View - ADTRAN Support Community
View - ADTRAN Support Community
View - ADTRAN Support Community
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
BGP Overview<br />
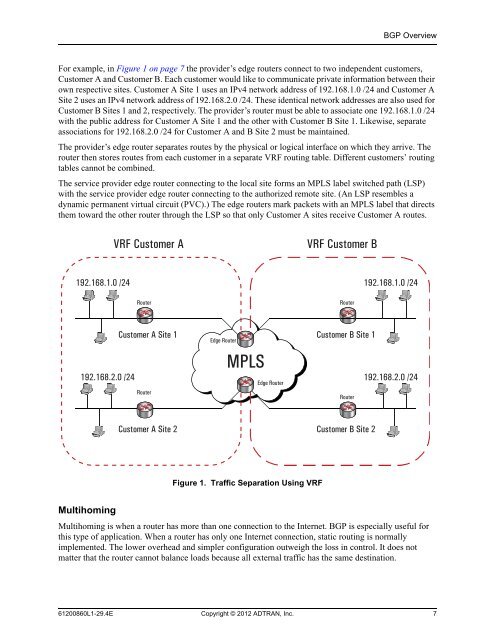
For example, in Figure 1 on page 7 the provider’s edge routers connect to two independent customers,<br />
Customer A and Customer B. Each customer would like to communicate private information between their<br />
own respective sites. Customer A Site 1 uses an IPv4 network address of 192.168.1.0 /24 and Customer A<br />
Site 2 uses an IPv4 network address of 192.168.2.0 /24. These identical network addresses are also used for<br />
Customer B Sites 1 and 2, respectively. The provider’s router must be able to associate one 192.168.1.0 /24<br />
with the public address for Customer A Site 1 and the other with Customer B Site 1. Likewise, separate<br />
associations for 192.168.2.0 /24 for Customer A and B Site 2 must be maintained.<br />
The provider’s edge router separates routes by the physical or logical interface on which they arrive. The<br />
router then stores routes from each customer in a separate VRF routing table. Different customers’ routing<br />
tables cannot be combined.<br />
The service provider edge router connecting to the local site forms an MPLS label switched path (LSP)<br />
with the service provider edge router connecting to the authorized remote site. (An LSP resembles a<br />
dynamic permanent virtual circuit (PVC).) The edge routers mark packets with an MPLS label that directs<br />
them toward the other router through the LSP so that only Customer A sites receive Customer A routes.<br />
VRF Customer A<br />
VRF Customer B<br />
192.168.1.0 /24<br />
192.168.1.0 /24<br />
Router<br />
Router<br />
192.168.2.0 /24<br />
Customer A Site 1<br />
Router<br />
Edge Router<br />
MPLS<br />
Edge Router<br />
Customer B Site 1<br />
Router<br />
192.168.2.0 /24<br />
Customer A Site 2<br />
Customer B Site 2<br />
Figure 1. Traffic Separation Using VRF<br />
Multihoming<br />
Multihoming is when a router has more than one connection to the Internet. BGP is especially useful for<br />
this type of application. When a router has only one Internet connection, static routing is normally<br />
implemented. The lower overhead and simpler configuration outweigh the loss in control. It does not<br />
matter that the router cannot balance loads because all external traffic has the same destination.<br />
61200860L1-29.4E Copyright © 2012 <strong>ADTRAN</strong>, Inc. 7