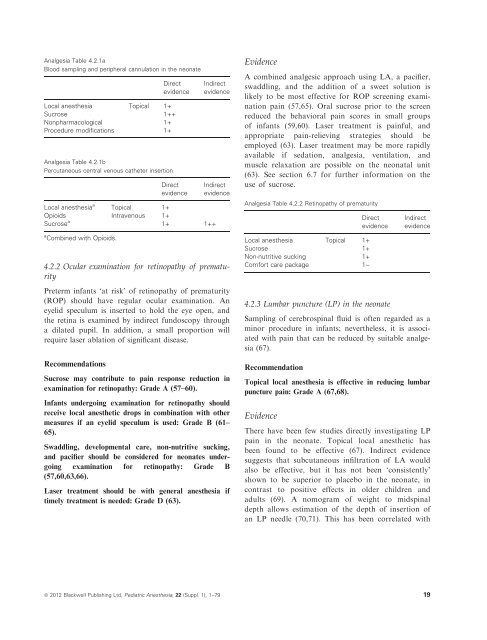
however, reductions <strong>in</strong> the response to pa<strong>in</strong> have beenobserved follow<strong>in</strong>g nontraditional analgesia such assucrose <strong>and</strong> physical <strong>and</strong> environmental measures, forexample, suckl<strong>in</strong>g or tactile stimulation, which are currentlynot known to have potentially harmful effects.A number of documents <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g reviews, guidel<strong>in</strong>e,<strong>and</strong> policy statements have been published recently onthe subject of procedural pa<strong>in</strong> management <strong>in</strong> the neonate(1–4). On the basis of the currently available evidence,the follow<strong>in</strong>g measures can be generallyrecommended for the management of procedural pa<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong> the neonate:RecommendationsBreast-feed<strong>in</strong>g should be encouraged dur<strong>in</strong>g the procedure,if feasible: Grade A (5–9).Nonpharmacological measures <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g non-nutritivesuck<strong>in</strong>g, ‘kangaroo care’, swaddl<strong>in</strong>g/facilitated tuck<strong>in</strong>g,tactile stimulation, <strong>and</strong> heel massage can be used forbrief procedures: Grade A (5,6,10–30).4.2.1 Blood sampl<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> the neonate(<strong>in</strong>cludes peripheral venous, arterial, <strong>and</strong>percutaneous central venous cannulation)Blood sampl<strong>in</strong>g is a necessary <strong>and</strong> rout<strong>in</strong>e part of neonatalcare. Where an <strong>in</strong>dwell<strong>in</strong>g arterial catheter is notavailable, then venepuncture (VP) or heel prick bloodsampl<strong>in</strong>g (HPBS) is used. All newborn babies <strong>in</strong> theUK have a HPBS as part of the UK screen<strong>in</strong>g regime.Neonates admitted to <strong>in</strong>tensive care or who are caredfor on postnatal wards will require frequent bloodsampl<strong>in</strong>g that has been identified <strong>in</strong> many studies as asignificant cause of pa<strong>in</strong> <strong>and</strong> morbidity. HPBS requiresappropriate tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g <strong>and</strong> is used to collect small bloodsamples such as blood glucose, bilirub<strong>in</strong> newbornscreen<strong>in</strong>g tests, <strong>and</strong> capillary blood gases. VP alsorequires tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g but is technically more difficult <strong>and</strong> isused to collect larger blood samples. The pr<strong>in</strong>ciples<strong>and</strong> techniques of pa<strong>in</strong> relief are applicable to other<strong>in</strong>vasive procedures such as peripheral arterial l<strong>in</strong>e<strong>in</strong>sertion <strong>and</strong> percutaneous central venous catheters(i.e., long l<strong>in</strong>e). Please also see sections 4.0 <strong>and</strong> 4.1 onthe general management of procedural pa<strong>in</strong>.RecommendationsSucrose or other sweet solutions can be used: Grade A(5,6,10–18,22,29,31–40).Nonpharmacological measures <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g tactile stimulation,breast-feed<strong>in</strong>g, non-nutritive suck<strong>in</strong>g, ‘kangaroocare’, <strong>and</strong> massage of the heel can be used for heel prickblood sampl<strong>in</strong>g: Grade A (12,19–28,30).Venepuncture (by a tra<strong>in</strong>ed practitioner) is preferred toheel lance for larger samples as it is less pa<strong>in</strong>ful: GradeA (18,41–43).Topical local anesthetics alone are <strong>in</strong>sufficient for heellance pa<strong>in</strong>: Grade A (44,45).Topical local anesthetics can be used for venepuncturepa<strong>in</strong>: Grade B (44–47).Us<strong>in</strong>g the whole plantar surface of the heel reduces thepa<strong>in</strong> of heel prick blood sampl<strong>in</strong>g: Grade B (48,49).Remifentanil <strong>and</strong> sucrose decreased central venous catheterpa<strong>in</strong>: Grade B: (36).Topical