- Page 1:
ibm.com/redbooks Front cover ABCs o
- Page 4 and 5:
Note: Before using this information
- Page 6 and 7:
3.10 Data sets eligible for EAV vol
- Page 8 and 9:
5.5 Implementing SMS policies. . .
- Page 10 and 11:
7.29 Accessing a data set with DFSM
- Page 12 and 13:
Trademarks IBM, the IBM logo, and i
- Page 14 and 15:
Paul Rogers is a Consulting IT Spec
- Page 16 and 17:
xiv ABCs of z/OS System Programming
- Page 18 and 19:
1.1 Introduction to DFSMS IBM 3494
- Page 20 and 21:
Network File System The Network Fil
- Page 22 and 23:
Using access methods, commands, and
- Page 24 and 25:
Distributed data management DFSMSds
- Page 26 and 27:
Shelf management DFSMSrmm groups in
- Page 28 and 29:
Availability management DFSMShsm ba
- Page 30 and 31:
key functions that enable multiple
- Page 32 and 33:
An access method is a DFSMSdfp comp
- Page 34 and 35:
including the operating system itse
- Page 36 and 37:
2.3 DFSMSdfp data set types Data se
- Page 38 and 39:
2.4 Types of VSAM data sets Types o
- Page 40 and 41:
Partitioned data set (PDS) Partitio
- Page 42 and 43:
► Extended-addressability, which
- Page 44 and 45:
method writes data on the first vol
- Page 46 and 47:
SMS calculates the average preferen
- Page 48 and 49:
Restriction: The following types of
- Page 50 and 51:
► REXX LISTDSI function ► CLIST
- Page 52 and 53:
Using CLIST OPENFILE INPUT/GETFILE
- Page 54 and 55:
2.12 z/OS UNIX files Following are
- Page 56 and 57:
Logical records and blocks To an ap
- Page 58 and 59:
2.14 Locating an existing data set
- Page 60 and 61:
2.15 Uncataloged and cataloged data
- Page 62 and 63:
2.17 VTOC and DSCBs VTOC DSCBs Figu
- Page 64 and 65:
2.18 VTOC index structure VOLUME LA
- Page 66 and 67:
2.19 Initializing a volume using IC
- Page 68 and 69:
52 ABCs of z/OS System Programming
- Page 70 and 71:
3.1 Traditional DASD capacity 885 C
- Page 72 and 73:
Large volume support design conside
- Page 74 and 75:
DASD virtual visibility Traditional
- Page 76 and 77:
3.4 WLM controlling PAVs zSeries WL
- Page 78 and 79:
3.5 Parallel Access Volumes (PAVs)
- Page 80 and 81:
3.6 HyperPAV feature for DS8000 ser
- Page 82 and 83:
For each z/OS image within the sysp
- Page 84 and 85:
Note: With the 3390 Model A, the mo
- Page 86 and 87:
Note the following points regarding
- Page 88 and 89:
EAS non-eligible data sets An EAS-i
- Page 90 and 91:
same as for previous 3390 model dev
- Page 92 and 93:
3.13 Using dynamic volume expansion
- Page 94 and 95:
3.15 Using Web browser GUI Need a U
- Page 96 and 97:
3.17 Increase capacity of volumes F
- Page 98 and 99:
3.19 Final capacity increase for vo
- Page 100 and 101:
VTOC index changes The index block
- Page 102 and 103:
The documentation is in Device Supp
- Page 104 and 105:
free space available following the
- Page 106 and 107:
Note: The refresh of the index occu
- Page 108 and 109:
Updating the VTOC following volume
- Page 110 and 111:
USEEAV(YES|NO) YES This means that
- Page 112 and 113:
Generally, for VSAM data set alloca
- Page 114 and 115:
attributes can reside in the extend
- Page 116 and 117:
Other methods for EATTR specificati
- Page 118 and 119:
3.30 Migration assistance tracker T
- Page 120 and 121:
3.31 Migration tracker commands SET
- Page 122 and 123:
106 ABCs of z/OS System Programming
- Page 124 and 125:
4.1 Overview of DFSMSdfp utilities
- Page 126 and 127:
4.2 IEBCOMPR utility Example 1 Exam
- Page 128 and 129: 4.3 IEBCOPY utility //COPY JOB ...
