Gasoline Price Changes - Federal Trade Commission
Gasoline Price Changes - Federal Trade Commission
Gasoline Price Changes - Federal Trade Commission
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
THE DYNAMIC OF SUPPLY, DEMAND, AND COMPETITION<br />
from either West Coast refineries through a pipeline or other terminals by truck – both at higher<br />
cost. 14<br />
F. Effects on <strong>Gasoline</strong> <strong>Price</strong>s in Phoenix, Tucson, and Other Parts of Arizona,<br />
and on the West Coast.<br />
The <strong>Commission</strong>’s <strong>Gasoline</strong> <strong>Price</strong> Monitoring project captured the impact of these events<br />
on gasoline prices in Phoenix, Tucson, and other parts of Arizona, as well as California,<br />
Washington, and Oregon.<br />
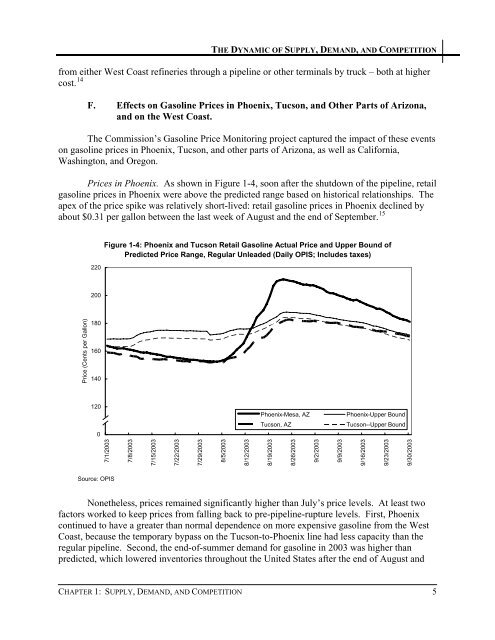
<strong>Price</strong>s in Phoenix. As shown in Figure 1-4, soon after the shutdown of the pipeline, retail<br />
gasoline prices in Phoenix were above the predicted range based on historical relationships. The<br />
apex of the price spike was relatively short-lived: retail gasoline prices in Phoenix declined by<br />
about $0.31 per gallon between the last week of August and the end of September. 15<br />
<strong>Price</strong> (Cents per Gallon)<br />
220<br />
200<br />
180<br />
160<br />
140<br />
120<br />
100 0<br />
7/1/2003<br />
Source: OPIS<br />
Figure 1-4: Phoenix and Tucson Retail <strong>Gasoline</strong> Actual <strong>Price</strong> and Upper Bound of<br />
Predicted <strong>Price</strong> Range, Regular Unleaded (Daily OPIS; Includes taxes)<br />
7/8/2003<br />
7/15/2003<br />
7/22/2003<br />
7/29/2003<br />
8/5/2003<br />
8/12/2003<br />
Phoenix-Mesa, AZ Phoenix-Upper Bound<br />
Tucson, AZ Tucson--Upper Bound<br />
Nonetheless, prices remained significantly higher than July’s price levels. At least two<br />
factors worked to keep prices from falling back to pre-pipeline-rupture levels. First, Phoenix<br />
continued to have a greater than normal dependence on more expensive gasoline from the West<br />
Coast, because the temporary bypass on the Tucson-to-Phoenix line had less capacity than the<br />
regular pipeline. Second, the end-of-summer demand for gasoline in 2003 was higher than<br />
predicted, which lowered inventories throughout the United States after the end of August and<br />
CHAPTER 1: SUPPLY, DEMAND, AND COMPETITION 5<br />
8/19/2003<br />
8/26/2003<br />
9/2/2003<br />
9/9/2003<br />
9/16/2003<br />
9/23/2003<br />
9/30/2003