English version - Hexagon Composites ASA
English version - Hexagon Composites ASA
English version - Hexagon Composites ASA
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
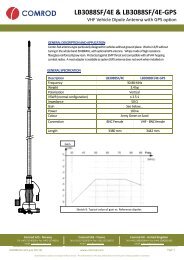
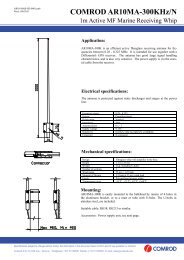
COMROD COMMUNICATION <strong>ASA</strong> – LISTING ON THE OSLO STOCK EXCHANGE<br />
7.1.4 Basis for consolidation<br />
The consolidated financial statements comprise Comrod AS and companies where Comrod AS has a<br />
controlling interest. A controlling interest is normally attained when the group owns, either directly or<br />
indirectly, more than 50% of the shares in a company, and the group is in a position to exercise actual<br />
control over the company.<br />
The purchase method is applied when accounting for business combinations. Companies which have<br />
been acquired or sold during the year are consolidated from/until the date when control is<br />
obtained/ceases.<br />
Intra-company transactions and balances, including internal earnings and unrealised profits/losses, are<br />
eliminated. Unrealised losses are correspondingly eliminated, provided there is no evidence of any<br />
impairment of the asset sold internally.<br />
The consolidated financial statements are prepared using uniform accounting policies for identical<br />
transactions and events in similar circumstances.<br />
7.1.5 Cash & cash equivalents<br />
Cash includes bank and cash balances. The cash-flow statement is prepared using the indirect method.<br />
7.1.6 Trade receivables<br />
Trade receivables are carried at amortised cost. The interest element is disregarded if it is insignificant.<br />
Should there be objective evidence of a fall in value, the difference between the carrying amount and<br />
the present value of future cash flows is recognised as a loss, discounted by the receivable amount’s<br />
effective interest rate.<br />
7.1.7 Hedging<br />
Before any hedging transaction is undertaken, the financial director will assess whether a derivative is<br />
to be used to hedge a) the fair value of an asset or liability, b) future cash flows from an investment,<br />
debt payment or future identified transaction or c) a net investment in a foreign operation.<br />
The group uses the following criteria to classify a derivative as a hedging instrument: (1) the hedge is<br />
expected to be highly effective in offsetting changes in fair value or cash flows attributable to an<br />
identified asset, and hedge effectiveness is expected to lie within the range 80%-125%, (2) hedge<br />
effectiveness can be measured reliably, (3) there is adequate documentation at the inception of the<br />
hedge to demonstrate that the hedge is highly effective, (4) in the case of cash flow hedges, the<br />
impending transaction must be highly probable, and (5) the hedge is regularly assessed and has proved<br />
to be effective throughout the reporting periods for which it is designated.<br />
(i) Fair value hedge<br />
Changes in the fair value of derivatives that are designated as fair value hedges are recognised in the<br />
income statement. Correspondingly, a change in the fair value of the hedged object is recognised in the<br />
income statement, as is the net gain or loss.<br />
Hedge accounting discontinues when:<br />
(a) The hedging instrument expires, is sold, terminated or exercised; or<br />
(b) The hedge no longer meets the criteria for hedging stated above.<br />
When hedge accounting is discontinued, the adjustments made to the carrying amount of the hedged<br />
object are amortized over the remaining life using the effective interest rate.<br />
(ii) Cash flow hedges<br />
57