ASReml-S reference manual - VSN International
ASReml-S reference manual - VSN International
ASReml-S reference manual - VSN International
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
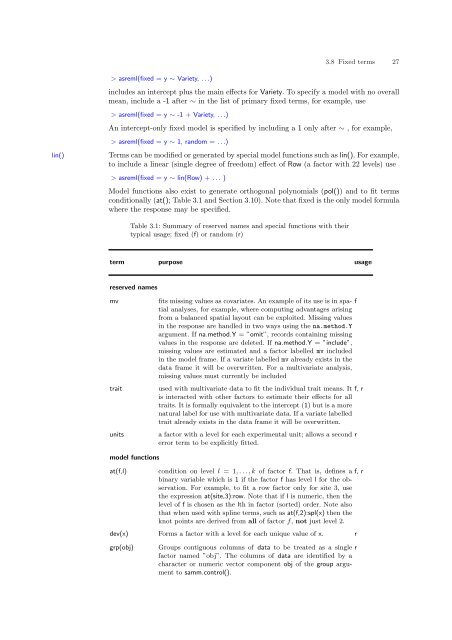
3.8 Fixed terms 27> asreml(fixed = y ∼ Variety, . . .)includes an intercept plus the main effects for Variety. To specify a model with no overallmean, include a -1 after ∼ in the list of primary fixed terms, for example, use> asreml(fixed = y ∼ -1 + Variety, . . .)An intercept-only fixed model is specified by including a 1 only after ∼ , for example,> asreml(fixed = y ∼ 1, random = . . .)lin()Terms can be modified or generated by special model functions such as lin(). For example,to include a linear (single degree of freedom) effect of Row (a factor with 22 levels) use> asreml(fixed = y ∼ lin(Row) + . . . )Model functions also exist to generate orthogonal polynomials (pol()) and to fit termsconditionally (at(); Table 3.1 and Section 3.10). Note that fixed is the only model formulawhere the response may be specified.Table 3.1: Summary of reserved names and special functions with theirtypical usage; fixed (f) or random (r)term purpose usagereserved namesmvtraitunitsfits missing values as covariates. An example of its use is in spatialanalyses, for example, where computing advantages arisingffrom a balanced spatial layout can be exploited. Missing valuesin the response are handled in two ways using the na.method.Yargument. If na.method.Y = ”omit”, records containing missingvalues in the response are deleted. If na.method.Y = ”include”,missing values are estimated and a factor labelled mv includedin the model frame. If a variate labelled mv already exists in thedata frame it will be overwritten. For a multivariate analysis,missing values must currently be includedused with multivariate data to fit the individual trait means. It f, ris interacted with other factors to estimate their effects for alltraits. It is formally equivalent to the intercept (1) but is a morenatural label for use with multivariate data. If a variate labelledtrait already exists in the data frame it will be overwritten.a factor with a level for each experimental unit; allows a seconderror term to be explicitly fitted.rmodel functionsat(f,l)condition on level l = 1, . . . , k of factor f. That is, defines a f, rbinary variable which is 1 if the factor f has level l for the observation.For example, to fit a row factor only for site 3, usethe expression at(site,3):row. Note that if l is numeric, then thelevel of f is chosen as the lth in factor (sorted) order. Note alsothat when used with spline terms, such as at(f,2):spl(x) then theknot points are derived from all of factor f, not just level 2.dev(x) Forms a factor with a level for each unique value of x. rgrp(obj)Groups contiguous columns of data to be treated as a single rfactor named ”obj”. The columns of data are identified by acharacter or numeric vector component obj of the group argumentto samm.control().