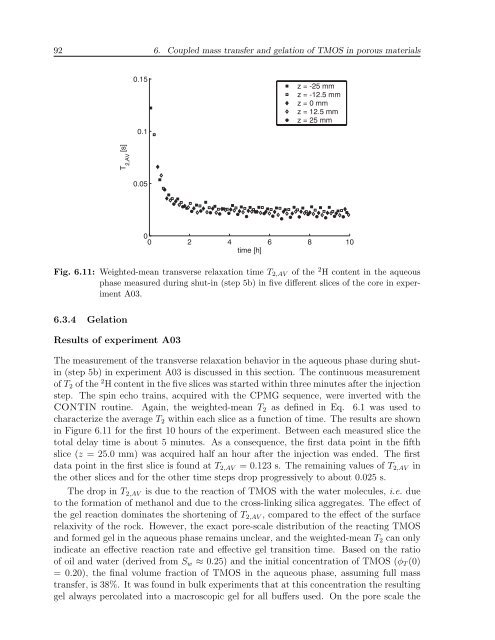
92 6. Coupled mass transfer and gelation of TMOS in porous materials0.150.1z = -25 mmz = -12.5 mmz = 0 mmz = 12.5 mmz = 25 mmT 2,AV[s]0.0500 2 4 6 8 10time [h]Fig. 6.11: Weighted-mean transverse relaxation time T 2,AV of the 2 H content in the aqueousphase measured during shut-in (step 5b) in five different slices of the core in experimentA03.6.3.4 GelationResults of experiment A03The measurement of the transverse relaxation behavior in the aqueous phase during shutin(step 5b) in experiment A03 is discussed in this section. The continuous measurementof T 2 of the 2 H content in the five slices was started within three minutes after the injectionstep. The spin echo trains, acquired with the CPMG sequence, were inverted with theCONTIN routine. Again, the weighted-mean T 2 as defined in Eq. 6.1 was used tocharacterize the average T 2 within each slice as a function of time. The results are shownin Figure 6.11 for the first 10 hours of the experiment. Between each measured slice thetotal delay time is about 5 minutes. As a consequence, the first data point in the fifthslice (z = 25.0 mm) was acquired half an hour after the injection was ended. The firstdata point in the first slice is found at T 2,AV = 0.123 s. The remaining values of T 2,AV inthe other slices and for the other time steps drop progressively to about 0.025 s.The drop in T 2,AV is due to the reaction of TMOS with the water molecules, i.e. dueto the formation of methanol and due to the cross-linking silica aggregates. The effect ofthe gel reaction dominates the shortening of T 2,AV , compared to the effect of the surfacerelaxivity of the rock. However, the exact pore-scale distribution of the reacting TMOSand formed gel in the aqueous phase remains unclear, and the weighted-mean T 2 can onlyindicate an effective reaction rate and effective gel transition time. Based on the ratioof oil and water (derived from S w ≈ 0.25) and the initial concentration of TMOS (φ T (0)= 0.20), the final volume fraction of TMOS in the aqueous phase, assuming full masstransfer, is 38%. It was found in bulk experiments that at this concentration the resultinggel always percolated into a macroscopic gel for all buffers used. On the pore scale the