Max Planck Institute for Astronomy - Annual Report 2005
Max Planck Institute for Astronomy - Annual Report 2005
Max Planck Institute for Astronomy - Annual Report 2005
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
(TFT) of the Canadian Space Agency is much more sensitive<br />
than NirCaM and thus will be able to faster turn<br />
the attention to very young galaxies with their highly<br />
redshifted Lyman-alpha-lines.<br />
Common to the three focal-plane instruments <strong>for</strong><br />
JWST presented above is that they have to be operated<br />
in a cryo-vacuum. For NirCaM and NirSpeC a temperature<br />
of – 240 °C suffices. Miri has to be cooled to below<br />
– 260 °C so that its own thermal emission will not outshine<br />
the cosmic infrared radiation. Miri’s infrared detectors<br />
have to be operated at – 268 °C, only 5 °C above absolute<br />
zero, in order to keep the »dark current« of the camera<br />
sufficiently low. Another common property of the instruments<br />
is that all of them have large »optical exchange<br />
additional<br />
pin<br />
electrical subassembly<br />
including the motor<br />
ratchet<br />
assembly<br />
support<br />
structure<br />
ring with 6 flexural<br />
rods<br />
index bearings<br />
ratchet<br />
subassembly<br />
filter wheel subassembly<br />
(with optical elements)<br />
IV.1 Instruments <strong>for</strong> the James Webb Space Telescope 91<br />
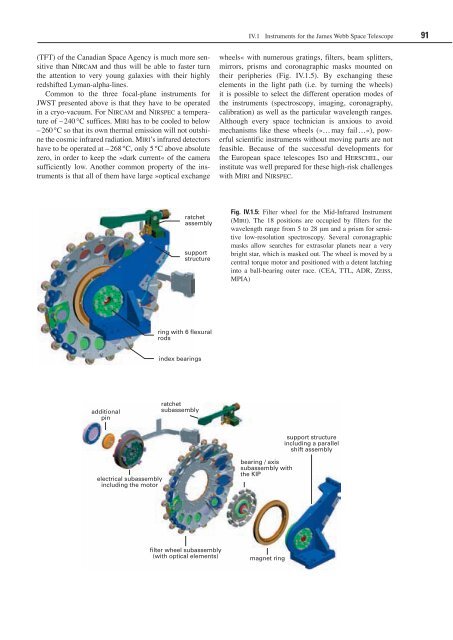
wheels« with numerous gratings, filters, beam splitters,<br />
mirrors, prisms and coronagraphic masks mounted on<br />
their peripheries (Fig. IV.1.5). By exchanging these<br />
elements in the light path (i.e. by turning the wheels)<br />
it is possible to select the different operation modes of<br />
the instruments (spectroscopy, imaging, coronagraphy,<br />
calibration) as well as the particular wavelength ranges.<br />
Although every space technician is anxious to avoid<br />
mechanisms like these wheels (»… may fail …«), powerful<br />
scientific instruments without moving parts are not<br />
feasible. Because of the successful developments <strong>for</strong><br />
the European space telescopes iSo and HerSCHel, our<br />
institute was well prepared <strong>for</strong> these high-risk challenges<br />
with Miri and NirSpeC.<br />
Fig. IV.1.5: Filter wheel <strong>for</strong> the Mid-Infrared Instrument<br />
(Miri). The 18 positions are occupied by filters <strong>for</strong> the<br />
wavelength range from 5 to 28 µm and a prism <strong>for</strong> sensitive<br />
low-resolution spectroscopy. Several coronagraphic<br />
masks allow searches <strong>for</strong> extrasolar planets near a very<br />
bright star, which is masked out. The wheel is moved by a<br />
central torque motor and positioned with a detent latching<br />
into a ball-bearing outer race. (CEA, TTL, ADR, ZeiSS,<br />
MPIA)<br />
bearing / axis<br />
subassembly with<br />
the KIP<br />
magnet ring<br />
support structure<br />
including a parallel<br />
shift assembly