Soins maternels intensifs (Maternal Intensive Care) en Belgique - KCE
Soins maternels intensifs (Maternal Intensive Care) en Belgique - KCE
Soins maternels intensifs (Maternal Intensive Care) en Belgique - KCE
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
146 <strong>Maternal</strong> <strong>Int<strong>en</strong>sive</strong> <strong>Care</strong> in Belgium <strong>KCE</strong> Reports 94<br />
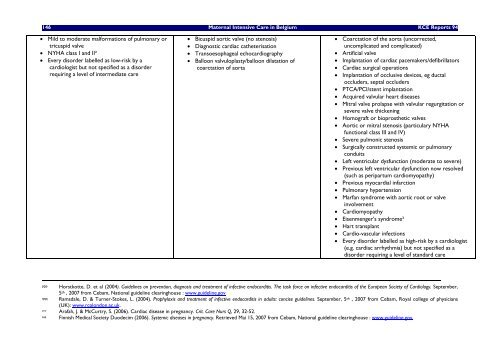
• Mild to moderate malformations of pulmonary or<br />
tricuspid valve<br />
• NYHA class I and II²<br />
• Every disorder labelled as low-risk by a<br />
cardiologist but not specified as a disorder<br />
requiring a level of intermediate care<br />
• Bicuspid aortic valve (no st<strong>en</strong>osis)<br />
• Diagnostic cardiac catheterisation<br />
• Transoesophageal echocardiography<br />
• Balloon valvuloplasty/balloon dilatation of<br />
coarctation of aorta<br />
• Coarctation of the aorta (uncorrected,<br />
uncomplicated and complicated)<br />
• Artificial valve<br />
• Implantation of cardiac pacemakers/defibrillators<br />
• Cardiac surgical operations<br />
• Implantation of occlusive devices, eg ductal<br />
occluders, septal occluders<br />
• PTCA/PCI/st<strong>en</strong>t implantation<br />
• Acquired valvular heart diseases<br />
• Mitral valve prolapse with valvular regurgitation or<br />
severe valve thick<strong>en</strong>ing<br />
• Homograft or bioprosthetic valves<br />
• Aortic or mitral st<strong>en</strong>osis (particulary NYHA<br />
functional class III and IV)<br />
• Severe pulmonic st<strong>en</strong>osis<br />
• Surgically constructed systemic or pulmonary<br />
conduits<br />
• Left v<strong>en</strong>tricular dysfunction (moderate to severe)<br />
• Previous left v<strong>en</strong>tricular dysfunction now resolved<br />
(such as peripartum cardiomyopathy)<br />
• Previous myocardial infarction<br />
• Pulmonary hypert<strong>en</strong>sion<br />
• Marfan syndrome with aortic root or valve<br />
involvem<strong>en</strong>t<br />
• Cardiomyopathy<br />
• Eis<strong>en</strong>m<strong>en</strong>ger’s syndrome²<br />
• Hart transplant<br />
• Cardio-vascular infections<br />
• Every disorder labelled as high-risk by a cardiologist<br />
(e.g. cardiac arrhythmia) but not specified as a<br />
disorder requiring a level of standard care<br />
ppp Horstkotte, D. et al (2004). Guidelines on prev<strong>en</strong>tion, diagnosis and treatm<strong>en</strong>t of infective <strong>en</strong>docarditis. The task force on infective <strong>en</strong>docarditis of the European Society of Cardiology. September,<br />
5 th , 2007 from Cebam, National guideline clearinghouse : www.guideline.gov<br />
qqq Ramsdale, D. & Turner-Stokes, L. (2004). Prophylaxis and treatm<strong>en</strong>t of infective <strong>en</strong>docarditis in adults: concise guidelines. September, 5 th , 2007 from Cebam, Royal college of physicians<br />
(UK): www.rcplondon.ac.uk.<br />
rrr Arafah, J. & McCurtry, S. (2006). Cardiac disease in pregnancy. Crit. <strong>Care</strong> Nurs Q, 29, 32-52.<br />
sss Finnish Medical Society Duodecim (2006). Systemic diseases in pregnancy. Retrieved Mai 15, 2007 from Cebam, National guideline clearinghouse : www.guideline.gov.