Self-Assembly of Synthetic and Biological Polymeric Systems of ...
Self-Assembly of Synthetic and Biological Polymeric Systems of ...
Self-Assembly of Synthetic and Biological Polymeric Systems of ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
10526 J. Phys. Chem. B, Vol. 113, No. 30, 2009 Juárez et al.<br />
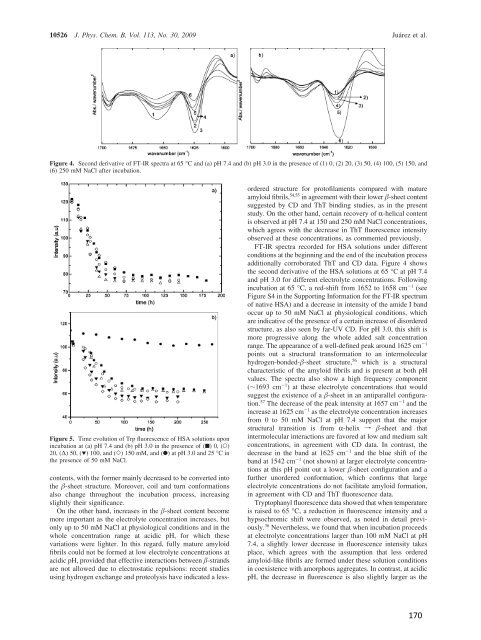
Figure 4. Second derivative <strong>of</strong> FT-IR spectra at 65 °C <strong>and</strong> (a) pH 7.4 <strong>and</strong> (b) pH 3.0 in the presence <strong>of</strong> (1) 0, (2) 20, (3) 50, (4) 100, (5) 150, <strong>and</strong><br />
(6) 250 mM NaCl after incubation.<br />
Figure 5. Time evolution <strong>of</strong> Trp fluorescence <strong>of</strong> HSA solutions upon<br />
incubation at (a) pH 7.4 <strong>and</strong> (b) pH 3.0 in the presence <strong>of</strong> (9) 0,(O)<br />
20, (∆) 50, (1) 100, <strong>and</strong> (]) 150 mM, <strong>and</strong> (b) at pH 3.0 <strong>and</strong> 25 °C in<br />
the presence <strong>of</strong> 50 mM NaCl.<br />
contents, with the former mainly decreased to be converted into<br />
the -sheet structure. Moreover, coil <strong>and</strong> turn conformations<br />
also change throughout the incubation process, increasing<br />
slightly their significance.<br />
On the other h<strong>and</strong>, increases in the -sheet content become<br />
more important as the electrolyte concentration increases, but<br />
only up to 50 mM NaCl at physiological conditions <strong>and</strong> in the<br />
whole concentration range at acidic pH, for which these<br />
variations were lighter. In this regard, fully mature amyloid<br />
fibrils could not be formed at low electrolyte concentrations at<br />
acidic pH, provided that effective interactions between -str<strong>and</strong>s<br />
are not allowed due to electrostatic repulsions: recent studies<br />
using hydrogen exchange <strong>and</strong> proteolysis have indicated a less-<br />
ordered structure for prot<strong>of</strong>ilaments compared with mature<br />
amyloid fibrils, 54,55 in agreement with their lower -sheet content<br />
suggested by CD <strong>and</strong> ThT binding studies, as in the present<br />
study. On the other h<strong>and</strong>, certain recovery <strong>of</strong> R-helical content<br />
is observed at pH 7.4 at 150 <strong>and</strong> 250 mM NaCl concentrations,<br />
which agrees with the decrease in ThT fluorescence intensity<br />
observed at these concentrations, as commented previously.<br />
FT-IR spectra recorded for HSA solutions under different<br />
conditions at the beginning <strong>and</strong> the end <strong>of</strong> the incubation process<br />
additionally corroborated ThT <strong>and</strong> CD data. Figure 4 shows<br />
the second derivative <strong>of</strong> the HSA solutions at 65 °C atpH7.4<br />
<strong>and</strong> pH 3.0 for different electrolyte concentrations. Following<br />
incubation at 65 °C, a red-shift from 1652 to 1658 cm -1 (see<br />
Figure S4 in the Supporting Information for the FT-IR spectrum<br />
<strong>of</strong> native HSA) <strong>and</strong> a decrease in intensity <strong>of</strong> the amide I b<strong>and</strong><br />
occur up to 50 mM NaCl at physiological conditions, which<br />
are indicative <strong>of</strong> the presence <strong>of</strong> a certain increase <strong>of</strong> disordered<br />
structure, as also seen by far-UV CD. For pH 3.0, this shift is<br />
more progressive along the whole added salt concentration<br />
range. The appearance <strong>of</strong> a well-defined peak around 1625 cm -1<br />
points out a structural transformation to an intermolecular<br />
hydrogen-bonded--sheet structure, 56 which is a structural<br />
characteristic <strong>of</strong> the amyloid fibrils <strong>and</strong> is present at both pH<br />
values. The spectra also show a high frequency component<br />
(∼1693 cm -1 ) at these electrolyte concentrations that would<br />
suggest the existence <strong>of</strong> a -sheet in an antiparallel configuration.<br />
57 The decrease <strong>of</strong> the peak intensity at 1657 cm -1 <strong>and</strong> the<br />
increase at 1625 cm -1 as the electrolyte concentration increases<br />
from 0 to 50 mM NaCl at pH 7.4 support that the major<br />
structural transition is from R-helix f -sheet <strong>and</strong> that<br />
intermolecular interactions are favored at low <strong>and</strong> medium salt<br />
concentrations, in agreement with CD data. In contrast, the<br />
decrease in the b<strong>and</strong> at 1625 cm -1 <strong>and</strong> the blue shift <strong>of</strong> the<br />
b<strong>and</strong> at 1542 cm -1 (not shown) at larger electrolyte concentrations<br />
at this pH point out a lower -sheet configuration <strong>and</strong> a<br />
further unordered conformation, which confirms that large<br />
electrolyte concentrations do not facilitate amyloid formation,<br />
in agreement with CD <strong>and</strong> ThT fluorescence data.<br />
Tryptophanyl fluorescence data showed that when temperature<br />
is raised to 65 °C, a reduction in fluorescence intensity <strong>and</strong> a<br />
hypsochromic shift were observed, as noted in detail previously.<br />
36 Nevertheless, we found that when incubation proceeds<br />
at electrolyte concentrations larger than 100 mM NaCl at pH<br />
7.4, a slightly lower decrease in fluorescence intensity takes<br />
place, which agrees with the assumption that less ordered<br />
amyloid-like fibrils are formed under these solution conditions<br />
in coexistence with amorphous aggregates. In contrast, at acidic<br />
pH, the decrease in fluorescence is also slightly larger as the<br />
170