- Page 2:
Engineering Geology
- Page 6:
Engineering Geology Second Edition
- Page 10:
Preface As noted in the Preface to
- Page 14:
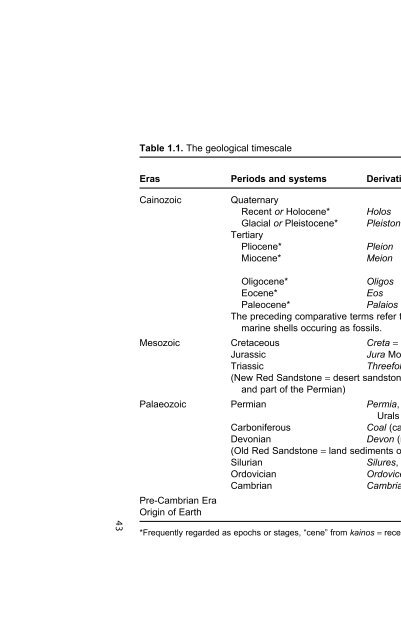
Contents 1. Rock Types and Stratigr
- Page 18:
Contents Field Instrumentation 344
- Page 22:
Chapter 1 Rock Types and Stratigrap
- Page 26:
Chapter 1 several tens of metres bu
- Page 30:
Chapter 1 Figure 1.4 Distribution o
- Page 34:
Chapter 1 Figure 1.5 Lapilli near C
- Page 38:
Chapter 1 Figure 1.7 (a) Ropy or pa
- Page 42:
Chapter 1 Figure 1.8 Columnar joint
- Page 46:
Chapter 1 Figure 1.9 Pegmatite vein
- Page 50:
Chapter 1 Figure 1.10 Thin section
- Page 54: Chapter 1 Figure 1.11 An old quarry
- Page 58: Chapter 1 a b Figure 1.13 (a) Gneis
- Page 62: Chapter 1 and the types of country
- Page 66: Chapter 1 A variety of minerals suc
- Page 70: Chapter 1 metasomatic activity is c
- Page 74: Chapter 1 derived by partial intras
- Page 78: Chapter 1 character (are they irreg
- Page 82: Chapter 1 the top. Individual grade
- Page 86: Chapter 1 Figure 1.20 Thin section
- Page 90: Chapter 1 Montmorillonite [(Mg,Al)
- Page 94: Chapter 1 Figure 1.22 Salt teepees
- Page 98: Chapter 1 The extent and regularity
- Page 102: Chapter 1 the lowest bed in the upp
- Page 108: E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 112: This page intentionally left blank
- Page 116: E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 120: E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 124: E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 128: E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 132: E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 136: E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 140: E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 144: E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 148: E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 152: E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 156:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 160:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 164:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 168:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 172:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 176:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 180:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 184:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 188:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 192:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 196:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 200:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 204:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 208:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 212:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 216:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 220:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 224:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 228:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 232:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 236:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 240:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 244:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 248:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 252:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 256:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 260:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 264:
Figure 3.29 Block diagram of a glac
- Page 268:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 272:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 276:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 280:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 284:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 288:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 292:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 296:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 300:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 304:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 308:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 312:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 316:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 320:
This page intentionally left blank
- Page 324:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 328:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 332:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 336:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 340:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 344:
162 Table 4.4. Relative values of p
- Page 348:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 352:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 356:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 360:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 364:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 368:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 372:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 376:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 380:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 384:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 388:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 392:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 396:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 400:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 404:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 408:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 412:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 416:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 420:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 424:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 428:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 432:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 436:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 440:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 444:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 448:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 452:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 456:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 460:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 464:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 468:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 472:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 476:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 480:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 484:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 488:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 492:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 496:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 500:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 504:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 508:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 512:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 516:
248 Table 5.21. Some properties of
- Page 520:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 524:
252 Table 5.22. Rock type classific
- Page 528:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 532:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 536:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 540:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 544:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 548:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 552:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 556:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 560:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 564:
272 Table 5.33. Some physical prope
- Page 568:
274 Table 5.34. Geomechanical prope
- Page 572:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 576:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 580:
280 Table 6.1. Some properties of B
- Page 584:
282 Table 6.2. Some properties of B
- Page 588:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 592:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 596:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 600:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 604:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 608:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 612:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 616:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 620:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 624:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 628:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 632:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 636:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 640:
This page intentionally left blank
- Page 644:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 648:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 652:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 656:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 660:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 664:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 668:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 672:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 676:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 680:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 684:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 688:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 692:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 696:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 700:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 704:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 708:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 712:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 716:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 720:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 724:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 728:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 732:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 736:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 740:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 744:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 748:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 752:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 756:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 760:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 764:
372 Table 7.7a. Excerpts from the e
- Page 768:
374 Table 7.7b. Key to the engineer
- Page 772:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 776:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 780:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 784:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 788:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 792:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 796:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 800:
390 Table 8.1. Modified Mercalli Sc
- Page 804:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 808:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 812:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 816:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 820:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 824:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 828:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 832:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 836:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 840:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 844:
412 Figure 8.15 (a) (b) (a) Rip-rap
- Page 848:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 852:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 856:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 860:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 864:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 868:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 872:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 876:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 880:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 884:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 888:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 892:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 896:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 900:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 904:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 908:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 912:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 916:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 920:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 924:
This page intentionally left blank
- Page 928:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 932:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 936:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 940:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 944:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 948:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 952:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 956:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 960:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 964:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 968:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 972:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 976:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 980:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 984:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 988:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 992:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 996:
488 Table 9.4. The rock mass rating
- Page 1000:
490 Table 9.6. Classification of in
- Page 1004:
492 Table 9.6. Classification of in
- Page 1008:
494 Table 9.6. Classification of in
- Page 1012:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1016:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1020:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1024:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1028:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1032:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1036:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1040:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1044:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1048:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1052:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1056:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1060:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1064:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1068:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1072:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1076:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1080:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1084:
532 Table 9.8. Typical compaction c
- Page 1088:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1092:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1096:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1100:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1104:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1108:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1112:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1116:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1120:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1124:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1128:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1132:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1136:
This page intentionally left blank
- Page 1140:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1144:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1148:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1152:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1156:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1160:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1164:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1168:
E n g i n e e r i n g G e o l o g y
- Page 1172:
I n d e x coastal protection, 410,
- Page 1176:
I n d e x grout, 526, 548 groutabil
- Page 1180:
I n d e x rebound, 513 recumbent fo
- Page 1184:
This page intentionally left blank