- Page 130 and 131: 4.4 IEBCOPY: Copy operation DATA.SE
- Page 132 and 133: 4.5 IEBCOPY: Compress operation DAT
- Page 134 and 135: Copying to z/OS UNIX IEBGENER can b
- Page 136 and 137: 4.8 IEBGENER: Copying data to tape
- Page 138 and 139: 4.10 IEHLIST LISTVTOC output CONTEN
- Page 140 and 141: Examples of IEHINITT In the example
- Page 142 and 143: 4.13 DFSMSdfp access methods DFSMSd
- Page 144 and 145: physical blocks. QSAM also guarante
- Page 146 and 147: The automatic class selection (ACS)
- Page 148 and 149: Command Functions DEFINE PAGESPACE
- Page 150 and 151: Note: These commands cannot be used
- Page 152 and 153: ► Capacity planning: Capacity pla
- Page 154 and 155: A GDS has sequentially ordered abso
- Page 156 and 157: The parameters are: NAME This speci
- Page 158 and 159: 4.21 Relative generation numbers A.
- Page 160 and 161: 4.23 PDS data set organization Adva
- Page 162 and 163: 4.24 Partitioned data set extended
- Page 164 and 165: 4.25 PDSE enhancements PDSE, two ad
- Page 166 and 167: 4.26 PDSE: Conversion Using DFSMSds
- Page 168 and 169: 4.27 Program objects in a PDSE Func
- Page 170 and 171: 4.28 Sequential access methods Sequ
- Page 172 and 173: 4.29 z/OS V1R9 QSAM - BSAM enhancem
- Page 174 and 175: 4.30 Virtual storage access method
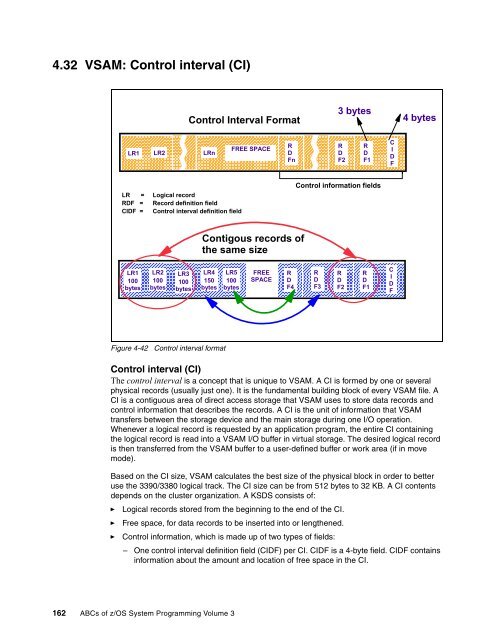
- Page 176 and 177: 4.31 VSAM terminology Logical recor
- Page 180 and 181: 4.33 VSAM data set components Clust
- Page 182 and 183: 4.34 VSAM key sequenced cluster (KS
- Page 184 and 185: The sequence is as follows: 1. VSAM
- Page 186 and 187: 4.37 VSAM: Typical ESDS processing
- Page 188 and 189: 4.39 VSAM: Typical RRDS processing
- Page 190 and 191: 4.41 VSAM: Data-in-virtual (DIV) DI
- Page 192 and 193: 4.43 VSAM resource pool VSAM resour
- Page 194 and 195: ► CIs are discarded as soon as th
- Page 196 and 197: SMB processing techniques If all of
- Page 198 and 199: MSG=SMBBIAS When you specify MSG =
- Page 200 and 201: 4.47 VSAM SMB enhancement with z/OS
- Page 202 and 203: 4.48 VSAM enhancements Data compres
- Page 204 and 205: 4.50 Data set separation syntax Dat
- Page 206 and 207: 4.51 Data facility sort (DFSORT) Pa
- Page 208 and 209: 4.52 z/OS Network File System (z/OS
- Page 210 and 211: 4.53 DFSMS optimizer (DFSMSopt) Fig
- Page 212 and 213: 4.54 Data Set Services (DFSMSdss) /
- Page 214 and 215: 4.55 DFSMSdss: Physical and logical
- Page 216 and 217: When to use logical processing Use
- Page 218 and 219: When to use physical processing Use
- Page 220 and 221: 4.59 Hierarchical Storage Manager (
- Page 222 and 223: Tasks for availability management f
- Page 224 and 225: - Release of unused, over-allocated
- Page 226 and 227: usually slower response time. Usual
- Page 228 and 229:
DATASSETSIZE(dssize) This specifies
- Page 230 and 231:
► Utilize OVERFLOW volumes for mi
- Page 232 and 233:
Before automatic secondary space ma
- Page 234 and 235:
For data sets larger than 58 K trac
- Page 236 and 237:
► Migration level 1 (ML1) volumes
- Page 238 and 239:
222 ABCs of z/OS System Programming
- Page 240 and 241:
value of a user-specified RETPD or
- Page 242 and 243:
The second-newest version is treate
- Page 244 and 245:
If the version has a specified rete
- Page 246 and 247:
ACS routines For both automatic and
- Page 248 and 249:
- System-managed automated tape lib
- Page 250 and 251:
4.75 What DFSMSrmm can manage Remov
- Page 252 and 253:
You can also use the DFSMSrmm built
- Page 254 and 255:
z/OS V1R8 enhancements DFSMSrmm hel
- Page 256 and 257:
5.1 Storage management ISMF dss Fig
- Page 258 and 259:
5.3 Goals and benefits of system-ma
- Page 260 and 261:
Improved data availability manageme