tetraca<strong>in</strong>e plus morph<strong>in</strong>e is superior to topicalanalgesia alone for central venous catheter pa<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong> ventilated<strong>in</strong>fants: Grade B (50,51).EvidenceA large number of studies have demonstrated thatsucrose before VP or HPBS reduces the behavioralpa<strong>in</strong> scores measured by a range of validated assessments(5,6,10–18,22,29,31–40,52). The dose of sucrosediffered across these studies.Reliev<strong>in</strong>g the pa<strong>in</strong> of HPBS has been challeng<strong>in</strong>gwith pharmacological methods. However, nonpharmacologicalmethods <strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g breast-feed<strong>in</strong>g, non-nutritivesuck<strong>in</strong>g, kangaroo care, <strong>and</strong> premassage of theheel before <strong>and</strong> dur<strong>in</strong>g HPBS have consistently demonstratedreduced behavioral pa<strong>in</strong> scores <strong>and</strong> physiologicalmarkers (12,19–28).VP appears to be less pa<strong>in</strong>ful than HPBS so is thepreferred option whenever practical (18,41,43). Topicallocal anesthesia (LA) can reduce the pa<strong>in</strong> of VP <strong>and</strong><strong>in</strong>sertion of central venous catheters (44–46,51,53).However, topical LA is not effective for HPBS (45).Morph<strong>in</strong>e with topical LA was more effective than LAalone for central venous l<strong>in</strong>e placement <strong>in</strong> ventilatedneonates (50,51). In addition, low-dose remifentanilcomb<strong>in</strong>ed with sucrose reduced the pa<strong>in</strong> of <strong>in</strong>sertion ofcentral venous catheters (36).HPBS pa<strong>in</strong> can be reduced with procedure modificationsuch as us<strong>in</strong>g an automated spr<strong>in</strong>g-loaded device,avoid<strong>in</strong>g squeez<strong>in</strong>g the heel, <strong>and</strong> us<strong>in</strong>g a wider area ofthe plantar surface of the heel (48,49,54–56).18 ª 2012 Blackwell Publish<strong>in</strong>g Ltd, Pediatric Anesthesia, 22 (Suppl. 1), 1–79
Analgesia Table 4.2.1aBlood sampl<strong>in</strong>g <strong>and</strong> peripheral cannulation <strong>in</strong> the neonateDirectevidenceLocal anesthesia Topical 1+Sucrose 1++Nonpharmacological 1+Procedure modifications 1+Analgesia Table 4.2.1bPercutaneous central venous catheter <strong>in</strong>sertionDirectevidenceIndirectevidenceIndirectevidenceLocal anesthesia a Topical 1+Opioids Intravenous 1+Sucrose a 1+ 1++a Comb<strong>in</strong>ed with Opioids.4.2.2 Ocular exam<strong>in</strong>ation for ret<strong>in</strong>opathy of prematurityPreterm <strong>in</strong>fants ‘at risk’ of ret<strong>in</strong>opathy of prematurity(ROP) should have regular ocular exam<strong>in</strong>ation. Aneyelid speculum is <strong>in</strong>serted to hold the eye open, <strong>and</strong>the ret<strong>in</strong>a is exam<strong>in</strong>ed by <strong>in</strong>direct fundoscopy througha dilated pupil. In addition, a small proportion willrequire laser ablation of significant disease.RecommendationsSucrose may contribute to pa<strong>in</strong> response reduction <strong>in</strong>exam<strong>in</strong>ation for ret<strong>in</strong>opathy: Grade A (57–60).Infants undergo<strong>in</strong>g exam<strong>in</strong>ation for ret<strong>in</strong>opathy shouldreceive local anesthetic drops <strong>in</strong> comb<strong>in</strong>ation with othermeasures if an eyelid speculum is used: Grade B (61–65).Swaddl<strong>in</strong>g, developmental care, non-nutritive suck<strong>in</strong>g,<strong>and</strong> pacifier should be considered for neonates undergo<strong>in</strong>gexam<strong>in</strong>ation for ret<strong>in</strong>opathy: Grade B(57,60,63,66).Laser treatment should be with general anesthesia iftimely treatment is needed: Grade D (63).EvidenceA comb<strong>in</strong>ed analgesic approach us<strong>in</strong>g LA, a pacifier,swaddl<strong>in</strong>g, <strong>and</strong> the addition of a sweet solution islikely to be most effective for ROP screen<strong>in</strong>g exam<strong>in</strong>ationpa<strong>in</strong> (57,65). Oral