Synthesis and Comparison of the Reactivity of Allyl Fluorides and ...
Synthesis and Comparison of the Reactivity of Allyl Fluorides and ...
Synthesis and Comparison of the Reactivity of Allyl Fluorides and ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
74<br />
Chapter Three<br />
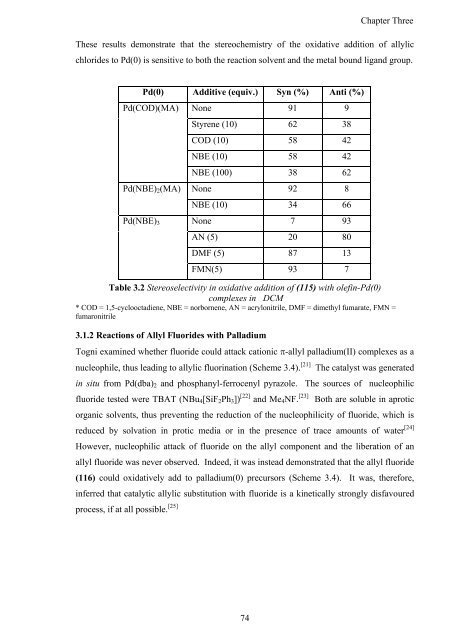
These results demonstrate that <strong>the</strong> stereochemistry <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> oxidative addition <strong>of</strong> allylic<br />
chlorides to Pd(0) is sensitive to both <strong>the</strong> reaction solvent <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> metal bound lig<strong>and</strong> group.<br />
Pd(0) Additive (equiv.) Syn (%) Anti (%)<br />
Pd(COD)(MA) None 91 9<br />
Styrene (10) 62 38<br />
COD (10) 58 42<br />
NBE (10) 58 42<br />
NBE (100) 38 62<br />
Pd(NBE)2(MA) None 92 8<br />
NBE (10) 34 66<br />
Pd(NBE)3 None 7 93<br />
AN (5) 20 80<br />
DMF (5) 87 13<br />
FMN(5) 93 7<br />
Table 3.2 Stereoselectivity in oxidative addition <strong>of</strong> (115) with olefin-Pd(0)<br />
complexes in DCM<br />
* COD = 1,5-cyclooctadiene, NBE = norbornene, AN = acrylonitrile, DMF = dimethyl fumarate, FMN =<br />
fumaronitrile<br />
3.1.2 Reactions <strong>of</strong> <strong>Allyl</strong> <strong>Fluorides</strong> with Palladium<br />
Togni examined whe<strong>the</strong>r fluoride could attack cationic �-allyl palladium(II) complexes as a<br />
nucleophile, thus leading to allylic fluorination (Scheme 3.4). [21] The catalyst was generated<br />
in situ from Pd(dba)2 <strong>and</strong> phosphanyl-ferrocenyl pyrazole. The sources <strong>of</strong> nucleophilic<br />
fluoride tested were TBAT (NBu4[SiF2Ph3]) [22] <strong>and</strong> Me4NF. [23] Both are soluble in aprotic<br />
organic solvents, thus preventing <strong>the</strong> reduction <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> nucleophilicity <strong>of</strong> fluoride, which is<br />
reduced by solvation in protic media or in <strong>the</strong> presence <strong>of</strong> trace amounts <strong>of</strong> water [24]<br />
However, nucleophilic attack <strong>of</strong> fluoride on <strong>the</strong> allyl component <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> liberation <strong>of</strong> an<br />
allyl fluoride was never observed. Indeed, it was instead demonstrated that <strong>the</strong> allyl fluoride<br />
(116) could oxidatively add to palladium(0) precursors (Scheme 3.4). It was, <strong>the</strong>refore,<br />
inferred that catalytic allylic substitution with fluoride is a kinetically strongly disfavoured<br />
process, if at all possible. [25]