Synthesis and Comparison of the Reactivity of Allyl Fluorides and ...
Synthesis and Comparison of the Reactivity of Allyl Fluorides and ...
Synthesis and Comparison of the Reactivity of Allyl Fluorides and ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
1.4 Building Block Approach to Organ<strong>of</strong>luorine Compounds<br />
19<br />
Chapter One<br />
Fluorinated building blocks are small readily available materials that already contain<br />
fluorine atoms, <strong>and</strong> for this reason <strong>the</strong>y are extremely valuable in syn<strong>the</strong>tic chemistry as<br />
<strong>the</strong>y negate <strong>the</strong> use <strong>of</strong> hazardous fluorinating reagents such as DAST. There are numerous<br />
papers that discuss <strong>the</strong>ir uses <strong>and</strong> a selective review <strong>of</strong> mono-, di- <strong>and</strong> tri-fluorinated<br />
building blocks will be presented here.<br />
Chlor<strong>of</strong>luorocarbenes are extremely useful building blocks due to <strong>the</strong> fact that <strong>the</strong>y react<br />
with electron rich alkenes, such as enol e<strong>the</strong>rs <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> corresponding products,<br />
alkoxycyclopropanes, can undergo solvolysis reactions leading to �-fluoro-Z-enals. These<br />
are extremely valuable <strong>and</strong> have been utilised by Johnson et al. in <strong>the</strong> syn<strong>the</strong>sis <strong>of</strong> steroid<br />
analogues. [51-54]<br />
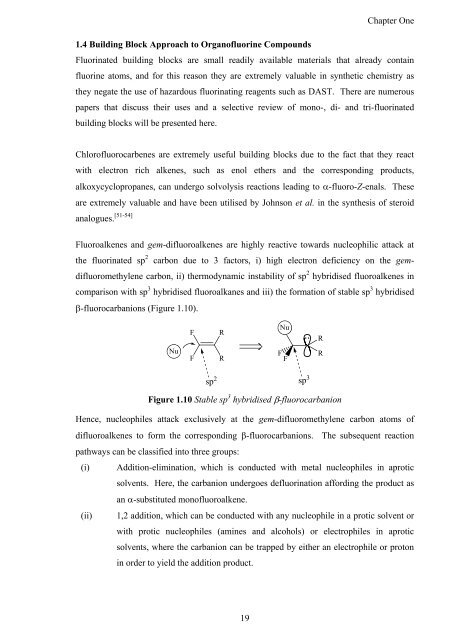
Fluoroalkenes <strong>and</strong> gem-difluoroalkenes are highly reactive towards nucleophilic attack at<br />
<strong>the</strong> fluorinated sp 2 carbon due to 3 factors, i) high electron deficiency on <strong>the</strong> gem-<br />
difluoromethylene carbon, ii) <strong>the</strong>rmodynamic instability <strong>of</strong> sp 2 hybridised fluoroalkenes in<br />
comparison with sp 3 hybridised fluoroalkanes <strong>and</strong> iii) <strong>the</strong> formation <strong>of</strong> stable sp 3 hybridised<br />
�-fluorocarbanions (Figure 1.10).<br />
Figure 1.10 Stable sp 3 hybridised �-fluorocarbanion<br />
Hence, nucleophiles attack exclusively at <strong>the</strong> gem-difluoromethylene carbon atoms <strong>of</strong><br />
difluoroalkenes to form <strong>the</strong> corresponding �-fluorocarbanions. The subsequent reaction<br />
pathways can be classified into three groups:<br />
(i) Addition-elimination, which is conducted with metal nucleophiles in aprotic<br />
solvents. Here, <strong>the</strong> carbanion undergoes defluorination affording <strong>the</strong> product as<br />
an �-substituted mon<strong>of</strong>luoroalkene.<br />
(ii) 1,2 addition, which can be conducted with any nucleophile in a protic solvent or<br />
with protic nucleophiles (amines <strong>and</strong> alcohols) or electrophiles in aprotic<br />
solvents, where <strong>the</strong> carbanion can be trapped by ei<strong>the</strong>r an electrophile or proton<br />
in order to yield <strong>the</strong> addition product.