RESPONSE - Insead
RESPONSE - Insead
RESPONSE - Insead
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Methodology Introduction<br />
8 Methodology<br />
8.1 Introduction<br />
Four incompany field experiments were designed and executed to assess the effectiveness of<br />
different training approaches on the development of social consciousness and Socially Responsible<br />
Behaviour (SRB) in individual managers. In this chapter, we present the measurements conducted<br />
before and after each training intervention, the characteristics of the settings and of the interventions<br />
identified, and the design executed in each setting.<br />
8.2 Measurements<br />
The assessment of the effectiveness of the training interventions was carried out via a webbased<br />
questionnaire, which assembled several existing scales (in part or in total) dedicated to the empirical<br />
evaluation of each of the theoretical variables in the model described above in Chapter 7.<br />
Table 27 summarizes the scales utilized and the theoretical constructs operationalized. The 63 item<br />
survey took about 30 minutes to complete 16 .<br />
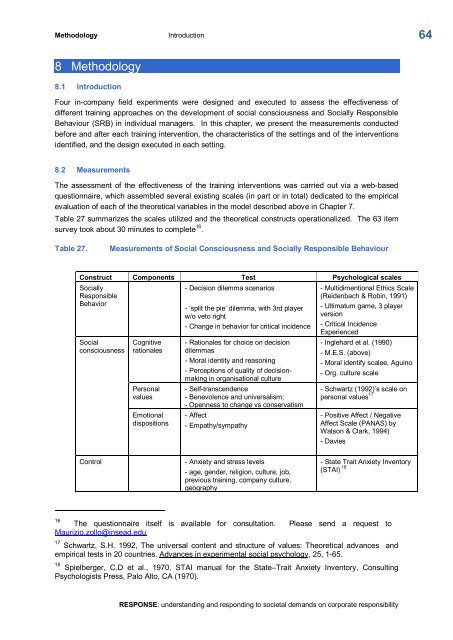
Table 27. Measurements of Social Consciousness and Socially Responsible Behaviour<br />
16<br />
Construct Components Test Psychological scales<br />
Socially<br />
Responsible<br />
Behavior<br />
Social<br />
consciousness<br />
Cognitive<br />
rationales<br />
Personal<br />
values<br />
Emotional<br />
dispositions<br />
Decision dilemma scenarios<br />
‘split the pie’ dilemma, with 3rd player<br />
w/o veto right<br />
Change in behavior for critical incidence<br />
Rationales for choice on decision<br />
dilemmas<br />
Moral identity and reasoning<br />
Perceptions of quality of decision<br />
making in organisational culture<br />
Selftranscendence<br />
Benevolence and universalism;<br />
Openness to change vs conservatism<br />
Affect<br />
Empathy/sympathy<br />
Control Anxiety and stress levels<br />
age, gender, religion, culture, job,<br />
previous training, company culture,<br />
geography<br />
Multidimentional Ethics Scale<br />
(Reidenbach & Robin, 1991)<br />
Ultimatum game, 3 player<br />
version<br />
Critical Incidence<br />
Experienced<br />
Inglehard et al. (1990)<br />
M.E.S. (above)<br />
Moral identify scalee, Aguino<br />
Org. culture scale<br />
Schwartz (1992)’s scale on<br />
personal values 17<br />
Positive Affect / Negative<br />
Affect Scale (PANAS) by<br />
Watson & Clark, 1994)<br />
Davies<br />
State Trait Anxiety Inventory<br />
(STAI) 18<br />
The questionnaire itself is available for consultation. Please send a request to<br />
Maurizio.zollo@insead.edu<br />
17 Schwartz, S.H. 1992, The universal content and structure of values: Theoretical advances and<br />
empirical tests in 20 countries. Advances in experimental social psychology, 25, 165.<br />
18 Spielberger, C.D et al., 1970, STAI manual for the State–Trait Anxiety Inventory, Consulting<br />
Psychologists Press, Palo Alto, CA (1970).<br />
<strong>RESPONSE</strong>: understanding and responding to societal demands on corporate responsibility<br />
64