sucrose prior to the screenreduced the behavioral pa<strong>in</strong> scores <strong>in</strong> small groupsof <strong>in</strong>fants (59,60). Laser treatment is pa<strong>in</strong>ful, <strong>and</strong>appropriate pa<strong>in</strong>-reliev<strong>in</strong>g strategies should beemployed (63). Laser treatment may be more rapidlyavailable if sedation, analgesia, ventilation, <strong>and</strong>muscle relaxation are possible on the neonatal unit(63). See section 6.7 for further <strong>in</strong>formation on theuse of sucrose.Analgesia Table 4.2.2 Ret<strong>in</strong>opathy of prematurityLocal anesthesia Topical 1+Sucrose 1+Non-nutritive suck<strong>in</strong>g 1+Comfort care package 1)Directevidence4.2.3 Lumbar puncture (LP) <strong>in</strong> the neonateIndirectevidenceSampl<strong>in</strong>g of cerebrosp<strong>in</strong>al fluid is often regarded as am<strong>in</strong>or procedure <strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>fants; nevertheless, it is associatedwith pa<strong>in</strong> that can be reduced by suitable analgesia(67).RecommendationTopical local anesthesia is effective <strong>in</strong> reduc<strong>in</strong>g lumbarpuncture pa<strong>in</strong>: Grade A (67,68).EvidenceThere have been few studies directly <strong>in</strong>vestigat<strong>in</strong>g LPpa<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong> the neonate. Topical local anesthetic hasbeen found to be effective (67). Indirect evidencesuggests that subcutaneous <strong>in</strong>filtration of LA wouldalso be effective, but it has not been ‘consistently’shown to be superior to placebo <strong>in</strong> the neonate, <strong>in</strong>contrast to positive effects <strong>in</strong> older children <strong>and</strong>adults (69). A nomogram of weight to midsp<strong>in</strong>aldepth allows estimation of the depth of <strong>in</strong>sertion ofan LP needle (70,71). This has been correlated withª 2012 Blackwell Publish<strong>in</strong>g Ltd, Pediatric Anesthesia, 22 (Suppl. 1), 1–79 19
- Page 1 and 2: PediatricAnesthesiaVolume 22 Supple
- Page 3 and 4: doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9592.2012.3838.
- Page 5 and 6: 1.6 Contact informationCorresponden
- Page 7 and 8: RecommendationsChildren’s self-re
- Page 9 and 10: Topical anesthetic preparations, fo
- Page 11 and 12: 2.7.6 Laparoscopic surgeryGood prac
- Page 13 and 14: In order to assess pain, effective
- Page 16 and 17: Postoperative painl NCCPC-PV (Non-C
- Page 18 and 19: 68 Broome ME, Richtsmeier A, Maikle
- Page 22 and 23: increased success rate (i.e., less
- Page 24 and 25: Newer preparations such as liposoma
- Page 26 and 27: Good practice pointLubricant contai
- Page 28 and 29: most effective. There are a number
- Page 30 and 31: 12 Bellieni C, Bagnoli F, Perrone S
- Page 32 and 33: venipuncture pain in a pediatric em
- Page 34 and 35: 172 van Twillert B, Bremer M, Faber
- Page 36 and 37: necessary to ensure that the patien
- Page 38 and 39: when compared with LA alone and sal
- Page 40 and 41: Peribulbar block improves early ana
- Page 42 and 43: Analgesia Table 5.5.1 Sub-umbilical
- Page 44 and 45: was more effective with less motor
- Page 46 and 47: with using landmark techniques (205
- Page 48 and 49: Good practice pointWound infiltrati
- Page 50 and 51: Analgesia Table 5.6.4 Urological Su
- Page 52 and 53: (298). Ketorolac did not influence
- Page 54 and 55: well as the epidural technique for
- Page 56 and 57: Good practice pointA multi-modal an
- Page 58 and 59: 14 Grainger J, Saravanappa N. Local
- Page 60 and 61: day-stay unit. Int J Paediatr Dent
- Page 62 and 63: tinuous epidural infusion in childr
- Page 64 and 65: 245 Morton NS, O’Brien K. Analges
- Page 66 and 67: 321 Taenzer AH, Clark C, Taenzer AH
- Page 68 and 69: Section 6.0AnalgesiaContents6.1 Ana
- Page 70 and 71:
enhance systemic absorption. Lidoca
- Page 73 and 74:
undergoes hepatic biotransformation
- Page 75 and 76:
tein binding are reduced and the ha
- Page 77 and 78:
a low-dose infusion but the child m
- Page 79 and 80:
Table 6.6.1 Paracetamol dosing guid
- Page 81:
steps that health care professional