- Page 262 and 263:
► Whether data sets are to be kep
- Page 264 and 265:
When the ACS routines are started a
- Page 266 and 267:
5.7 Assigning data to be system-man
- Page 268 and 269:
Even though data class is optional,
- Page 270 and 271:
You can use the ACCESSIBILITY attri
- Page 272 and 273:
If you do not explicitly assign a m
- Page 274 and 275:
5.12 Using storage groups DFSMShsm-
- Page 276 and 277:
5.13 Using aggregate backup and rec
- Page 278 and 279:
5.14 Automatic Class Selection (ACS
- Page 280 and 281:
5.15 SMS configuration An SMS confi
- Page 282 and 283:
5.16 SMS control data sets SMS Figu
- Page 284 and 285:
5.17 Implementing DFSMS Enabling th
- Page 286 and 287:
► Gain experience with the operat
- Page 288 and 289:
Specify SHAREOPTIONS(3,3) for the A
- Page 290 and 291:
Defining the SMS base configuration
- Page 292 and 293:
5.21 Creating ACS routines Storage
- Page 294 and 295:
5.22 DFSMS setup for z/OS IEASYSxx
- Page 296 and 297:
5.23 Starting SMS and activating a
- Page 298 and 299:
5.24 Control SMS processing with op
- Page 300 and 301:
5.25 Displaying the SMS configurati
- Page 302 and 303:
exception. If it is clear that a PD
- Page 304 and 305:
sets (see Figure 5-27 on page 287).
- Page 306 and 307:
Using a high level qualifier (HLQ)
- Page 308 and 309:
5.30 Establishing installation stan
- Page 310 and 311:
5.32 Data class attributes Data cla
- Page 312 and 313:
5.34 Simplifying JCL use Figure 5-3
- Page 314 and 315:
► The AVGREC attribute indicates
- Page 316 and 317:
Considerations when specifying spac
- Page 318 and 319:
5.38 SMS PDSE support SMS PDSE supp
- Page 320 and 321:
5.40 Allocating new PDSEs //ALLOC E
- Page 322 and 323:
Production batch refers to data cre
- Page 324 and 325:
tape are stored as a tape data set
- Page 326 and 327:
5.44 ISMF: Product relationships IS
- Page 328 and 329:
5.45 ISMF: What you can do with ISM
- Page 330 and 331:
5.46 ISMF: Accessing ISMF Panel Hel
- Page 332 and 333:
5.48 ISMF: Obtaining information ab
- Page 334 and 335:
5.49 ISMF: Data set option Figure 5
- Page 336 and 337:
5.51 ISMF: Management Class option
- Page 338 and 339:
5.53 ISMF: Storage Class option Fig
- Page 340 and 341:
324 ABCs of z/OS System Programming
- Page 342 and 343:
6.1 Catalogs ICF structure 1 ICF st
- Page 344 and 345:
6.2 The basic catalog structure (BC
- Page 346 and 347:
6.3 The VSAM volume data set (VVDS)
- Page 348 and 349:
6.4 Catalogs by function SYSCAT VOL
- Page 350 and 351:
User catalogs The difference betwee
- Page 352 and 353:
Multilevel aliases You can augment
- Page 354 and 355:
Defining a cataloged data set When
- Page 356 and 357:
The example in Figure 6-9 on page 3
- Page 358 and 359:
6.8 Using multiple catalogs CATALOG
- Page 360 and 361:
If you need to share data sets acro
- Page 362 and 363:
► List a user catalog connector i
- Page 364 and 365:
Note: When you delete a data set, t
- Page 366 and 367:
DELET6 JOB ... //STEP1 EXEC PGM=IDC
- Page 368 and 369:
Note: The command will result in er
- Page 370 and 371:
You can later recover the backup co
- Page 372 and 373:
Aliases to the catalog can be defin
- Page 374 and 375:
► Physical errors The records on
- Page 376 and 377:
Because APF authorization is establ
- Page 378 and 379:
3. Use EXAMINE and DIAGNOSE to ensu
- Page 380 and 381:
5. Use REPRO MERGECAT to split the
- Page 382 and 383:
The two types of buffer are used to
- Page 384 and 385:
Catalog report output This MODIFY c
- Page 386 and 387:
Restarting the catalog address spac
- Page 388 and 389:
► MODIFY CATALOG,LIST The LIST co
- Page 390 and 391:
Recover from performance slow downs
- Page 392 and 393:
