- Page 1 and 2:
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA Los Angele
- Page 3 and 4:
TABLE OF CONTENTS LIST OF FIGURES .
- Page 5 and 6:
3.3.2.4 Final subjects and right di
- Page 7 and 8:
LIST OF FIGURES Figure 1. Location
- Page 9 and 10:
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS .intrans intr
- Page 11 and 12:
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS There are many peo
- Page 13 and 14:
Marshallese teachers in Majuro: Isa
- Page 15 and 16:
VITA October 29, 1974 Born, Mesa, A
- Page 17 and 18:
ABSTRACT OF THE DISSERTATION Subjec
- Page 19 and 20:
Chapter 1. Introduction Why study l
- Page 21 and 22:
Figure 1. Location of the Republic
- Page 23 and 24:
their late childhood years. All con
- Page 25 and 26:
fewer then 10,000 speakers. These l
- Page 27 and 28:
phonological and information status
- Page 29 and 30:
three secondary places of articulat
- Page 31 and 32:
Table 5. Marshallese diphthongs (ad
- Page 33 and 34:
showing the orthography used by the
- Page 35 and 36:
Demonstratives also have a human/no
- Page 37 and 38:
(11) E-ar den#ōt ladik ro. E-ar de
- Page 39 and 40:
languages, in which "a disjunctive
- Page 41 and 42:
(30) a. Mary e-kar lotak ilo Namori
- Page 43 and 44:
2.2.5 Adjectives 6 Marshallese has
- Page 45 and 46:
When ka- prefixes to an intransitiv
- Page 47 and 48:
In examples containing the causativ
- Page 49 and 50:
However, this verb is more complica
- Page 51 and 52:
When the verb contains a high vowel
- Page 53 and 54:
(64) Oror eo, piik eo e-ar kokkure.
- Page 55 and 56:
(70) ar 'toward the lagoon side' ā
- Page 57 and 58:
intransitive or transitive form (if
- Page 59 and 60:
Ungrammatical examples, in which th
- Page 61 and 62:
2.2.6.4.5 Underlyingly transitive -
- Page 63 and 64:
(94) intransitive transitive Englis
- Page 65 and 66:
(100) I-lukkuun kōnaan eon#ōd ek.
- Page 67 and 68:
(104) Noun Verb Source at 'hat' ata
- Page 69 and 70:
an 'won't', negative future. (109)
- Page 71 and 72:
There is also an adverb that relate
- Page 73 and 74: . *Kw-ar le ke lok mōn#ā eo n#an
- Page 75 and 76: morphemes are possible. Based on th
- Page 77 and 78: (141) Laddik nana eo e-ar etal im k
- Page 79 and 80: In addition to the standard relativ
- Page 81 and 82: (153) Leddik eo e-ar koot-e būruo-
- Page 83 and 84: Table 12. Possessive classifiers 13
- Page 85 and 86: (165) Bōlen i-naaj wia a-n Mary ju
- Page 87 and 88: 2.3.3.1 Verbless sentences There is
- Page 89 and 90: 2.3.3.2 Sentences with overt verbs
- Page 91 and 92: (188) Ritti bwebwenato eo mokta ipp
- Page 93 and 94: (198) *Ke John e-j kōnono ippā-n
- Page 95 and 96: (205) a. I-jaje e-j ke ka-ire kaula
- Page 97 and 98: ta 'what' (210) a. Ta ko kidu ko re
- Page 99 and 100: with a plural agreement clitic (220
- Page 101 and 102: 2.3.4.2.3.3 Class 3 There are also
- Page 103 and 104: 2.3.4.2.5 Resumptive elements With
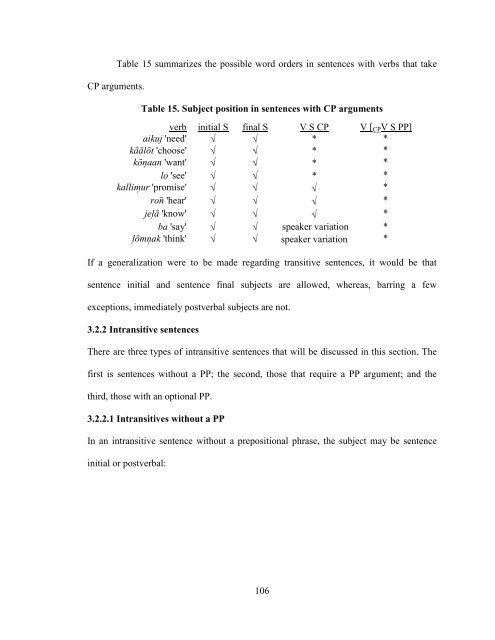
- Page 105 and 106: equired in an indirect wh- question
- Page 107 and 108: . Mary e-ar ron# n#āāt eo Jikko e
- Page 109 and 110: 3.1 Introduction Chapter 3. Basic W
- Page 111 and 112: sentence final This term refers to
- Page 113 and 114: have right dislocated subjects. I w
- Page 115 and 116: But it is possible for the PP argum
- Page 117 and 118: First, the subject may be sentence
- Page 119 and 120: The generalization for those transi
- Page 121 and 122: *V S CP b.*E-kōnaan pastō eo bwe
- Page 123: V S CP b. E-ar jelā kōrā eo bwe
- Page 127 and 128: V PP S (293) Re-j kōnono ippā-n l
- Page 129 and 130: This sentence includes a pause of a
- Page 131 and 132: Sentences with internal subjects la
- Page 133 and 134: Right dislocation refers to a proce
- Page 135 and 136: (272) Rej bōkĜok bwiro ko [pause]
- Page 137 and 138: Gundel (1974) and Chafe (1976, 1987
- Page 139 and 140: 3.3.2.2 Indefinites A second diagno
- Page 141 and 142: If we first investigate whether the
- Page 143 and 144: The second context in which these s
- Page 145 and 146: information status of internal subj
- Page 147 and 148: Mokilese also allows variable word
- Page 149 and 150: (329) a. Mwet sac arulac puhlaik. p
- Page 151 and 152: Chapter 4. The Structure of Marshal
- Page 153 and 154: V S (289) b. E-ju ni eo. 3s.agr-be.
