Barbieri Thesis - BioMedical Materials program (BMM)
Barbieri Thesis - BioMedical Materials program (BMM)
Barbieri Thesis - BioMedical Materials program (BMM)
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Chapter 4 – Conntrol<br />
of mechanical<br />
and degraddation<br />
properties s in composites<br />
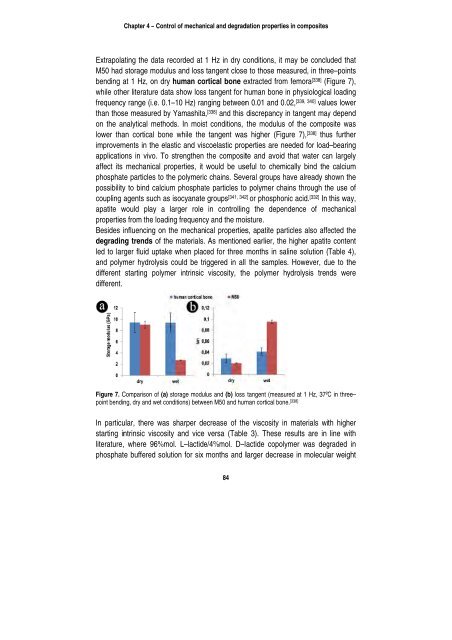
Extrapolaating<br />
the data recorded at 1 Hz in dry c<br />
M50 had storage moduulus<br />
and loss tangent close<br />
bending aat<br />
1 Hz, on dry<br />
human cortical<br />
bone e<br />
while otheer<br />
literature data<br />
show loss s tangent for h<br />
frequencyy<br />
range (i.e. 00.1–10<br />
Hz) ran nging between<br />
than thosse<br />
measured bby<br />
Yamashita,<br />
on the annalytical<br />
methhods.<br />
In mois<br />
lower thaan<br />
cortical boone<br />
while the<br />
improvemments<br />
in the eelastic<br />
and vis<br />
applicatioons<br />
in vivo. TTo<br />
strengthen<br />
affect its mechanical pproperties,<br />
it<br />
phosphatte<br />
particles to the polymeric<br />
possibilityy<br />
to bind calcium<br />
phosphat<br />
coupling agents such aas<br />
isocyanate<br />
apatite wwould<br />
play a larger role<br />
propertiess<br />
from the loading<br />
frequenc<br />
Besides iinfluencing<br />
onn<br />
the mechan<br />
degradinng<br />
trends of tthe<br />
materials.<br />
led to larrger<br />
fluid uptaake<br />
when plac<br />
and polymmer<br />
hydrolysis<br />
could be tr<br />
different starting polymer<br />
intrinsic<br />
different.<br />
[338] conditions, it may m be conclu<br />
e to those mea asured, in thre<br />
extracted from m femora<br />
human bone i<br />
n 0.01 and 0.0<br />
and this discrepancy i<br />
t conditions, the modulus<br />
tangent wass<br />
higher (Figu<br />
scoelastic propperties<br />
are ne<br />
the compositte<br />
and avoid<br />
would be useeful<br />
to chemi<br />
c chains. Seveeral<br />
groups ha<br />
te particles too<br />
polymer cha<br />
groups [341, 3422]<br />
or phosphon<br />
in controllingg<br />
the depen<br />
cy and the moiisture.<br />
ical propertiess,<br />
apatite part<br />
As mentioneed<br />
earlier, the<br />
ced for three months in sa<br />
iggered in all the samples<br />
viscosity, the<br />
polymer h<br />
[338] (F<br />
n physiologica<br />
02, [339, 340] valu<br />
n tangent ma<br />
of the compo<br />
ure 7), [338] thu<br />
eeded for load<br />
that water ca<br />
cally bind the<br />
ave already s<br />
ains through th<br />
nic acid. [332] uded that<br />
ee–points<br />
Figure 7),<br />
al loading<br />
ues lower<br />
y depend<br />
osite was<br />
us further<br />
d–bearing<br />
an largely<br />
e calcium<br />
hown the<br />
he use of<br />
In this way,<br />
ndence of me echanical<br />
ticles also affe ected the<br />
higher apatite e content<br />
line solution (Table ( 4),<br />
. However, due<br />
to the<br />
ydrolysis tren nds were<br />
Figure 7. CComparison<br />
of (aa)<br />
storage modul lus and (b) loss tangent (measured<br />
at 1 Hz, 37º<br />
point bendinng,<br />
dry and wet cconditions)<br />
betwe een M50 and humman<br />
cortical bone e. [338]<br />
C in three–<br />
In particuular,<br />
there waas<br />
sharper de ecrease of thee<br />
viscosity in materials with<br />
higher<br />
starting inntrinsic<br />
viscossity<br />
and vice versa (Tablee<br />
3). These results r are in line with<br />
literature, , where 96%mmol.<br />
L–lactide e/4%mol. D–lactide<br />
copoly ymer was deg graded in<br />
phosphatte<br />
buffered soolution<br />
for six months and llarger<br />
decreas se in molecular<br />
weight<br />
84