2. Define or alter your existing ca
- Page 394 and 395:
7.1 VSAM share options Share option
- Page 396 and 397:
7.2 Base VSAM buffering Three types
- Page 398 and 399:
7.3 Base VSAM locking Figure 7-3 Ex
- Page 400 and 401:
7.5 VSAM record-level sharing intro
- Page 402 and 403:
► Non-CICS jobs can have read-onl
- Page 404 and 405:
7.8 Buffering under VSAM RLS CICS R
- Page 406 and 407:
7.9 VSAM RLS locking control interv
- Page 408 and 409:
7.10 VSAM RLS/CICS data set recover
- Page 410 and 411:
7.11 Transactional recovery Commite
- Page 412 and 413:
7.13 VSAM RLS implementation Update
- Page 414 and 415:
Cache structures Coupling Facility
- Page 416 and 417:
7.15 Update PARMLIB with VSAM RLS p
- Page 418 and 419:
7.16 Define sharing control data se
- Page 420 and 421:
Tip: Place the SHCDSs on separate v
- Page 422 and 423:
Command ===> Figure 7-22 CF cache u
- Page 424 and 425:
7.18 Update data sets with log para
- Page 426 and 427:
7.19 The SMSVSAM address space RLS
- Page 428 and 429:
7.20 Interacting with VSAM RLS Inte
- Page 430 and 431:
To learn about other DISPLAY comman
- Page 432 and 433:
to use this specification or the sp
- Page 434 and 435:
► RECOVERY REQUIRED This field in
- Page 436 and 437:
DFSMStvs is a follow-on project/cap
- Page 438 and 439:
Like CICS, DFSMStvs does not perfor
- Page 440 and 441:
It is RRS that provides the means t
- Page 442 and 443:
7.27 Unit of work and unit of recov
- Page 444 and 445:
► Log of logs (optional, shared w
- Page 446 and 447:
7.30 Application considerations Bre
- Page 448 and 449:
7.31 DFSMStvs logging implementatio
- Page 450 and 451:
LABEL JOB ... //STEP10 EXEC PGM=IXC
- Page 452 and 453:
7.33 Update PARMLIB with DFSMStvs p
- Page 454 and 455:
7.34 The DFSMStvs instance CICSA R/
- Page 456 and 457:
Changes to parameters other than AK
- Page 458 and 459:
7.36 Summary Figure 7-48 Summary Ba
- Page 460 and 461:
444 ABCs of z/OS System Programming
- Page 462 and 463:
8.1 Overview of DASD types Traditio
- Page 464 and 465:
8.2 Redundant array of independent
- Page 466 and 467:
8.3 Seascape architecture Powerful
- Page 468 and 469:
► Data copy sharing Data copy sha
- Page 470 and 471:
NVS cache NVS is used to store a se
- Page 472 and 473:
8.6 ESS major components Figure 8-6
- Page 474 and 475:
8.8 FICON host adapters FICON host
- Page 476 and 477:
8.9 ESS disks Eight-packs Set of 8
- Page 478 and 479:
8.10 ESS device adapters SSA 160 De
- Page 480 and 481:
8.11 SSA loops SSA operation 4 link
- Page 482 and 483:
8.12 RAID-10 RAID-10 configurations
- Page 484 and 485:
8.13 Storage balancing with RAID-10
- Page 486 and 487:
Peer-to-peer remote copy (PPRC) PPR
- Page 488 and 489:
8.15 ESS performance features Prior
- Page 490 and 491:
8.16 IBM TotalStorage DS6000 Enterp
- Page 492 and 493:
DS6000 expansion enclosure (Model 1
- Page 494 and 495:
support for one or two expansion fr
- Page 496 and 497:
The DS8300 models can support eithe
- Page 498 and 499:
consolidations where separate stora
- Page 500 and 501:
Copy Services include the following
- Page 502 and 503:
TotalStorage Expert helps storage a
- Page 504 and 505:
identifying the data set and descri
- Page 506 and 507:
Table 8-4 Types of labels Code Mean
- Page 508 and 509:
equired. Therefore, the resulting t
- Page 510 and 511:
Drive designed for automation solut
- Page 512 and 513:
3494 models and features IBM 3494 o
- Page 514 and 515:
Each FICON channel in the VTS can s
- Page 516 and 517:
In addition to the 3494 VTS compone
- Page 518 and 519:
► Consolidation Another benefit i
- Page 520 and 521:
Online resources ► z/OS DFSMShsm
- Page 522:
ABCs of z/OS System Programming Vol