- Page 155 and 156: (339) a. Bilal e-naaj ke etal n#an
- Page 157 and 158: (347) a. Kidu eo e-kar kōpl-e. dog
- Page 159 and 160: 4.1.2 Adverbs and the negative Anot
- Page 161 and 162: When combined with constituency evi
- Page 163 and 164: such as wh- or focus movement. Sinc
- Page 165 and 166: (364) AgrSP prom AgrS e 3s AgrS' T
- Page 167 and 168: (367) a. R-ar bar unojidrikdrik kō
- Page 169 and 170: correct, as illustrated by the fact
- Page 171 and 172: Bajjek must precede the internal su
- Page 173 and 174: vP coordination; and across the boa
- Page 175 and 176:
In order for this to be the correct
- Page 177 and 178:
(384) AgrSP AgrS e 3s AgrS' T 4.2.5
- Page 179 and 180:
features. Therefore, if the subject
- Page 181 and 182:
position higher in the structure th
- Page 183 and 184:
Given this ordering, if bar precede
- Page 185 and 186:
(398) a. Li individuano facilmente,
- Page 187 and 188:
(401) [R-ar tutu i ar] im [r-ar eon
- Page 189 and 190:
(409) R-ar tutu [i lik leddik ro] i
- Page 191 and 192:
However, there are two flaws with t
- Page 193 and 194:
phonological pattern seems to be on
- Page 195 and 196:
(415) AgrSPm tl AgrS r 3pl AgrS' Vj
- Page 197 and 198:
4.4 The structure of sentences with
- Page 199 and 200:
*V S O PP (423) [FocP [AgrSP [AccP
- Page 201 and 202:
Table 19. Subject position with CP
- Page 203 and 204:
specifier of the verb phrase. If th
- Page 205 and 206:
But there are no sentence modifying
- Page 207 and 208:
5.1 Introduction Chapter 5. Passive
- Page 209 and 210:
words, how do we really know that M
- Page 211 and 212:
intransitive form of the verb. Alte
- Page 213 and 214:
(444) a. R-ar lemelm jaki ko ilo mw
- Page 215 and 216:
(452) Ilo manit in Majel, leddik re
- Page 217 and 218:
Agent phrases headed by these three
- Page 219 and 220:
(462) *Nuknuk eo a-ō e-būrōrō i
- Page 221 and 222:
(469) a. Mon wia eo e-ar etal. plac
- Page 223 and 224:
c. *Irooj ro r-ar bōnbōn in leroo
- Page 225 and 226:
the stative form. For example, jebj
- Page 227 and 228:
Stative sentences also allow postve
- Page 229 and 230:
. E-abwinmake likao eo jān jine-n.
- Page 231 and 232:
c. *Leddik eo e-kar den#den# in lad
- Page 233 and 234:
Instead, Collins proposes the struc
- Page 235 and 236:
(514) This structure also includes
- Page 237 and 238:
(515) DPj amimōno ko 'the handcraf
- Page 239 and 240:
5.5.2 Sentences internal subjects a
- Page 241 and 242:
(518) In passives, the VP must move
- Page 243 and 244:
(519) AgrSP AgrS r 3pl In accordanc
- Page 245 and 246:
But in a sentence containing an ipp
- Page 247 and 248:
5.7 Summary In this chapter, I have
- Page 249 and 250:
verbs have two important properties
- Page 251 and 252:
The data presented in Table 21 show
- Page 253 and 254:
(532) c. *Kōrā ro r-ar lōmnak in
- Page 255 and 256:
Despite appearing to occupy the sam
- Page 257 and 258:
It is difficult to distinguish betw
- Page 259 and 260:
(551) a. Ri-jerakrōk ro r-ar i-tok
- Page 261 and 262:
6.5.2 Monoclausal infinitives - typ
- Page 263 and 264:
The subject may also be sentence fi
- Page 265 and 266:
(572) Kweilok eo e-ar ijjino in Wat
- Page 267 and 268:
(578) a. *E-ar kajjion# taktō eo i
- Page 269 and 270:
Wurmbrand shows that, in the case o
- Page 271 and 272:
difficulty articulating the differe
- Page 273 and 274:
However, dummy subject are not poss
- Page 275 and 276:
(601) AgrSP AgrS e 3s AgrS' TP T Th
- Page 277 and 278:
(604) DPj jaki ko 'the mats' AgrSP
- Page 279 and 280:
and incorporates with Voice. Thus a
- Page 281 and 282:
others. The behavior of the differe
- Page 283 and 284:
verbs that moved to X, we would exp
- Page 285 and 286:
internal, then the movement of the
- Page 287 and 288:
Chapter 7. Conclusions and Discussi
- Page 289 and 290:
References Abo, Takaji, Byron W. Be
- Page 291 and 292:
Chomsky, Noam. 2000. Minimalist Inq
- Page 293 and 294:
Kayne, Richard S. 1994. The Antisym
- Page 295 and 296:
Rizzi, Luigi. 2001. On the position