ASReml-S reference manual - VSN International
ASReml-S reference manual - VSN International
ASReml-S reference manual - VSN International
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
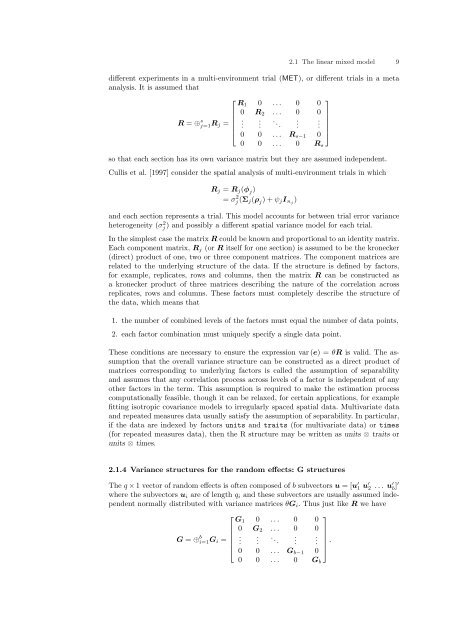
2.1 The linear mixed model 9different experiments in a multi-environment trial (MET), or different trials in a metaanalysis. It is assumed that⎡⎤R 1 0 . . . 0 00 R 2 . . . 0 0R = ⊕ s j=1R j =. ⎢ . . .. . . ⎥⎣0 0 . . . R s−1 0⎦0 0 . . . 0 R sso that each section has its own variance matrix but they are assumed independent.Cullis et al. [1997] consider the spatial analysis of multi-environment trials in whichR j = R j (φ j )= σ 2 j (Σ j (ρ j ) + ψ j I nj )and each section represents a trial. This model accounts for between trial error varianceheterogeneity (σj 2 ) and possibly a different spatial variance model for each trial.In the simplest case the matrix R could be known and proportional to an identity matrix.Each component matrix, R j (or R itself for one section) is assumed to be the kronecker(direct) product of one, two or three component matrices. The component matrices arerelated to the underlying structure of the data. If the structure is defined by factors,for example, replicates, rows and columns, then the matrix R can be constructed asa kronecker product of three matrices describing the nature of the correlation acrossreplicates, rows and columns. These factors must completely describe the structure ofthe data, which means that1. the number of combined levels of the factors must equal the number of data points,2. each factor combination must uniquely specify a single data point.These conditions are necessary to ensure the expression var (e) = θR is valid. The assumptionthat the overall variance structure can be constructed as a direct product ofmatrices corresponding to underlying factors is called the assumption of separabilityand assumes that any correlation process across levels of a factor is independent of anyother factors in the term. This assumption is required to make the estimation processcomputationally feasible, though it can be relaxed, for certain applications, for examplefitting isotropic covariance models to irregularly spaced spatial data. Multivariate dataand repeated measures data usually satisfy the assumption of separability. In particular,if the data are indexed by factors units and traits (for multivariate data) or times(for repeated measures data), then the R structure may be written as units ⊗ traits orunits ⊗ times.2.1.4 Variance structures for the random effects: G structuresThe q × 1 vector of random effects is often composed of b subvectors u = [u ′ 1 u ′ 2 . . . u ′ b ]′where the subvectors u i are of length q i and these subvectors are usually assumed independentnormally distributed with variance matrices θG i . Thus just like R we have⎡⎤G 1 0 . . . 0 00 G 2 . . . 0 0G = ⊕ b i=1G i =⎢.. . .. . . ⎥⎣0 0 . . . G b−1 0⎦ .0 0 . . . 0 G b